Welcome to Subscribe On Youtube
117. Populating Next Right Pointers in Each Node II
Description
Given a binary tree
struct Node {
int val;
Node *left;
Node *right;
Node *next;
}
Populate each next pointer to point to its next right node. If there is no next right node, the next pointer should be set to NULL.
Initially, all next pointers are set to NULL.
Example 1:
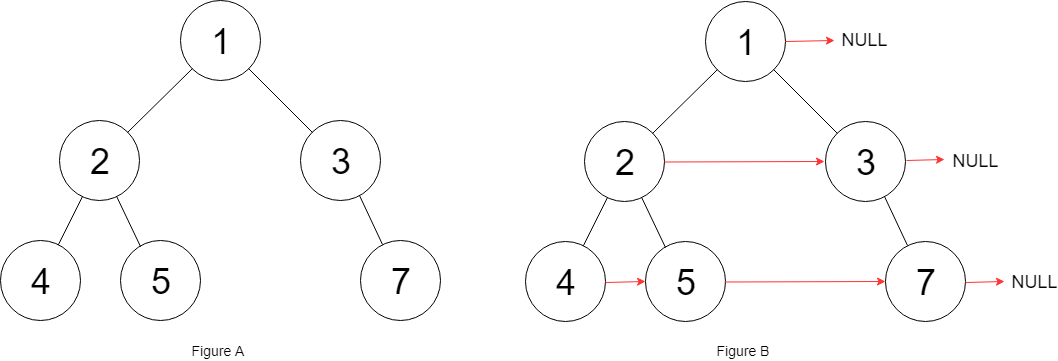
Input: root = [1,2,3,4,5,null,7] Output: [1,#,2,3,#,4,5,7,#] Explanation: Given the above binary tree (Figure A), your function should populate each next pointer to point to its next right node, just like in Figure B. The serialized output is in level order as connected by the next pointers, with '#' signifying the end of each level.
Example 2:
Input: root = [] Output: []
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[0, 6000]. -100 <= Node.val <= 100
Follow-up:
- You may only use constant extra space.
- The recursive approach is fine. You may assume implicit stack space does not count as extra space for this problem.
Solutions
Solution 1: BFS
We use a queue $q$ for level order traversal. Each time we traverse a level, we connect the nodes of the current level in order.
The time complexity is $O(n)$, and the space complexity is $O(n)$. Here, $n$ is the number of nodes in the binary tree.
Solution 2: Space Optimization
The space complexity of Solution 1 is relatively high because it requires a queue to store the nodes of each level. We can implement it with constant space.
We define two pointers $prev$ and $next$, which point to the previous node and the first node of the next level, respectively. When traversing the nodes of the current level, we string the nodes of the next level together and find the first node of the next level. After the current level is traversed, we assign the first node $next$ of the next level to $node$ and continue to traverse.
The time complexity is $O(n)$, where $n$ is the number of nodes in the binary tree. The space complexity is $O(1)$.
-
/* // Definition for a Node. class Node { public int val; public Node left; public Node right; public Node next; public Node() {} public Node(int _val) { val = _val; } public Node(int _val, Node _left, Node _right, Node _next) { val = _val; left = _left; right = _right; next = _next; } }; */ class Solution { private Node prev, next; public Node connect(Node root) { Node node = root; while (node != null) { prev = null; next = null; while (node != null) { modify(node.left); modify(node.right); node = node.next; } node = next; } return root; } private void modify(Node curr) { if (curr == null) { return; } if (next == null) { next = curr; } if (prev != null) { prev.next = curr; } prev = curr; } } -
/* // Definition for a Node. class Node { public: int val; Node* left; Node* right; Node* next; Node() : val(0), left(NULL), right(NULL), next(NULL) {} Node(int _val) : val(_val), left(NULL), right(NULL), next(NULL) {} Node(int _val, Node* _left, Node* _right, Node* _next) : val(_val), left(_left), right(_right), next(_next) {} }; */ class Solution { public: Node* connect(Node* root) { Node* node = root; Node* prev = nullptr; Node* next = nullptr; auto modify = [&](Node* curr) { if (!curr) { return; } if (!next) { next = curr; } if (prev) { prev->next = curr; } prev = curr; }; while (node) { prev = next = nullptr; while (node) { modify(node->left); modify(node->right); node = node->next; } node = next; } return root; } }; -
""" # Definition for a Node. class Node: def __init__(self, val: int = 0, left: 'Node' = None, right: 'Node' = None, next: 'Node' = None): self.val = val self.left = left self.right = right self.next = next """ class Solution: def connect(self, root: "Node") -> "Node": def modify(curr): nonlocal prev_node, next_node if curr is None: return if next_node is None: # next level's first node next_node = curr # "if next_node is None" logic can be replaced by: # next_node = next_node or curr if prev_node: prev_node.next = curr prev_node = curr node = root while node: prev_node = next_node = None while node: # process for every level modify(node.left) modify(node.right) node = node.next node = next_node return root # use dummyHead.next to find each level's first node class