Welcome to Subscribe On Youtube
289. Game of Life
Description
According to Wikipedia's article: "The Game of Life, also known simply as Life, is a cellular automaton devised by the British mathematician John Horton Conway in 1970."
The board is made up of an m x n grid of cells, where each cell has an initial state: live (represented by a 1) or dead (represented by a 0). Each cell interacts with its eight neighbors (horizontal, vertical, diagonal) using the following four rules (taken from the above Wikipedia article):
- Any live cell with fewer than two live neighbors dies as if caused by under-population.
- Any live cell with two or three live neighbors lives on to the next generation.
- Any live cell with more than three live neighbors dies, as if by over-population.
- Any dead cell with exactly three live neighbors becomes a live cell, as if by reproduction.
The next state is created by applying the above rules simultaneously to every cell in the current state, where births and deaths occur simultaneously. Given the current state of the m x n grid board, return the next state.
Example 1:
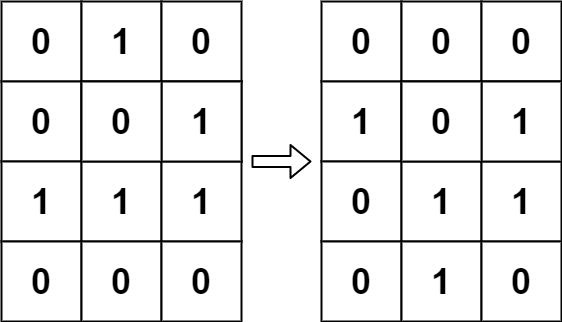
Input: board = [[0,1,0],[0,0,1],[1,1,1],[0,0,0]] Output: [[0,0,0],[1,0,1],[0,1,1],[0,1,0]]
Example 2:
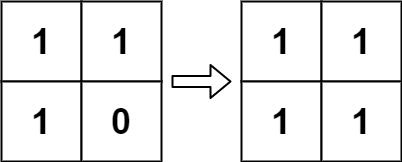
Input: board = [[1,1],[1,0]] Output: [[1,1],[1,1]]
Constraints:
m == board.lengthn == board[i].length1 <= m, n <= 25board[i][j]is0or1.
Follow up:
- Could you solve it in-place? Remember that the board needs to be updated simultaneously: You cannot update some cells first and then use their updated values to update other cells.
- In this question, we represent the board using a 2D array. In principle, the board is infinite, which would cause problems when the active area encroaches upon the border of the array (i.e., live cells reach the border). How would you address these problems?
Solutions
Solution 1: In-place marking
Let’s define two new states. State $2$ indicates that the living cell becomes dead in the next state, and state $-1$ indicates that the dead cell becomes alive in the next state. Therefore, for the current grid we are traversing, if the grid is greater than $0$, it means that the current grid is a living cell, otherwise it is a dead cell.
So we can traverse the entire board, for each grid, count the number of living neighbors around the grid, and use the variable $live$ to represent it. If the current grid is a living cell, then when $live \lt 2$ or $live \gt 3$, the next state of the current grid is a dead cell, that is, state $2$; if the current grid is a dead cell, then when $live = 3$, the next state of the current grid is an active cell, that is, state $-1$.
Finally, we traverse the board again, and update the grid with state $2$ to a dead cell, and update the grid with state $-1$ to an active cell.
The time complexity is $O(m \times n)$, where $m$ and $n$ are the number of rows and columns of the board, respectively. We need to traverse the entire board. And the space complexity is $O(1)$.
