Welcome to Subscribe On Youtube
Question
Formatted question description: https://leetcode.ca/all/173.html
Implement the BSTIterator class that represents an iterator over the in-order traversal of a binary search tree (BST):
BSTIterator(TreeNode root)Initializes an object of theBSTIteratorclass. Therootof the BST is given as part of the constructor. The pointer should be initialized to a non-existent number smaller than any element in the BST.boolean hasNext()Returnstrueif there exists a number in the traversal to the right of the pointer, otherwise returnsfalse.int next()Moves the pointer to the right, then returns the number at the pointer.
Notice that by initializing the pointer to a non-existent smallest number, the first call to next() will return the smallest element in the BST.
You may assume that next() calls will always be valid. That is, there will be at least a next number in the in-order traversal when next() is called.
Example 1:
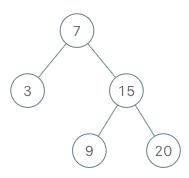
Input ["BSTIterator", "next", "next", "hasNext", "next", "hasNext", "next", "hasNext", "next", "hasNext"] [[[7, 3, 15, null, null, 9, 20]], [], [], [], [], [], [], [], [], []] Output [null, 3, 7, true, 9, true, 15, true, 20, false] Explanation BSTIterator bSTIterator = new BSTIterator([7, 3, 15, null, null, 9, 20]); bSTIterator.next(); // return 3 bSTIterator.next(); // return 7 bSTIterator.hasNext(); // return True bSTIterator.next(); // return 9 bSTIterator.hasNext(); // return True bSTIterator.next(); // return 15 bSTIterator.hasNext(); // return True bSTIterator.next(); // return 20 bSTIterator.hasNext(); // return False
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[1, 105]. 0 <= Node.val <= 106- At most
105calls will be made tohasNext, andnext.
Follow up:
- Could you implement
next()andhasNext()to run in averageO(1)time and useO(h)memory, wherehis the height of the tree?
Algorithm
The non-recursive form of the in-order traversal of the binary tree requires an additional definition of a stack to assist. The building rule of the binary search tree is left<root<right, and the in-order traversal can extract all nodes from small to large.
Code
-
import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.Collections; import java.util.List; import java.util.Stack; public class Binary_Search_Tree_Iterator { /** * Definition for binary tree * public class TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode left; * TreeNode right; * TreeNode(int x) { val = x; } * } */ public class BSTIterator { Stack<TreeNode> sk; // @note:@memorize: important feature, min is always going left branch to leaf public BSTIterator(TreeNode root) { sk = new Stack<>(); // all the way to leftmost leaf while (root != null) { sk.push(root); root = root.left; } } /** @return whether we have a next smallest number */ public boolean hasNext() { return !sk.isEmpty(); } /** @return the next smallest number */ public int next() { TreeNode minNode = sk.pop(); TreeNode current = minNode; // update stack, possible next time min is frmo its right-then-left branch if (current.right != null) { current = current.right; // same logic as in constructor while (current != null) { sk.push(current.left); current = current.left; } } return minNode.val; } } /** * Your BSTIterator will be called like this: * BSTIterator i = new BSTIterator(root); * while (i.hasNext()) v[f()] = i.next(); */ } ############ /** * Definition for a binary tree node. * public class TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode left; * TreeNode right; * TreeNode() {} * TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; } * TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) { * this.val = val; * this.left = left; * this.right = right; * } * } */ class BSTIterator { private Deque<TreeNode> stack = new LinkedList<>(); public BSTIterator(TreeNode root) { for (; root != null; root = root.left) { stack.offerLast(root); } } public int next() { TreeNode cur = stack.pollLast(); for (TreeNode node = cur.right; node != null; node = node.left) { stack.offerLast(node); } return cur.val; } public boolean hasNext() { return !stack.isEmpty(); } } /** * Your BSTIterator object will be instantiated and called as such: * BSTIterator obj = new BSTIterator(root); * int param_1 = obj.next(); * boolean param_2 = obj.hasNext(); */ -
// OJ: https://leetcode.com/problems/binary-search-tree-iterator/ // Time: O(1) amortized // Space: O(H) class BSTIterator { private: stack<TreeNode*> s; void pushNodes(TreeNode *node) { while (node) { s.push(node); node = node->left; } } public: BSTIterator(TreeNode* root) { pushNodes(root); } int next() { auto node = s.top(); s.pop(); pushNodes(node->right); return node->val; } bool hasNext() { return s.size(); } }; -
