Welcome to Subscribe On Youtube
114. Flatten Binary Tree to Linked List
Description
Given the root of a binary tree, flatten the tree into a "linked list":
- The "linked list" should use the same
TreeNodeclass where therightchild pointer points to the next node in the list and theleftchild pointer is alwaysnull. - The "linked list" should be in the same order as a pre-order traversal of the binary tree.
Example 1:
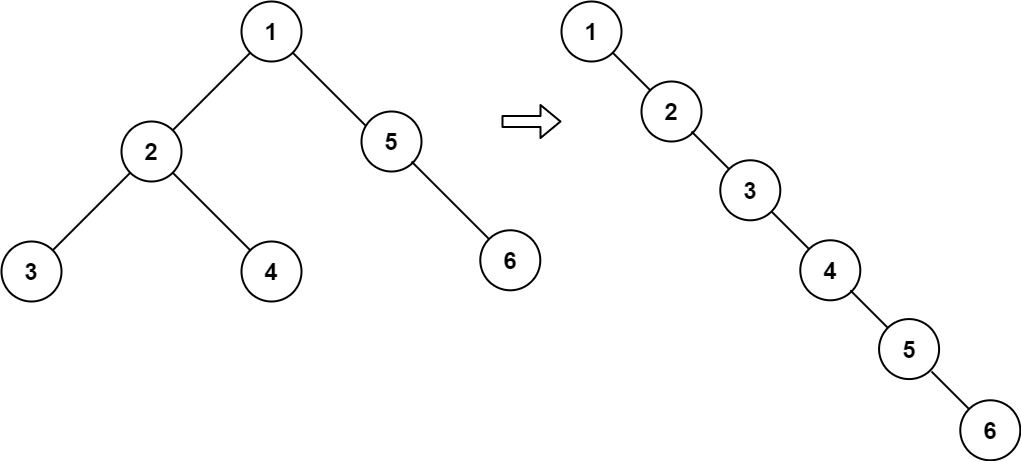
Input: root = [1,2,5,3,4,null,6] Output: [1,null,2,null,3,null,4,null,5,null,6]
Example 2:
Input: root = [] Output: []
Example 3:
Input: root = [0] Output: [0]
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[0, 2000]. -100 <= Node.val <= 100
Follow up: Can you flatten the tree in-place (with O(1) extra space)?
Solutions
Solution 1: Find Predecessor Node
The visit order of preorder traversal is “root, left subtree, right subtree”. After the last node of the left subtree is visited, the right subtree node of the root node will be visited next.
Therefore, for the current node, if its left child node is not null, we find the rightmost node of the left subtree as the predecessor node, and then assign the right child node of the current node to the right child node of the predecessor node. Then assign the left child node of the current node to the right child node of the current node, and set the left child node of the current node to null. Then take the right child node of the current node as the next node and continue processing until all nodes are processed.
The time complexity is $O(n)$, where $n$ is the number of nodes in the tree. The space complexity is $O(1)$.
Flatten process:
1
/ \
2 5
/ \ \
3 4 6
1
/ \
2 5
\ \
3 6
\
4
1
\
2
\
3
\
4
\
5
\
6
-
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * public class TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode left; * TreeNode right; * TreeNode() {} * TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; } * TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) { * this.val = val; * this.left = left; * this.right = right; * } * } */ class Solution { public void flatten(TreeNode root) { while (root != null) { if (root.left != null) { TreeNode pre = root.left; while (pre.right != null) { pre = pre.right; } pre.right = root.right; root.right = root.left; root.left = null; } root = root.right; } } } -
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * struct TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode *left; * TreeNode *right; * TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {} * TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {} * TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {} * }; */ class Solution { public: void flatten(TreeNode* root) { while (root) { if (root->left) { TreeNode* pre = root->left; while (pre->right) { pre = pre->right; } pre->right = root->right; root->right = root->left; root->left = nullptr; } root = root->right; } } }; -
# Definition for a binary tree node. # class TreeNode: # def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None): # self.val = val # self.left = left # self.right = right class Solution: # stack, pre-order interation def flatten(self, root: TreeNode) -> None: """ Do not return anything, modify root in-place instead. """ if not root: return stack = [root] prev = TreeNode(0) # dummy node while stack: current = stack.pop() if current.right: stack.append(current.right) if current.left: stack.append(current.left) prev.left = None prev.right = current prev = current ########### class Solution: # no stack def flatten(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> None: """ Do not return anything, modify root in-place instead. """ while root: if root.left: pre = root.left while pre.right: # start feom right pre = pre.right pre.right = root.right root.right = root.left root.left = None root = root.right -
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * type TreeNode struct { * Val int * Left *TreeNode * Right *TreeNode * } */ func flatten(root *TreeNode) { for root != nil { left, right := root.Left, root.Right root.Left = nil if left != nil { root.Right = left for left.Right != nil { left = left.Right } left.Right = right } root = root.Right } } -
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * class TreeNode { * val: number * left: TreeNode | null * right: TreeNode | null * constructor(val?: number, left?: TreeNode | null, right?: TreeNode | null) { * this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val) * this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left) * this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right) * } * } */ /** Do not return anything, modify root in-place instead. */ function flatten(root: TreeNode | null): void { while (root !== null) { if (root.left !== null) { let pre = root.left; while (pre.right !== null) { pre = pre.right; } pre.right = root.right; root.right = root.left; root.left = null; } root = root.right; } } -
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * function TreeNode(val, left, right) { * this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val) * this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left) * this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right) * } */ /** * @param {TreeNode} root * @return {void} Do not return anything, modify root in-place instead. */ var flatten = function (root) { while (root) { if (root.left) { let pre = root.left; while (pre.right) { pre = pre.right; } pre.right = root.right; root.right = root.left; root.left = null; } root = root.right; } }; -
// Definition for a binary tree node. // #[derive(Debug, PartialEq, Eq)] // pub struct TreeNode { // pub val: i32, // pub left: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>, // pub right: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>, // } // // impl TreeNode { // #[inline] // pub fn new(val: i32) -> Self { // TreeNode { // val, // left: None, // right: None // } // } // } use std::rc::Rc; use std::cell::RefCell; impl Solution { #[allow(dead_code)] pub fn flatten(root: &mut Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>) { if root.is_none() { return; } let mut v: Vec<Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>> = Vec::new(); // Initialize the vector Self::pre_order_traverse(&mut v, root); // Traverse the vector let n = v.len(); for i in 0..n - 1 { v[i].as_ref().unwrap().borrow_mut().left = None; v[i].as_ref().unwrap().borrow_mut().right = v[i + 1].clone(); } } #[allow(dead_code)] fn pre_order_traverse( v: &mut Vec<Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>>, root: &Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>> ) { if root.is_none() { return; } v.push(root.clone()); let left = root.as_ref().unwrap().borrow().left.clone(); let right = root.as_ref().unwrap().borrow().right.clone(); Self::pre_order_traverse(v, &left); Self::pre_order_traverse(v, &right); } }