Welcome to Subscribe On Youtube
143. Reorder List
Description
You are given the head of a singly linked-list. The list can be represented as:
L0 → L1 → … → Ln - 1 → Ln
Reorder the list to be on the following form:
L0 → Ln → L1 → Ln - 1 → L2 → Ln - 2 → …
You may not modify the values in the list's nodes. Only nodes themselves may be changed.
Example 1:
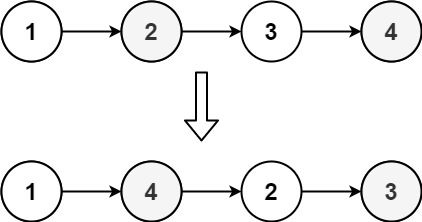
Input: head = [1,2,3,4] Output: [1,4,2,3]
Example 2:
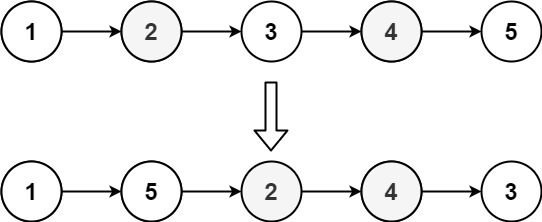
Input: head = [1,2,3,4,5] Output: [1,5,2,4,3]
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the list is in the range
[1, 5 * 104]. 1 <= Node.val <= 1000
Solutions
-
/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * public class ListNode { * int val; * ListNode next; * ListNode() {} * ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; } * ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; } * } */ class Solution { public void reorderList(ListNode head) { ListNode fast = head, slow = head; while (fast.next != null && fast.next.next != null) { slow = slow.next; fast = fast.next.next; } ListNode cur = slow.next; slow.next = null; ListNode pre = null; while (cur != null) { ListNode t = cur.next; cur.next = pre; pre = cur; cur = t; } cur = head; while (pre != null) { ListNode t = pre.next; pre.next = cur.next; cur.next = pre; cur = pre.next; pre = t; } } } -
/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * struct ListNode { * int val; * ListNode *next; * ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {} * ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {} * ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {} * }; */ class Solution { public: void reorderList(ListNode* head) { ListNode* fast = head; ListNode* slow = head; while (fast->next && fast->next->next) { slow = slow->next; fast = fast->next->next; } ListNode* cur = slow->next; slow->next = nullptr; ListNode* pre = nullptr; while (cur) { ListNode* t = cur->next; cur->next = pre; pre = cur; cur = t; } cur = head; while (pre) { ListNode* t = pre->next; pre->next = cur->next; cur->next = pre; cur = pre->next; pre = t; } } }; -
# Definition for singly-linked list. # class ListNode: # def __init__(self, val=0, next=None): # self.val = val # self.next = next class Solution: def reorderList(self, head: Optional[ListNode]) -> None: fast = slow = head while fast.next and fast.next.next: slow = slow.next fast = fast.next.next cur = slow.next slow.next = None pre = None while cur: t = cur.next cur.next = pre pre, cur = cur, t cur = head while pre: t = pre.next pre.next = cur.next cur.next = pre cur, pre = pre.next, t -
/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * type ListNode struct { * Val int * Next *ListNode * } */ func reorderList(head *ListNode) { fast, slow := head, head for fast.Next != nil && fast.Next.Next != nil { slow, fast = slow.Next, fast.Next.Next } cur := slow.Next slow.Next = nil var pre *ListNode for cur != nil { t := cur.Next cur.Next = pre pre, cur = cur, t } cur = head for pre != nil { t := pre.Next pre.Next = cur.Next cur.Next = pre cur, pre = pre.Next, t } } -
/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * class ListNode { * val: number * next: ListNode | null * constructor(val?: number, next?: ListNode | null) { * this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val) * this.next = (next===undefined ? null : next) * } * } */ /** Do not return anything, modify head in-place instead. */ function reorderList(head: ListNode | null): void { let slow = head; let fast = head; while (fast != null && fast.next != null) { slow = slow.next; fast = fast.next.next; } let next = slow.next; slow.next = null; while (next != null) { [next.next, slow, next] = [slow, next, next.next]; } let left = head; let right = slow; while (right.next != null) { const next = left.next; left.next = right; right = right.next; left.next.next = next; left = left.next.next; } } -
/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * function ListNode(val, next) { * this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val) * this.next = (next===undefined ? null : next) * } */ /** * @param {ListNode} head * @return {void} Do not return anything, modify head in-place instead. */ var reorderList = function (head) { let slow = head; let fast = head; while (fast.next && fast.next.next) { slow = slow.next; fast = fast.next.next; } let cur = slow.next; slow.next = null; let pre = null; while (cur) { const t = cur.next; cur.next = pre; pre = cur; cur = t; } cur = head; while (pre) { const t = pre.next; pre.next = cur.next; cur.next = pre; cur = pre.next; pre = t; } }; -
/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * public class ListNode { * public int val; * public ListNode next; * public ListNode(int val=0, ListNode next=null) { * this.val = val; * this.next = next; * } * } */ public class Solution { public void ReorderList(ListNode head) { ListNode slow = head; ListNode fast = head; while (fast.next != null && fast.next.next != null) { slow = slow.next; fast = fast.next.next; } ListNode cur = slow.next; slow.next = null; ListNode pre = null; while (cur != null) { ListNode t = cur.next; cur.next = pre; pre = cur; cur = t; } cur = head; while (pre != null) { ListNode t = pre.next; pre.next = cur.next; cur.next = pre; cur = pre.next; pre = t; } } } -
// Definition for singly-linked list. // #[derive(PartialEq, Eq, Clone, Debug)] // pub struct ListNode { // pub val: i32, // pub next: Option<Box<ListNode>> // } // // impl ListNode { // #[inline] // fn new(val: i32) -> Self { // ListNode { // next: None, // val // } // } // } use std::collections::VecDeque; impl Solution { pub fn reorder_list(head: &mut Option<Box<ListNode>>) { let mut tail = &mut head.as_mut().unwrap().next; let mut head = tail.take(); let mut deque = VecDeque::new(); while head.is_some() { let next = head.as_mut().unwrap().next.take(); deque.push_back(head); head = next; } let mut flag = false; while !deque.is_empty() { *tail = if flag { deque.pop_front().unwrap() } else { deque.pop_back().unwrap() }; tail = &mut tail.as_mut().unwrap().next; flag = !flag; } } }