# Definition for a binary tree node. # class TreeNode: # def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None): # self.val = val # self.left = left # self.right = right class BSTIterator: def __init__(self, root: TreeNode): self.stack = [] self._leftmost_inorder(root) def _leftmost_inorder(self, node): while node: self.stack.append(node) node = node.left def next(self) -> int: cur = self.stack.pop() node = cur.right self._leftmost_inorder(node) return cur.val def hasNext(self) -> bool: return len(self.stack) > 0 # Your BSTIterator object will be instantiated and called as such: # obj = BSTIterator(root) # param_1 = obj.next() # param_2 = obj.hasNext() ############# # Definition for a binary tree node. # class TreeNode: # def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None): # self.val = val # self.left = left # self.right = right class BSTIterator: def __init__(self, root: TreeNode): self.stack = [] while root: self.stack.append(root) root = root.left def next(self) -> int: cur = self.stack.pop() node = cur.right while node: # deplicated while block self.stack.append(node) node = node.left return cur.val def hasNext(self) -> bool: return len(self.stack) > 0 # Your BSTIterator object will be instantiated and called as such: # obj = BSTIterator(root) # param_1 = obj.next() # param_2 = obj.hasNext() -
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * type TreeNode struct { * Val int * Left *TreeNode * Right *TreeNode * } */ type BSTIterator struct { stack []*TreeNode } func Constructor(root *TreeNode) BSTIterator { var stack []*TreeNode for ; root != nil; root = root.Left { stack = append(stack, root) } return BSTIterator{ stack: stack, } } func (this *BSTIterator) Next() int { cur := this.stack[len(this.stack)-1] this.stack = this.stack[:len(this.stack)-1] for node := cur.Right; node != nil; node = node.Left { this.stack = append(this.stack, node) } return cur.Val } func (this *BSTIterator) HasNext() bool { return len(this.stack) > 0 } /** * Your BSTIterator object will be instantiated and called as such: * obj := Constructor(root); * param_1 := obj.Next(); * param_2 := obj.HasNext(); */ -
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * class TreeNode { * val: number * left: TreeNode | null * right: TreeNode | null * constructor(val?: number, left?: TreeNode | null, right?: TreeNode | null) { * this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val) * this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left) * this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right) * } * } */ class BSTIterator { private stack: TreeNode[]; constructor(root: TreeNode | null) { this.stack = []; const dfs = (root: TreeNode | null) => { if (root == null) { return; } this.stack.push(root); dfs(root.left); }; dfs(root); } next(): number { const { val, right } = this.stack.pop(); if (right) { let cur = right; while (cur != null) { this.stack.push(cur); cur = cur.left; } } return val; } hasNext(): boolean { return this.stack.length !== 0; } } /** * Your BSTIterator object will be instantiated and called as such: * var obj = new BSTIterator(root) * var param_1 = obj.next() * var param_2 = obj.hasNext() */ -
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * function TreeNode(val, left, right) { * this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val) * this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left) * this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right) * } */ /** * @param {TreeNode} root */ var BSTIterator = function (root) { this.stack = []; for (; root != null; root = root.left) { this.stack.push(root); } }; /** * @return {number} */ BSTIterator.prototype.next = function () { let cur = this.stack.pop(); let node = cur.right; for (; node != null; node = node.left) { this.stack.push(node); } return cur.val; }; /** * @return {boolean} */ BSTIterator.prototype.hasNext = function () { return this.stack.length > 0; }; /** * Your BSTIterator object will be instantiated and called as such: * var obj = new BSTIterator(root) * var param_1 = obj.next() * var param_2 = obj.hasNext() */ -
// Definition for a binary tree node. // #[derive(Debug, PartialEq, Eq)] // pub struct TreeNode { // pub val: i32, // pub left: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>, // pub right: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>, // } // // impl TreeNode { // #[inline] // pub fn new(val: i32) -> Self { // TreeNode { // val, // left: None, // right: None // } // } // } struct BSTIterator { stack: Vec<Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>>, } use std::rc::Rc; use std::cell::RefCell; /** * `&self` means the method takes an immutable reference. * If you need a mutable reference, change it to `&mut self` instead. */ impl BSTIterator { fn dfs( mut root: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>, stack: &mut Vec<Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>>, ) { if root.is_some() { let left = root.as_mut().unwrap().borrow_mut().left.take(); stack.push(root); Self::dfs(left, stack); } } fn new(root: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>) -> Self { let mut stack = vec![]; Self::dfs(root, &mut stack); BSTIterator { stack } } fn next(&mut self) -> i32 { let node = self.stack.pop().unwrap().unwrap(); let mut node = node.borrow_mut(); if node.right.is_some() { Self::dfs(node.right.take(), &mut self.stack) } node.val } fn has_next(&self) -> bool { self.stack.len() != 0 } } /** * Your BSTIterator object will be instantiated and called as such: * let obj = BSTIterator::new(root); * let ret_1: i32 = obj.next(); * let ret_2: bool = obj.has_next(); */