Welcome to Subscribe On Youtube
305. Number of Islands II
Description
You are given an empty 2D binary grid grid of size m x n. The grid represents a map where 0's represent water and 1's represent land. Initially, all the cells of grid are water cells (i.e., all the cells are 0's).
We may perform an add land operation which turns the water at position into a land. You are given an array positions where positions[i] = [ri, ci] is the position (ri, ci) at which we should operate the ith operation.
Return an array of integers answer where answer[i] is the number of islands after turning the cell (ri, ci) into a land.
An island is surrounded by water and is formed by connecting adjacent lands horizontally or vertically. You may assume all four edges of the grid are all surrounded by water.
Example 1:
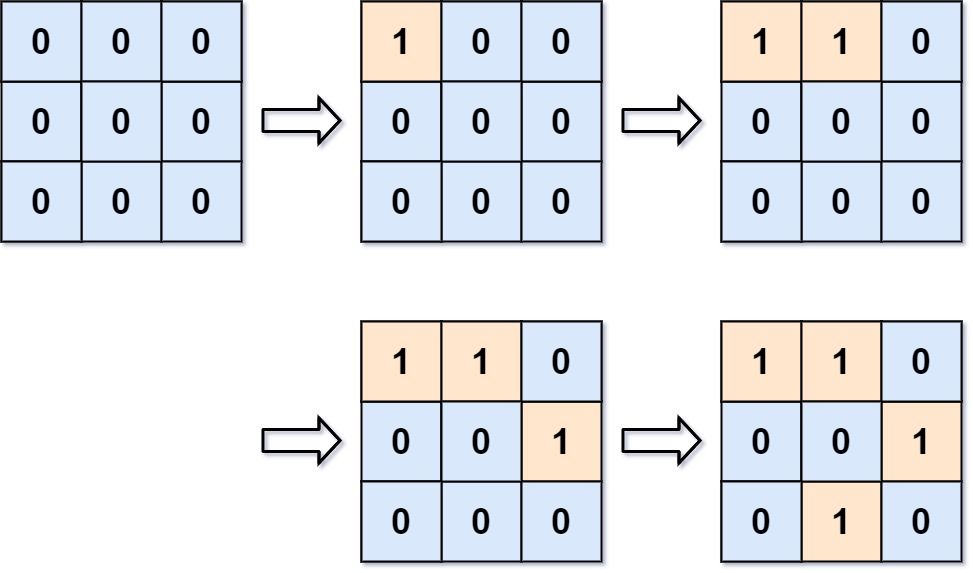
Input: m = 3, n = 3, positions = [[0,0],[0,1],[1,2],[2,1]] Output: [1,1,2,3] Explanation: Initially, the 2d grid is filled with water. - Operation #1: addLand(0, 0) turns the water at grid[0][0] into a land. We have 1 island. - Operation #2: addLand(0, 1) turns the water at grid[0][1] into a land. We still have 1 island. - Operation #3: addLand(1, 2) turns the water at grid[1][2] into a land. We have 2 islands. - Operation #4: addLand(2, 1) turns the water at grid[2][1] into a land. We have 3 islands.
Example 2:
Input: m = 1, n = 1, positions = [[0,0]] Output: [1]
Constraints:
1 <= m, n, positions.length <= 1041 <= m * n <= 104positions[i].length == 20 <= ri < m0 <= ci < n
Follow up: Could you solve it in time complexity O(k log(mn)), where k == positions.length?
Solutions
Solution 1: Union-Find
We use a two-dimensional array $grid$ to represent a map, where $0$ and $1$ represent water and land respectively. Initially, all cells in $grid$ are water cells (i.e., all cells are $0$), and we use a variable $cnt$ to record the number of islands. The connectivity between islands can be maintained by a union-find set $uf$.
Next, we traverse each position $(i, j)$ in the array $positions$. If $grid[i][j]$ is $1$, it means that this position is already land, and we directly add $cnt$ to the answer; otherwise, we change the value of $grid[i][j]$ to $1$, and increase the value of $cnt$ by $1$. Then, we traverse the four directions of up, down, left, and right of this position. If a certain direction is $1$, and this position does not belong to the same connected component as $(i, j)$, then we merge this position with $(i, j)$, and decrease the value of $cnt$ by $1$. After traversing the four directions of up, down, left, and right of this position, we add $cnt$ to the answer.
