Welcome to Subscribe On Youtube
2. Add Two Numbers
Description
You are given two non-empty linked lists representing two non-negative integers. The digits are stored in reverse order, and each of their nodes contains a single digit. Add the two numbers and return the sum as a linked list.
You may assume the two numbers do not contain any leading zero, except the number 0 itself.
Example 1:
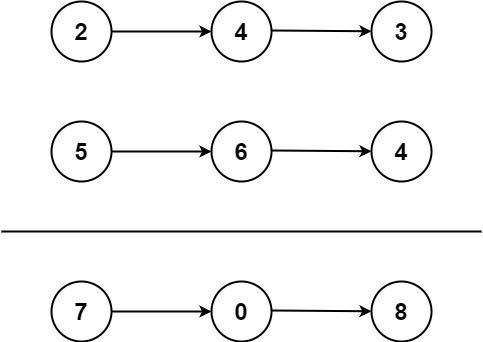
Input: l1 = [2,4,3], l2 = [5,6,4] Output: [7,0,8] Explanation: 342 + 465 = 807.
Example 2:
Input: l1 = [0], l2 = [0] Output: [0]
Example 3:
Input: l1 = [9,9,9,9,9,9,9], l2 = [9,9,9,9] Output: [8,9,9,9,0,0,0,1]
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in each linked list is in the range
[1, 100]. 0 <= Node.val <= 9- It is guaranteed that the list represents a number that does not have leading zeros.
Solutions
Solution 1: Simulation
We traverse two linked lists $l_1$ and $l_2$ at the same time, and use the variable $carry$ to indicate whether there is a carry.
Each time we traverse, we take out the current bit of the corresponding linked list, calculate the sum with the carry $carry$, and then update the value of the carry. Then we add the current bit to the answer linked list. If both linked lists are traversed, and the carry is $0$, the traversal ends.
Finally, we return the head node of the answer linked list.
The time complexity is $O(\max (m, n))$, where $m$ and $n$ are the lengths of the two linked lists. We need to traverse the entire position of the two linked lists, and each position only needs $O(1)$ time. Ignoring the space consumption of the answer, the space complexity is $O(1)$.
-
/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * public class ListNode { * int val; * ListNode next; * ListNode() {} * ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; } * ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; } * } */ class Solution { public ListNode addTwoNumbers(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) { ListNode dummy = new ListNode(0); int carry = 0; ListNode cur = dummy; while (l1 != null || l2 != null || carry != 0) { int s = (l1 == null ? 0 : l1.val) + (l2 == null ? 0 : l2.val) + carry; carry = s / 10; cur.next = new ListNode(s % 10); cur = cur.next; l1 = l1 == null ? null : l1.next; l2 = l2 == null ? null : l2.next; } return dummy.next; } } -
/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * struct ListNode { * int val; * ListNode *next; * ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {} * ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {} * ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {} * }; */ class Solution { public: ListNode* addTwoNumbers(ListNode* l1, ListNode* l2) { ListNode* dummy = new ListNode(); int carry = 0; ListNode* cur = dummy; while (l1 || l2 || carry) { int s = (l1 ? l1->val : 0) + (l2 ? l2->val : 0) + carry; carry = s / 10; cur->next = new ListNode(s % 10); cur = cur->next; l1 = l1 ? l1->next : nullptr; l2 = l2 ? l2->next : nullptr; } return dummy->next; } }; -
# Definition for singly-linked list. # class ListNode: # def __init__(self, val=0, next=None): # self.val = val # self.next = next class Solution: def addTwoNumbers( self, l1: Optional[ListNode], l2: Optional[ListNode] ) -> Optional[ListNode]: dummy = ListNode() carry, curr = 0, dummy while l1 or l2 or carry: s = (l1.val if l1 else 0) + (l2.val if l2 else 0) + carry carry, val = divmod(s, 10) curr.next = ListNode(val) curr = curr.next l1 = l1.next if l1 else None l2 = l2.next if l2 else None return dummy.next -
/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * type ListNode struct { * Val int * Next *ListNode * } */ func addTwoNumbers(l1 *ListNode, l2 *ListNode) *ListNode { dummy := &ListNode{} carry := 0 cur := dummy for l1 != nil || l2 != nil || carry != 0 { s := carry if l1 != nil { s += l1.Val } if l2 != nil { s += l2.Val } carry = s / 10 cur.Next = &ListNode{s % 10, nil} cur = cur.Next if l1 != nil { l1 = l1.Next } if l2 != nil { l2 = l2.Next } } return dummy.Next } -
