Welcome to Subscribe On Youtube
118. Pascal’s Triangle
Description
Given an integer numRows, return the first numRows of Pascal's triangle.
In Pascal's triangle, each number is the sum of the two numbers directly above it as shown:
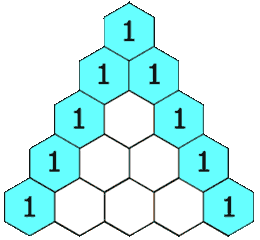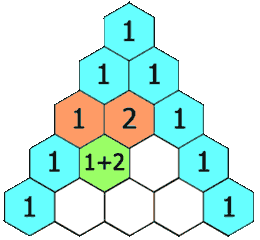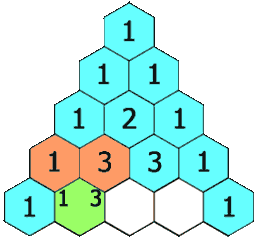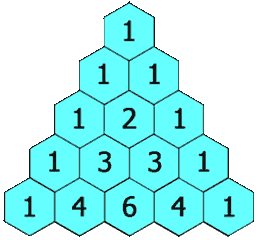
Example 1:
Input: numRows = 5 Output: [[1],[1,1],[1,2,1],[1,3,3,1],[1,4,6,4,1]]
Example 2:
Input: numRows = 1 Output: [[1]]
Constraints:
1 <= numRows <= 30
Solutions
Solution 1: Simulation
First, we create an answer array $f$, and then set the first row of $f$ to $[1]$. Next, starting from the second row, the first and last elements of each row are $1$, and the other elements are calculated by $f[i][j] = f[i - 1][j - 1] + f[i - 1][j]$.
The time complexity is $O(n^2)$, and the space complexity is $O(n^2)$. Here, $n$ is the number of rows.
-
class Solution { public List<List<Integer>> generate(int numRows) { List<List<Integer>> f = new ArrayList<>(); f.add(List.of(1)); for (int i = 0; i < numRows - 1; ++i) { List<Integer> g = new ArrayList<>(); g.add(1); for (int j = 0; j < f.get(i).size() - 1; ++j) { g.add(f.get(i).get(j) + f.get(i).get(j + 1)); } g.add(1); f.add(g); } return f; } } -
class Solution { public: vector<vector<int>> generate(int numRows) { vector<vector<int>> f; f.push_back(vector<int>(1, 1)); for (int i = 0; i < numRows - 1; ++i) { vector<int> g; g.push_back(1); for (int j = 0; j < f[i].size() - 1; ++j) { g.push_back(f[i][j] + f[i][j + 1]); } g.push_back(1); f.push_back(g); } return f; } }; -
class Solution: def generate(self, numRows: int) -> List[List[int]]: f = [[1]] for i in range(numRows - 1): g = [1] + [a + b for a, b in pairwise(f[-1])] + [1] f.append(g) return f -
func generate(numRows int) [][]int { f := [][]int{[]int{1} } for i := 0; i < numRows-1; i++ { g := []int{1} for j := 0; j < len(f[i])-1; j++ { g = append(g, f[i][j]+f[i][j+1]) } g = append(g, 1) f = append(f, g) } return f } -
function generate(numRows: number): number[][] { const f: number[][] = [[1]]; for (let i = 0; i < numRows - 1; ++i) { const g: number[] = [1]; for (let j = 0; j < f[i].length - 1; ++j) { g.push(f[i][j] + f[i][j + 1]); } g.push(1); f.push(g); } return f; } -
/** * @param {number} numRows * @return {number[][]} */ var generate = function (numRows) { const f = [[1]]; for (let i = 0; i < numRows - 1; ++i) { const g = [1]; for (let j = 0; j < f[i].length - 1; ++j) { g.push(f[i][j] + f[i][j + 1]); } g.push(1); f.push(g); } return f; }; -
impl Solution { #[allow(dead_code)] pub fn generate(num_rows: i32) -> Vec<Vec<i32>> { let mut ret_vec: Vec<Vec<i32>> = Vec::new(); let mut cur_vec: Vec<i32> = Vec::new(); for i in 0..num_rows as usize { let mut new_vec: Vec<i32> = vec![1; i + 1]; for j in 1..i { new_vec[j] = cur_vec[j - 1] + cur_vec[j]; } cur_vec = new_vec.clone(); ret_vec.push(new_vec); } ret_vec } } -
public class Solution { public IList<IList<int>> Generate(int numRows) { var f = new List<IList<int>> { new List<int> { 1 } }; for (int i = 1; i < numRows; ++i) { var g = new List<int> { 1 }; for (int j = 1; j < f[i - 1].Count; ++j) { g.Add(f[i - 1][j - 1] + f[i - 1][j]); } g.Add(1); f.Add(g); } return f; } }