-
class Solution { public void gameOfLife(int[][] board) { int m = board.length, n = board[0].length; for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i) { for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) { int live = -board[i][j]; for (int x = i - 1; x <= i + 1; ++x) { for (int y = j - 1; y <= j + 1; ++y) { if (x >= 0 && x < m && y >= 0 && y < n && board[x][y] > 0) { ++live; } } } if (board[i][j] == 1 && (live < 2 || live > 3)) { board[i][j] = 2; } if (board[i][j] == 0 && live == 3) { board[i][j] = -1; } } } for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i) { for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) { if (board[i][j] == 2) { board[i][j] = 0; } else if (board[i][j] == -1) { board[i][j] = 1; } } } } } -
class Solution { public: void gameOfLife(vector<vector<int>>& board) { int m = board.size(), n = board[0].size(); for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i) { for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) { int live = -board[i][j]; for (int x = i - 1; x <= i + 1; ++x) { for (int y = j - 1; y <= j + 1; ++y) { if (x >= 0 && x < m && y >= 0 && y < n && board[x][y] > 0) { ++live; } } } if (board[i][j] == 1 && (live < 2 || live > 3)) { board[i][j] = 2; } if (board[i][j] == 0 && live == 3) { board[i][j] = -1; } } } for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i) { for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) { if (board[i][j] == 2) { board[i][j] = 0; } else if (board[i][j] == -1) { board[i][j] = 1; } } } } }; -
class Solution: def gameOfLife(self, board: List[List[int]]) -> None: m, n = len(board), len(board[0]) for i in range(m): for j in range(n): live = -board[i][j] for x in range(i - 1, i + 2): for y in range(j - 1, j + 2): if 0 <= x < m and 0 <= y < n and board[x][y] > 0: live += 1 if board[i][j] and (live < 2 or live > 3): board[i][j] = 2 if board[i][j] == 0 and live == 3: board[i][j] = -1 for i in range(m): for j in range(n): if board[i][j] == 2: board[i][j] = 0 elif board[i][j] == -1: board[i][j] = 1 -
func gameOfLife(board [][]int) { m, n := len(board), len(board[0]) for i := 0; i < m; i++ { for j, v := range board[i] { live := -v for x := i - 1; x <= i+1; x++ { for y := j - 1; y <= j+1; y++ { if x >= 0 && x < m && y >= 0 && y < n && board[x][y] > 0 { live++ } } } if v == 1 && (live < 2 || live > 3) { board[i][j] = 2 } if v == 0 && live == 3 { board[i][j] = -1 } } } for i := 0; i < m; i++ { for j, v := range board[i] { if v == 2 { board[i][j] = 0 } if v == -1 { board[i][j] = 1 } } } } -
/** Do not return anything, modify board in-place instead. */ function gameOfLife(board: number[][]): void { const m = board.length; const n = board[0].length; for (let i = 0; i < m; ++i) { for (let j = 0; j < n; ++j) { let live = -board[i][j]; for (let x = i - 1; x <= i + 1; ++x) { for (let y = j - 1; y <= j + 1; ++y) { if (x >= 0 && x < m && y >= 0 && y < n && board[x][y] > 0) { ++live; } } } if (board[i][j] === 1 && (live < 2 || live > 3)) { board[i][j] = 2; } if (board[i][j] === 0 && live === 3) { board[i][j] = -1; } } } for (let i = 0; i < m; ++i) { for (let j = 0; j < n; ++j) { if (board[i][j] === 2) { board[i][j] = 0; } if (board[i][j] === -1) { board[i][j] = 1; } } } } -
public class Solution { public void GameOfLife(int[][] board) { int m = board.Length; int n = board[0].Length; for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i) { for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) { int live = -board[i][j]; for (int x = i - 1; x <= i + 1; ++x) { for (int y = j - 1; y <= j + 1; ++y) { if (x >= 0 && x < m && y >= 0 && y < n && board[x][y] > 0) { ++live; } } } if (board[i][j] == 1 && (live < 2 || live > 3)) { board[i][j] = 2; } if (board[i][j] == 0 && live == 3) { board[i][j] = -1; } } } for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i) { for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) { if (board[i][j] == 2) { board[i][j] = 0; } if (board[i][j] == -1) { board[i][j] = 1; } } } } } -
const DIR: [(i32, i32); 8] = [ (-1, 0), (1, 0), (0, -1), (0, 1), (-1, -1), (-1, 1), (1, -1), (1, 1), ]; impl Solution { #[allow(dead_code)] pub fn game_of_life(board: &mut Vec<Vec<i32>>) { let n = board.len(); let m = board[0].len(); let mut weight_vec: Vec<Vec<i32>> = vec![vec![0; m]; n]; // Initialize the weight vector for i in 0..n { for j in 0..m { if board[i][j] == 0 { continue; } for (dx, dy) in DIR { let x = (i as i32) + dx; let y = (j as i32) + dy; if Self::check_bounds(x, y, n as i32, m as i32) { weight_vec[x as usize][y as usize] += 1; } } } } // Update the board for i in 0..n { for j in 0..m { if weight_vec[i][j] < 2 { board[i][j] = 0; } else if weight_vec[i][j] <= 3 { if board[i][j] == 0 && weight_vec[i][j] == 3 { board[i][j] = 1; } } else { board[i][j] = 0; } } } } #[allow(dead_code)] fn check_bounds(i: i32, j: i32, n: i32, m: i32) -> bool { i >= 0 && i < n && j >= 0 && j < m } }