Welcome to Subscribe On Youtube
236. Lowest Common Ancestor of a Binary Tree
Description
Given a binary tree, find the lowest common ancestor (LCA) of two given nodes in the tree.
According to the definition of LCA on Wikipedia: “The lowest common ancestor is defined between two nodes p and q as the lowest node in T that has both p and q as descendants (where we allow a node to be a descendant of itself).”
Example 1:
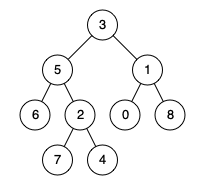
Input: root = [3,5,1,6,2,0,8,null,null,7,4], p = 5, q = 1 Output: 3 Explanation: The LCA of nodes 5 and 1 is 3.
Example 2:

Input: root = [3,5,1,6,2,0,8,null,null,7,4], p = 5, q = 4 Output: 5 Explanation: The LCA of nodes 5 and 4 is 5, since a node can be a descendant of itself according to the LCA definition.
Example 3:
Input: root = [1,2], p = 1, q = 2 Output: 1
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[2, 105]. -109 <= Node.val <= 109- All
Node.valare unique. p != qpandqwill exist in the tree.
Solutions
The LCA of two nodes p and q in a binary tree is the lowest node in T that has both p and q as descendants (where we allow a node to be a descendant of itself).
The idea behind the solution is to recursively search for the nodes p and q in the left and right subtrees. There are a few cases to consider:
- If either
porqmatches the current node, this node must be part of the LCA. - If
pandqare found in different subtrees of a node, this node is their LCA. -
If
pandqare found in the same subtree, continue searching in that subtree for the LCA. -
Base Case: If the current node is
None, or if it matches eitherporq, return the current node. This means we have found one of the nodes we’re looking for, or we’ve reached the end of a path without finding either, in which case we returnNone. -
Recursive Search: The function recursively searches the left and right subtrees for
pandq. - Identifying LCA:
- If both
leftandrightsearch calls return non-null values, it means we’ve foundpandqin different subtrees of the current node. Hence, the current node is the LCA. - If only one of the search calls returns a non-null value, it means both
pandqare located in the same subtree, or only one of the nodes was found. Return the non-null result.
- If both
-
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * public class TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode left; * TreeNode right; * TreeNode(int x) { val = x; } * } */ class Solution { public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) { if (root == null || root == p || root == q) return root; TreeNode left = lowestCommonAncestor(root.left, p, q); TreeNode right = lowestCommonAncestor(root.right, p, q); if (left == null) return right; if (right == null) return left; return root; } } -
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * struct TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode *left; * TreeNode *right; * TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {} * }; */ class Solution { public: TreeNode* lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode* root, TreeNode* p, TreeNode* q) { if (!root || root == p || root == q) return root; TreeNode* left = lowestCommonAncestor(root->left, p, q); TreeNode* right = lowestCommonAncestor(root->right, p, q); if (left && right) return root; return left ? left : right; } }; -
# Definition for a binary tree node. # class TreeNode: # def __init__(self, x): # self.val = x # self.left = None # self.right = None class Solution: def lowestCommonAncestor( self, root: 'TreeNode', p: 'TreeNode', q: 'TreeNode' ) -> 'TreeNode': if root is None or root == p or root == q: return root left = self.lowestCommonAncestor(root.left, p, q) right = self.lowestCommonAncestor(root.right, p, q) return root if left and right else (left or right) ############ # Definition for a binary tree node. # class TreeNode(object): # def __init__(self, x): # self.val = x # self.left = None # self.right = None class Solution(object): def lowestCommonAncestor(self, root, p, q): """ :type root: TreeNode :type p: TreeNode :type q: TreeNode :rtype: TreeNode """ if not root: return root left = self.lowestCommonAncestor(root.left, p, q) right = self.lowestCommonAncestor(root.right, p, q) if left and right: return root if root == p or root == q: return root if left: return left if right: return right return None -
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * type TreeNode struct { * Val int * Left *TreeNode * Right *TreeNode * } */ func lowestCommonAncestor(root, p, q *TreeNode) *TreeNode { if root == nil || root == p || root == q { return root } left := lowestCommonAncestor(root.Left, p, q) right := lowestCommonAncestor(root.Right, p, q) if left == nil { return right } if right == nil { return left } return root } -
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * class TreeNode { * val: number * left: TreeNode | null * right: TreeNode | null * constructor(val?: number, left?: TreeNode | null, right?: TreeNode | null) { * this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val) * this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left) * this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right) * } * } */ function lowestCommonAncestor( root: TreeNode | null, p: TreeNode | null, q: TreeNode | null, ): TreeNode | null { const find = (root: TreeNode | null) => { if (root == null || root == p || root == q) { return root; } const left = find(root.left); const right = find(root.right); if (left != null && right != null) { return root; } if (left != null) { return left; } return right; }; return find(root); } -
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * function TreeNode(val) { * this.val = val; * this.left = this.right = null; * } */ /** * @param {TreeNode} root * @param {TreeNode} p * @param {TreeNode} q * @return {TreeNode} */ var lowestCommonAncestor = function (root, p, q) { if (!root || root == p || root == q) return root; const left = lowestCommonAncestor(root.left, p, q); const right = lowestCommonAncestor(root.right, p, q); if (!left) return right; if (!right) return left; return root; }; -
// Definition for a binary tree node. // #[derive(Debug, PartialEq, Eq)] // pub struct TreeNode { // pub val: i32, // pub left: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>, // pub right: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>, // } // // impl TreeNode { // #[inline] // pub fn new(val: i32) -> Self { // TreeNode { // val, // left: None, // right: None // } // } // } use std::rc::Rc; use std::cell::RefCell; impl Solution { fn find( root: &Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>, p: &Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>, q: &Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>> ) -> Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>> { if root.is_none() || root == p || root == q { return root.clone(); } let node = root.as_ref().unwrap().borrow(); let left = Self::find(&node.left, p, q); let right = Self::find(&node.right, p, q); match (left.is_some(), right.is_some()) { (true, false) => left, (false, true) => right, (false, false) => None, (true, true) => root.clone(), } } pub fn lowest_common_ancestor( root: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>, p: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>, q: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>> ) -> Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>> { Self::find(&root, &p, &q) } }