Welcome to Subscribe On Youtube
311. Sparse Matrix Multiplication
Description
Given two sparse matrices mat1 of size m x k and mat2 of size k x n, return the result of mat1 x mat2. You may assume that multiplication is always possible.
Example 1:
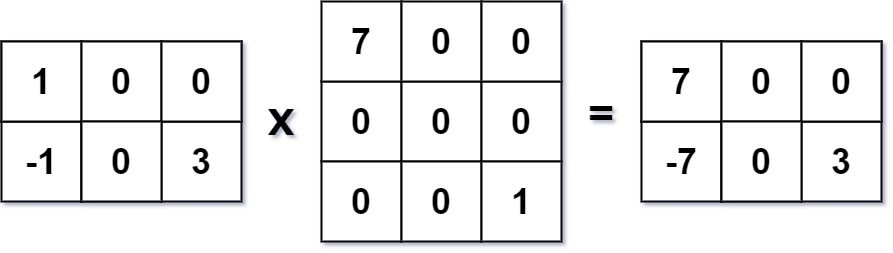
Input: mat1 = [[1,0,0],[-1,0,3]], mat2 = [[7,0,0],[0,0,0],[0,0,1]] Output: [[7,0,0],[-7,0,3]]
Example 2:
Input: mat1 = [[0]], mat2 = [[0]] Output: [[0]]
Constraints:
m == mat1.lengthk == mat1[i].length == mat2.lengthn == mat2[i].length1 <= m, n, k <= 100-100 <= mat1[i][j], mat2[i][j] <= 100
Solutions
Solution 1: Direct Multiplication
We can directly calculate each element in the result matrix according to the definition of matrix multiplication.
The time complexity is $O(m \times n \times k)$, and the space complexity is $O(m \times n)$. Where $m$ and $n$ are the number of rows of matrix $mat1$ and the number of columns of matrix $mat2$ respectively, and $k$ is the number of columns of matrix $mat1$ or the number of rows of matrix $mat2$.
Solution 2: Preprocessing
We can preprocess the sparse representation of the two matrices, i.e., $g1[i]$ represents the column index and value of all non-zero elements in the $i$th row of matrix $mat1$, and $g2[i]$ represents the column index and value of all non-zero elements in the $i$th row of matrix $mat2$.
Next, we traverse each row $i$, traverse each element $(k, x)$ in $g1[i]$, traverse each element $(j, y)$ in $g2[k]$, then $mat1[i][k] \times mat2[k][j]$ will correspond to $ans[i][j]$ in the result matrix, and we can accumulate all the results.
The time complexity is $O(m \times n \times k)$, and the space complexity is $O(m \times n)$. Where $m$ and $n$ are the number of rows of matrix $mat1$ and the number of columns of matrix $mat2$ respectively, and $k$ is the number of columns of matrix $mat1$ or the number of rows of matrix $mat2$.
-
class Solution { public int[][] multiply(int[][] mat1, int[][] mat2) { int m = mat1.length, n = mat2[0].length; int[][] ans = new int[m][n]; var g1 = f(mat1); var g2 = f(mat2); for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i) { for (int[] p : g1[i]) { int k = p[0], x = p[1]; for (int[] q : g2[k]) { int j = q[0], y = q[1]; ans[i][j] += x * y; } } } return ans; } private List<int[]>[] f(int[][] mat) { int m = mat.length, n = mat[0].length; List<int[]>[] g = new List[m]; Arrays.setAll(g, i -> new ArrayList<>()); for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i) { for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) { if (mat[i][j] != 0) { g[i].add(new int[] {j, mat[i][j]}); } } } return g; } } -
class Solution { public: vector<vector<int>> multiply(vector<vector<int>>& mat1, vector<vector<int>>& mat2) { int m = mat1.size(), n = mat2[0].size(); vector<vector<int>> ans(m, vector<int>(n)); auto g1 = f(mat1), g2 = f(mat2); for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i) { for (auto& [k, x] : g1[i]) { for (auto& [j, y] : g2[k]) { ans[i][j] += x * y; } } } return ans; } vector<vector<pair<int, int>>> f(vector<vector<int>>& mat) { int m = mat.size(), n = mat[0].size(); vector<vector<pair<int, int>>> g(m); for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i) { for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) { if (mat[i][j]) { g[i].emplace_back(j, mat[i][j]); } } } return g; } }; -
class Solution: def multiply(self, mat1: List[List[int]], mat2: List[List[int]]) -> List[List[int]]: def f(mat: List[List[int]]) -> List[List[int]]: g = [[] for _ in range(len(mat))] for i, row in enumerate(mat): for j, x in enumerate(row): if x: g[i].append((j, x)) return g g1 = f(mat1) g2 = f(mat2) m, n = len(mat1), len(mat2[0]) ans = [[0] * n for _ in range(m)] for i in range(m): for k, x in g1[i]: for j, y in g2[k]: ans[i][j] += x * y return ans -
func multiply(mat1 [][]int, mat2 [][]int) [][]int { m, n := len(mat1), len(mat2[0]) ans := make([][]int, m) for i := range ans { ans[i] = make([]int, n) } f := func(mat [][]int) [][][2]int { m, n := len(mat), len(mat[0]) g := make([][][2]int, m) for i := range g { g[i] = make([][2]int, 0, n) for j := range mat[i] { if mat[i][j] != 0 { g[i] = append(g[i], [2]int{j, mat[i][j]}) } } } return g } g1, g2 := f(mat1), f(mat2) for i := range g1 { for _, p := range g1[i] { k, x := p[0], p[1] for _, q := range g2[k] { j, y := q[0], q[1] ans[i][j] += x * y } } } return ans } -
function multiply(mat1: number[][], mat2: number[][]): number[][] { const [m, n] = [mat1.length, mat2[0].length]; const ans: number[][] = Array.from({ length: m }, () => Array.from({ length: n }, () => 0)); const f = (mat: number[][]): number[][][] => { const [m, n] = [mat.length, mat[0].length]; const ans: number[][][] = Array.from({ length: m }, () => []); for (let i = 0; i < m; ++i) { for (let j = 0; j < n; ++j) { if (mat[i][j] !== 0) { ans[i].push([j, mat[i][j]]); } } } return ans; }; const g1 = f(mat1); const g2 = f(mat2); for (let i = 0; i < m; ++i) { for (const [k, x] of g1[i]) { for (const [j, y] of g2[k]) { ans[i][j] += x * y; } } } return ans; }