Implement an iterator over a binary search tree (BST). Your iterator will be initialized with the root node of a BST.
Calling next() will return the next smallest number in the BST.
Example:
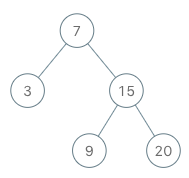
BSTIterator iterator = new BSTIterator(root); iterator.next(); // return 3 iterator.next(); // return 7 iterator.hasNext(); // return true iterator.next(); // return 9 iterator.hasNext(); // return true iterator.next(); // return 15 iterator.hasNext(); // return true iterator.next(); // return 20 iterator.hasNext(); // return false
Note:
next()andhasNext()should run in average O(1) time and uses O(h) memory, where h is the height of the tree.- You may assume that
next()call will always be valid, that is, there will be at least a next smallest number in the BST whennext()is called.
Difficulty:
MediumLock:
NormalCompany:
Alibaba Amazon Apple Bloomberg Cisco eBay Facebook Google LinkedIn Microsoft Oracle Qualtrics Splunk UberProblem Solution
173-Binary-Search-Tree-IteratorAll Problems:
Link to All Problems
All contents and pictures on this website come from the Internet and are updated regularly every week. They are for personal study and research only, and should not be used for commercial purposes. Thank you for your cooperation.