The time complexity is $O(k \times \alpha(m \times n))$ or $O(k \times \log(m \times n))$, where $k$ is the length of $positions$, and $\alpha$ is the inverse function of the Ackermann function. In this problem, $\alpha(m \times n)$ can be considered as a very small constant.
-
class UnionFind { private final int[] p; private final int[] size; public UnionFind(int n) { p = new int[n]; size = new int[n]; for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) { p[i] = i; size[i] = 1; } } public int find(int x) { if (p[x] != x) { p[x] = find(p[x]); } return p[x]; } public boolean union(int a, int b) { int pa = find(a), pb = find(b); if (pa == pb) { return false; } if (size[pa] > size[pb]) { p[pb] = pa; size[pa] += size[pb]; } else { p[pa] = pb; size[pb] += size[pa]; } return true; } } class Solution { public List<Integer> numIslands2(int m, int n, int[][] positions) { int[][] grid = new int[m][n]; UnionFind uf = new UnionFind(m * n); int[] dirs = {-1, 0, 1, 0, -1}; int cnt = 0; List<Integer> ans = new ArrayList<>(); for (var p : positions) { int i = p[0], j = p[1]; if (grid[i][j] == 1) { ans.add(cnt); continue; } grid[i][j] = 1; ++cnt; for (int k = 0; k < 4; ++k) { int x = i + dirs[k], y = j + dirs[k + 1]; if (x >= 0 && x < m && y >= 0 && y < n && grid[x][y] == 1 && uf.union(i * n + j, x * n + y)) { --cnt; } } ans.add(cnt); } return ans; } } -
class UnionFind { public: UnionFind(int n) { p = vector<int>(n); size = vector<int>(n, 1); iota(p.begin(), p.end(), 0); } bool unite(int a, int b) { int pa = find(a), pb = find(b); if (pa == pb) { return false; } if (size[pa] > size[pb]) { p[pb] = pa; size[pa] += size[pb]; } else { p[pa] = pb; size[pb] += size[pa]; } return true; } int find(int x) { if (p[x] != x) { p[x] = find(p[x]); } return p[x]; } private: vector<int> p, size; }; class Solution { public: vector<int> numIslands2(int m, int n, vector<vector<int>>& positions) { int grid[m][n]; memset(grid, 0, sizeof(grid)); UnionFind uf(m * n); int dirs[5] = {-1, 0, 1, 0, -1}; int cnt = 0; vector<int> ans; for (auto& p : positions) { int i = p[0], j = p[1]; if (grid[i][j]) { ans.push_back(cnt); continue; } grid[i][j] = 1; ++cnt; for (int k = 0; k < 4; ++k) { int x = i + dirs[k], y = j + dirs[k + 1]; if (x >= 0 && x < m && y >= 0 && y < n && grid[x][y] && uf.union(i * n + j, x * n + y)) { --cnt; } } ans.push_back(cnt); } return ans; } }; -
class Solution: def numIslands2(self, m: int, n: int, positions: List[List[int]]) -> List[int]: def check(i, j): return 0 <= i < m and 0 <= j < n and grid[i][j] == 1 def find(x): if p[x] != x: p[x] = find(p[x]) return p[x] p = list(range(m * n)) grid = [[0] * n for _ in range(m)] res = [] cur = 0 # current island count for i, j in positions: if grid[i][j] == 1: # already counted, same as previous island count res.append(cur) continue grid[i][j] = 1 cur += 1 for x, y in [(-1, 0), (1, 0), (0, -1), (0, 1)]: if check(i + x, j + y) and find(i * n + j) != find((i + x) * n + j + y): p[find(i * n + j)] = find((i + x) * n + j + y) cur -= 1 # 1 0 1 # 0 1 0 # for above, if setting 1st-row 2nd-col 0-to-1 # cur will -1 for 3 times # but cur += 1 after grid[i][j] = 1 so cur final result is 1 res.append(cur) return res ############ class UnionFind(object): def __init__(self, m, n): self.dad = [i for i in range(m * n)] self.rank = [0 for _ in range(m * n)] def find(self, x): if self.dad[x] != x: self.dad[x] = self.find(self.dad[x]) return self.dad[x] def union(self, xy): # xy is a tuple (x,y), with x and y value inside x, y = map(self.find, xy) if x == y: return False if self.rank[x] > self.rank[y]: self.dad[y] = x elif self.rank[x] < self.rank[y]: self.dad[x] = y else: self.dad[y] = x # search to the left, to find parent self.rank[x] += 1 # now x a parent, so +1 its rank return True class Solution(object): def numIslands2(self, m, n, positions): """ :type m: int :type n: int :type positions: List[List[int]] :rtype: List[int] """ uf = UnionFind(m, n) ans = 0 ret = [] dirs = [(0, -1), (0, 1), (1, 0), (-1, 0)] grid = set() for i, j in positions: ans += 1 grid |= {(i, j)} for di, dj in dirs: ni, nj = i + di, j + dj if 0 <= ni < m and 0 <= nj < n and (ni, nj) in grid: if uf.union((ni * n + nj, i * n + j)): ans -= 1 ret.append(ans) return ret ################ class UnionFind: def __init__(self, n: int): self.p = list(range(n)) self.size = [1] * n def find(self, x: int): if self.p[x] != x: self.p[x] = self.find(self.p[x]) return self.p[x] def union(self, a: int, b: int) -> bool: pa, pb = self.find(a - 1), self.find(b - 1) if pa == pb: return False if self.size[pa] > self.size[pb]: self.p[pb] = pa self.size[pa] += self.size[pb] else: self.p[pa] = pb self.size[pb] += self.size[pa] return True class Solution: def numIslands2(self, m: int, n: int, positions: List[List[int]]) -> List[int]: uf = UnionFind(m * n) grid = [[0] * n for _ in range(m)] ans = [] dirs = (-1, 0, 1, 0, -1) cnt = 0 for i, j in positions: if grid[i][j]: ans.append(cnt) continue grid[i][j] = 1 cnt += 1 for a, b in pairwise(dirs): x, y = i + a, j + b if ( 0 <= x < m and 0 <= y < n and grid[x][y] and uf.union(i * n + j, x * n + y) ): cnt -= 1 ans.append(cnt) return ans -
type unionFind struct { p, size []int } func newUnionFind(n int) *unionFind { p := make([]int, n) size := make([]int, n) for i := range p { p[i] = i size[i] = 1 } return &unionFind{p, size} } func (uf *unionFind) find(x int) int { if uf.p[x] != x { uf.p[x] = uf.find(uf.p[x]) } return uf.p[x] } func (uf *unionFind) union(a, b int) bool { pa, pb := uf.find(a), uf.find(b) if pa == pb { return false } if uf.size[pa] > uf.size[pb] { uf.p[pb] = pa uf.size[pa] += uf.size[pb] } else { uf.p[pa] = pb uf.size[pb] += uf.size[pa] } return true } func numIslands2(m int, n int, positions [][]int) (ans []int) { uf := newUnionFind(m * n) grid := make([][]int, m) for i := range grid { grid[i] = make([]int, n) } dirs := [5]int{-1, 0, 1, 0, -1} cnt := 0 for _, p := range positions { i, j := p[0], p[1] if grid[i][j] == 1 { ans = append(ans, cnt) continue } grid[i][j] = 1 cnt++ for k := 0; k < 4; k++ { x, y := i+dirs[k], j+dirs[k+1] if x >= 0 && x < m && y >= 0 && y < n && grid[x][y] == 1 && uf.union(i*n+j, x*n+y) { cnt-- } } ans = append(ans, cnt) } return } -
class UnionFind { p: number[]; size: number[]; constructor(n: number) { this.p = Array(n) .fill(0) .map((_, i) => i); this.size = Array(n).fill(1); } find(x: number): number { if (this.p[x] !== x) { this.p[x] = this.find(this.p[x]); } return this.p[x]; } union(a: number, b: number): boolean { const [pa, pb] = [this.find(a), this.find(b)]; if (pa === pb) { return false; } if (this.size[pa] > this.size[pb]) { this.p[pb] = pa; this.size[pa] += this.size[pb]; } else { this.p[pa] = pb; this.size[pb] += this.size[pa]; } return true; } } function numIslands2(m: number, n: number, positions: number[][]): number[] { const grid: number[][] = Array.from({ length: m }, () => Array(n).fill(0)); const uf = new UnionFind(m * n); const ans: number[] = []; const dirs: number[] = [-1, 0, 1, 0, -1]; let cnt = 0; for (const [i, j] of positions) { if (grid[i][j]) { ans.push(cnt); continue; } grid[i][j] = 1; ++cnt; for (let k = 0; k < 4; ++k) { const [x, y] = [i + dirs[k], j + dirs[k + 1]]; if (x < 0 || x >= m || y < 0 || y >= n || !grid[x][y]) { continue; } if (uf.union(i * n + j, x * n + y)) { --cnt; } } ans.push(cnt); } return ans; }