Welcome to Subscribe On Youtube
Question
Formatted question description: https://leetcode.ca/all/276.html
You are painting a fence of n posts with k different colors. You must paint the posts following these rules:
- Every post must be painted exactly one color.
- There cannot be three or more consecutive posts with the same color.
Given the two integers n and k, return the number of ways you can paint the fence.
Example 1:
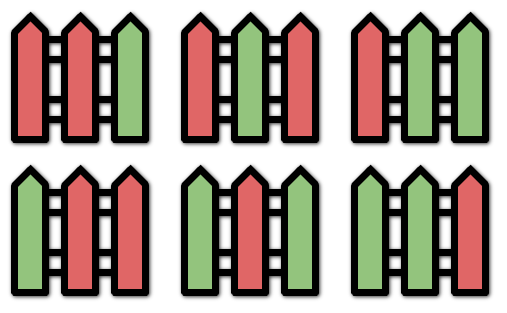
Input: n = 3, k = 2 Output: 6 Explanation: All the possibilities are shown. Note that painting all the posts red or all the posts green is invalid because there cannot be three posts in a row with the same color.
Example 2:
Input: n = 1, k = 1 Output: 1
Example 3:
Input: n = 7, k = 2 Output: 42
Constraints:
1 <= n <= 501 <= k <= 105- The testcases are generated such that the answer is in the range
[0, 231 - 1]for the givennandk.
Algorithm
If n == 0 or k == 0, painting the fence as required is not feasible, therefore the function should return 0.
This solution employs dynamic programming. It involves initializing a 2D array dp with n rows and 2 columns. In this array:
dp[i][1]indicates the count of possible ways to paint the firsti + 1fence posts, with thei-th post painted the same color as the one before it.- Conversely,
dp[i][0]signifies the number of ways to paint the firsti + 1fence posts, with thei-th post painted a different color from its predecessor.
Initially, set dp[0][0] = 0 and dp[0][1] = k, reflecting the scenario with just one post. For i > 0:
dp[i][0] = dp[i - 1][1]because for thei-th post to match the color of its predecessor, it must adopt the configuration of the previous post having a unique color.dp[i][1] = (dp[i - 1][0] + dp[i - 1][1]) * (k - 1)because to paint thei-th post a different color from thei-1-th post, you havek - 1color options available. This calculation sums the possible configurations from the previous post and multiplies by the color options excluding the color used previously.
To obtain the total configurations for painting the fence, sum the last row values of dp: dp[n - 1][0] + dp[n - 1][1], which gives the final answer.
Code
-
public class Paint_Fence { public static void main(String[] args) { Paint_Fence out = new Paint_Fence(); Solution s1 = out.new Solution(); Solution_noArray s2 = out.new Solution_noArray(); System.out.println(s1.numWays(3, 2)); // 6 System.out.println(s2.numWays(3, 2)); } class Solution { public int numWays(int n, int k) { if (n == 0 || k == 0) return 0; // `dp[i][0]` same color // `dp[i][1]` different color int[][] dp = new int[n][2]; dp[0][0] = 0; dp[0][1] = k; for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) { dp[i][0] = dp[i - 1][1]; // or else 3-posts the same color dp[i][1] = (dp[i - 1][0] + dp[i - 1][1]) * (k - 1); } return dp[n - 1][0] + dp[n - 1][1]; } } public class Solution_noArray { public int numWays(int n, int k) { if (n == 0) return 0; int same = 0, diff = k; for (int i = 2; i <= n; ++i) { int t = diff; diff = (same + diff) * (k - 1); same = t; } return same + diff; } } } ############ class Solution { public int numWays(int n, int k) { int[][] dp = new int[n][2]; dp[0][0] = k; for (int i = 1; i < n; ++i) { dp[i][0] = (dp[i - 1][0] + dp[i - 1][1]) * (k - 1); dp[i][1] = dp[i - 1][0]; } return dp[n - 1][0] + dp[n - 1][1]; } } -
// OJ: https://leetcode.com/problems/paint-fence/ // Time: O(N) // Space: O(1) class Solution { public: int numWays(int n, int k) { if (k == 1 && n >= 3) return 0; int dp[2] = {k, 0}; for (int i = 1; i < n; ++i) { int next[2] = {(k - 1) * (dp[0] + dp[1]), dp[0]}; swap(next, dp); } return dp[0] + dp[1]; } }; -
class Solution: def numWays(self, n: int, k: int) -> int: # `dp[i][0]` same color # `dp[i][1]` different color dp = [[0] * 2 for _ in range(n)] dp[0][1] = k for i in range(1, n): dp[i][0] = dp[i - 1][1] # same as previous, or else 3-posts the same color dp[i][1] = (dp[i - 1][0] + dp[i - 1][1]) * (k - 1) # not the same as previous return sum(dp[-1]) ############ class Solution(object): def numWays(self, n, k): """ :type n: int :type k: int :rtype: int """ if n > 2 and k == 1: return 0 if n < 2: return n * k pre = k * k ppre = k for i in range(2, n): tmp = pre pre = (k - 1) * (pre + ppre) ppre = tmp return pre -
func numWays(n int, k int) int { dp := make([][]int, n) for i := range dp { dp[i] = make([]int, 2) } dp[0][0] = k for i := 1; i < n; i++ { dp[i][0] = (dp[i-1][0] + dp[i-1][1]) * (k - 1) dp[i][1] = dp[i-1][0] } return dp[n-1][0] + dp[n-1][1] } -
function numWays(n: number, k: number): number { const f: number[] = Array(n).fill(0); const g: number[] = Array(n).fill(0); f[0] = k; for (let i = 1; i < n; ++i) { f[i] = (f[i - 1] + g[i - 1]) * (k - 1); g[i] = f[i - 1]; } return f[n - 1] + g[n - 1]; }