Solution: def connect(self, root: 'Node') -> 'Node': dummyHead = Node(0) pre = dummyHead real_root = root while root: if root.left: # @note: here pre is same as dummyHead, pointing to 1st node of this level. this is before pre is updated to be other nodes pre.next = root.left pre = pre.next if root.right: pre.next = root.right pre = pre.next root = root.next if not root: # reach the end of current layer # shift pre back to the beginning, # get ready to point to the first element in next layer, # just like the same code before while loop pre = dummyHead # root comes down one level below to the first available non null node root = dummyHead.next # reset dummyhead back to default null, so that later it will point to next level's first node dummyHead.next = None return real_root ############### """ # Definition for a Node. class Node: def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None, next=None): self.val = val self.left = left self.right = right self.next = next """ from collections import deque class Solution: # recursion, dfs def connect(self, root: 'Node') -> 'Node': if not root: return None # Initialize a queue with the root node and its level (0). queue = deque([(root, 0)]) # Process nodes level by level. while queue: current_node, level = queue.popleft() # If there's another node in the queue with the same level, # connect the current node's next pointer to the next node in the queue. if queue and queue[0][1] == level: current_node.next = queue[0][0] # Enqueue left and right children if they exist, along with their level. if current_node.left: queue.append((current_node.left, level + 1)) if current_node.right: queue.append((current_node.right, level + 1)) return root ############### # Definition for binary tree with next pointer. # class TreeLinkNode: # def __init__(self, x): # self.val = x # self.left = None # self.right = None # self.next = None class Solution: # @param root, a tree link node # @return nothing def connect(self, root): p = root pre = None head = None while p: if p.left: if pre: pre.next = p.left pre = p.left if p.right: if pre: pre.next = p.right pre = p.right if not head: head = p.left or p.right if p.next: p = p.next else: p = head head = None pre = None -
/** * Definition for a Node. * type Node struct { * Val int * Left *Node * Right *Node * Next *Node * } */ func connect(root *Node) *Node { node := root var prev, next *Node modify := func(curr *Node) { if curr == nil { return } if next == nil { next = curr } if prev != nil { prev.Next = curr } prev = curr } for node != nil { prev, next = nil, nil for node != nil { modify(node.Left) modify(node.Right) node = node.Next } node = next } return root } -
/** * Definition for Node. * class Node { * val: number * left: Node | null * right: Node | null * next: Node | null * constructor(val?: number, left?: Node, right?: Node, next?: Node) { * this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val) * this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left) * this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right) * this.next = (next===undefined ? null : next) * } * } */ function connect(root: Node | null): Node | null { const modify = (curr: Node | null): void => { if (!curr) { return; } next = next || curr; if (prev) { prev.next = curr; } prev = curr; }; let node = root; let [prev, next] = [null, null]; while (node) { while (node) { modify(node.left); modify(node.right); node = node.next; } node = next; [prev, next] = [null, null]; } return root; } -
/* // Definition for a Node. public class Node { public int val; public Node left; public Node right; public Node next; public Node() {} public Node(int _val) { val = _val; } public Node(int _val, Node _left, Node _right, Node _next) { val = _val; left = _left; right = _right; next = _next; } } */ public class Solution { private Node prev, next; public Node Connect(Node root) { Node node = root; while (node != null) { prev = null; next = null; while (node != null) { modify(node.left); modify(node.right); node = node.next; } node = next; } return root; } private void modify(Node curr) { if (curr == null) { return; } if (next == null) { next = curr; } if (prev != null) { prev.next = curr; } prev = curr; } }