Welcome to Subscribe On Youtube
261. Graph Valid Tree
Description
You have a graph of n nodes labeled from 0 to n - 1. You are given an integer n and a list of edges where edges[i] = [ai, bi] indicates that there is an undirected edge between nodes ai and bi in the graph.
Return true if the edges of the given graph make up a valid tree, and false otherwise.
Example 1:
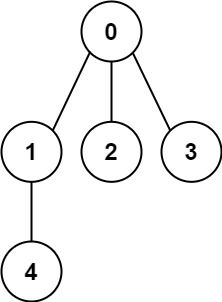
Input: n = 5, edges = [[0,1],[0,2],[0,3],[1,4]] Output: true
Example 2:
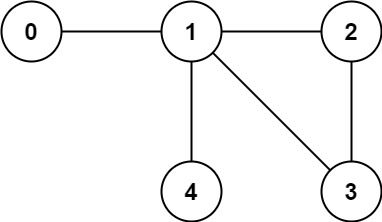
Input: n = 5, edges = [[0,1],[1,2],[2,3],[1,3],[1,4]] Output: false
Constraints:
1 <= n <= 20000 <= edges.length <= 5000edges[i].length == 20 <= ai, bi < nai != bi- There are no self-loops or repeated edges.
Solutions
Union find.
-
class Solution { private int[] p; public boolean validTree(int n, int[][] edges) { p = new int[n]; for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) { p[i] = i; } for (int[] e : edges) { int a = e[0], b = e[1]; if (find(a) == find(b)) { return false; } p[find(a)] = find(b); --n; } return n == 1; } private int find(int x) { if (p[x] != x) { p[x] = find(p[x]); } return p[x]; } } -
class Solution { public: vector<int> p; bool validTree(int n, vector<vector<int>>& edges) { p.resize(n); for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) p[i] = i; for (auto& e : edges) { int a = e[0], b = e[1]; if (find(a) == find(b)) return 0; p[find(a)] = find(b); --n; } return n == 1; } int find(int x) { if (p[x] != x) p[x] = find(p[x]); return p[x]; } }; -
class Solution: def validTree(self, n: int, edges: List[List[int]]) -> bool: def find(x): if p[x] != x: p[x] = find(p[x]) return p[x] p = list(range(n)) for a, b in edges: if find(a) == find(b): return False p[find(a)] = find(b) n -= 1 return n == 1 -
func validTree(n int, edges [][]int) bool { p := make([]int, n) for i := range p { p[i] = i } var find func(x int) int find = func(x int) int { if p[x] != x { p[x] = find(p[x]) } return p[x] } for _, e := range edges { a, b := e[0], e[1] if find(a) == find(b) { return false } p[find(a)] = find(b) n-- } return n == 1 } -
/** * @param {number} n * @param {number[][]} edges * @return {boolean} */ var validTree = function (n, edges) { let p = new Array(n); for (let i = 0; i < n; ++i) { p[i] = i; } function find(x) { if (p[x] != x) { p[x] = find(p[x]); } return p[x]; } for (const [a, b] of edges) { if (find(a) == find(b)) { return false; } p[find(a)] = find(b); --n; } return n == 1; };