Welcome to Subscribe On Youtube
108. Convert Sorted Array to Binary Search Tree
Description
Given an integer array nums where the elements are sorted in ascending order, convert it to a height-balanced binary search tree.
Example 1:
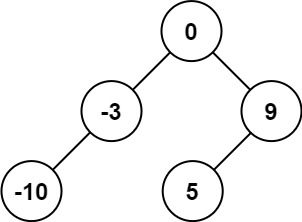
Input: nums = [-10,-3,0,5,9] Output: [0,-3,9,-10,null,5] Explanation: [0,-10,5,null,-3,null,9] is also accepted: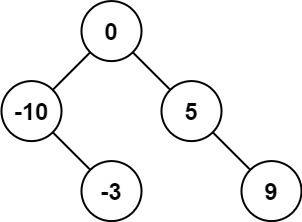
Example 2:
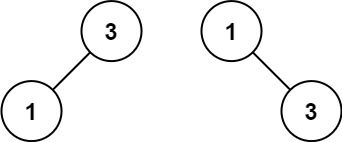
Input: nums = [1,3] Output: [3,1] Explanation: [1,null,3] and [3,1] are both height-balanced BSTs.
Constraints:
1 <= nums.length <= 104-104 <= nums[i] <= 104numsis sorted in a strictly increasing order.
Solutions
Solution 1: Binary Search + Recursion
We design a recursive function $dfs(l, r)$, which indicates that the node values of the current binary search tree to be constructed are all within the index range $[l, r]$ of the array nums. This function returns the root node of the constructed binary search tree.
The execution process of the function $dfs(l, r)$ is as follows:
- If $l > r$, it means the current array is empty, return
null. - If $l \leq r$, take the element with the index $mid = \lfloor \frac{l + r}{2} \rfloor$ in the array as the root node of the current binary search tree, where $\lfloor x \rfloor$ represents rounding down $x$.
- Recursively construct the left subtree of the current binary search tree, whose root node value is the element with the index $mid - 1$ in the array, and the node values of the left subtree are all within the index range $[l, mid - 1]$ of the array.
- Recursively construct the right subtree of the current binary search tree, whose root node value is the element with the index $mid + 1$ in the array, and the node values of the right subtree are all within the index range $[mid + 1, r]$ of the array.
- Return the root node of the current binary search tree.
The answer is the return value of the function $dfs(0, n - 1)$.
The time complexity is $O(n)$, and the space complexity is $O(\log n)$. Here, $n$ is the length of the array nums.
-
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * public class TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode left; * TreeNode right; * TreeNode() {} * TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; } * TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) { * this.val = val; * this.left = left; * this.right = right; * } * } */ class Solution { private int[] nums; public TreeNode sortedArrayToBST(int[] nums) { this.nums = nums; return dfs(0, nums.length - 1); } private TreeNode dfs(int l, int r) { if (l > r) { return null; } int mid = (l + r) >> 1; TreeNode left = dfs(l, mid - 1); TreeNode right = dfs(mid + 1, r); return new TreeNode(nums[mid], left, right); } } -
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * struct TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode *left; * TreeNode *right; * TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {} * TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {} * TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {} * }; */ class Solution { public: TreeNode* sortedArrayToBST(vector<int>& nums) { function<TreeNode*(int, int)> dfs = [&](int l, int r) -> TreeNode* { if (l > r) { return nullptr; } int mid = (l + r) >> 1; auto left = dfs(l, mid - 1); auto right = dfs(mid + 1, r); return new TreeNode(nums[mid], left, right); }; return dfs(0, nums.size() - 1); } }; -
# Definition for a binary tree node. # class TreeNode: # def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None): # self.val = val # self.left = left # self.right = right class Solution: def sortedArrayToBST(self, nums: List[int]) -> Optional[TreeNode]: def dfs(l, r): if l > r: return None mid = (l + r) >> 1 left = dfs(l, mid - 1) right = dfs(mid + 1, r) return TreeNode(nums[mid], left, right) return dfs(0, len(nums) - 1) ############ # Definition for a binary tree node. # class TreeNode(object): # def __init__(self, x): # self.val = x # self.left = None # self.right = None class Solution(object): def sortedArrayToBST(self, nums): """ :type nums: List[int] :rtype: TreeNode """ if nums: midPos = len(nums) / 2 mid = nums[midPos] root = TreeNode(mid) root.left = self.sortedArrayToBST(nums[:midPos]) root.right = self.sortedArrayToBST(nums[midPos + 1:]) return root -
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * type TreeNode struct { * Val int * Left *TreeNode * Right *TreeNode * } */ func sortedArrayToBST(nums []int) *TreeNode { var dfs func(int, int) *TreeNode dfs = func(l, r int) *TreeNode { if l > r { return nil } mid := (l + r) >> 1 left, right := dfs(l, mid-1), dfs(mid+1, r) return &TreeNode{nums[mid], left, right} } return dfs(0, len(nums)-1) } -
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * class TreeNode { * val: number * left: TreeNode | null * right: TreeNode | null * constructor(val?: number, left?: TreeNode | null, right?: TreeNode | null) { * this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val) * this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left) * this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right) * } * } */ function sortedArrayToBST(nums: number[]): TreeNode | null { const n = nums.length; if (n === 0) { return null; } const mid = n >> 1; return new TreeNode( nums[mid], sortedArrayToBST(nums.slice(0, mid)), sortedArrayToBST(nums.slice(mid + 1)), ); } -
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * function TreeNode(val, left, right) { * this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val) * this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left) * this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right) * } */ /** * @param {number[]} nums * @return {TreeNode} */ var sortedArrayToBST = function (nums) { const dfs = (l, r) => { if (l > r) { return null; } const mid = (l + r) >> 1; const left = dfs(l, mid - 1); const right = dfs(mid + 1, r); return new TreeNode(nums[mid], left, right); }; return dfs(0, nums.length - 1); }; -
// Definition for a binary tree node. // #[derive(Debug, PartialEq, Eq)] // pub struct TreeNode { // pub val: i32, // pub left: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>, // pub right: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>, // } // // impl TreeNode { // #[inline] // pub fn new(val: i32) -> Self { // TreeNode { // val, // left: None, // right: None // } // } // } use std::rc::Rc; use std::cell::RefCell; impl Solution { fn to_bst(nums: &Vec<i32>, start: usize, end: usize) -> Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>> { if start >= end { return None; } let mid = start + (end - start) / 2; Some( Rc::new( RefCell::new(TreeNode { val: nums[mid], left: Self::to_bst(nums, start, mid), right: Self::to_bst(nums, mid + 1, end), }) ) ) } pub fn sorted_array_to_bst(nums: Vec<i32>) -> Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>> { Self::to_bst(&nums, 0, nums.len()) } } -
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * public class TreeNode { * public int val; * public TreeNode left; * public TreeNode right; * public TreeNode(int val=0, TreeNode left=null, TreeNode right=null) { * this.val = val; * this.left = left; * this.right = right; * } * } */ public class Solution { private int[] nums; public TreeNode SortedArrayToBST(int[] nums) { this.nums = nums; return dfs(0, nums.Length - 1); } private TreeNode dfs(int l, int r) { if (l > r) { return null; } int mid = (l + r) >> 1; return new TreeNode(nums[mid], dfs(l, mid - 1), dfs(mid + 1, r)); } }