/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * class ListNode { * val: number * next: ListNode | null * constructor(val?: number, next?: ListNode | null) { * this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val) * this.next = (next===undefined ? null : next) * } * } */ function addTwoNumbers(l1: ListNode | null, l2: ListNode | null): ListNode | null { const dummy = new ListNode(); let cur = dummy; let sum = 0; while (sum !== 0 || l1 != null || l2 != null) { if (l1 != null) { sum += l1.val; l1 = l1.next; } if (l2 != null) { sum += l2.val; l2 = l2.next; } cur.next = new ListNode(sum % 10); cur = cur.next; sum = Math.floor(sum / 10); } return dummy.next; } -
/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * function ListNode(val, next) { * this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val) * this.next = (next===undefined ? null : next) * } */ /** * @param {ListNode} l1 * @param {ListNode} l2 * @return {ListNode} */ var addTwoNumbers = function (l1, l2) { const dummy = new ListNode(); let carry = 0; let cur = dummy; while (l1 || l2 || carry) { const s = (l1?.val || 0) + (l2?.val || 0) + carry; carry = Math.floor(s / 10); cur.next = new ListNode(s % 10); cur = cur.next; l1 = l1?.next; l2 = l2?.next; } return dummy.next; }; -
/** * Definition for a singly-linked list. * class ListNode { * public $val = 0; * public $next = null; * function __construct($val = 0, $next = null) { * $this->val = $val; * $this->next = $next; * } * } */ class Solution { /** * @param ListNode $l1 * @param ListNode $l2 * @return ListNode */ function addTwoNumbers($l1, $l2) { $dummy = new ListNode(0); $current = $dummy; $carry = 0; while ($l1 !== null || $l2 !== null) { $x = $l1 !== null ? $l1->val : 0; $y = $l2 !== null ? $l2->val : 0; $sum = $x + $y + $carry; $carry = (int) ($sum / 10); $current->next = new ListNode($sum % 10); $current = $current->next; if ($l1 !== null) { $l1 = $l1->next; } if ($l2 !== null) { $l2 = $l2->next; } } if ($carry > 0) { $current->next = new ListNode($carry); } return $dummy->next; } } -
# Definition for singly-linked list. # class ListNode # attr_accessor :val, :next # def initialize(val = 0, _next = nil) # @val = val # @next = _next # end # end # @param {ListNode} l1 # @param {ListNode} l2 # @return {ListNode} def add_two_numbers(l1, l2) dummy = ListNode.new() carry = 0 cur = dummy while !l1.nil? || !l2.nil? || carry > 0 s = (l1.nil? ? 0 : l1.val) + (l2.nil? ? 0 : l2.val) + carry carry = s / 10 cur.next = ListNode.new(s % 10) cur = cur.next l1 = l1.nil? ? l1 : l1.next l2 = l2.nil? ? l2 : l2.next end dummy.next end -
/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * public class ListNode { * public int val; * public ListNode next; * public ListNode(int val=0, ListNode next=null) { * this.val = val; * this.next = next; * } * } */ public class Solution { public ListNode AddTwoNumbers(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) { ListNode dummy = new ListNode(); int carry = 0; ListNode cur = dummy; while (l1 != null || l2 != null || carry != 0) { int s = (l1 == null ? 0 : l1.val) + (l2 == null ? 0 : l2.val) + carry; carry = s / 10; cur.next = new ListNode(s % 10); cur = cur.next; l1 = l1 == null ? null : l1.next; l2 = l2 == null ? null : l2.next; } return dummy.next; } } -
import std/[strutils, algorithm] type Node[int] = ref object value: int next: Node[int] SinglyLinkedList[T] = object head, tail: Node[T] proc append[T](list: var SinglyLinkedList[T], data: T = nil): void = var node = Node[T](value: data) if list.head.isNil: list.head = node list.tail = node else: list.tail.next = node list.tail = node proc preview[T](list: SinglyLinkedList[T]): string = var s: seq[T] var n = list.head while not n.isNil: s.add n.value n = n.next result = s.join(" -> ") proc addTwoNumbers(l1: var SinglyLinkedList, l2: var SinglyLinkedList): SinglyLinkedList[int] = var aggregate: SinglyLinkedList psum: seq[char] temp_la, temp_lb: seq[int] while not l1.head.isNil: temp_la.add(l1.head.value) l1.head = l1.head.next while not l2.head.isNil: temp_lb.add(l2.head.value) l2.head = l2.head.next psum = reversed($(reversed(temp_la).join("").parseInt() + reversed(temp_lb).join("").parseInt())) for i in psum: aggregate.append(($i).parseInt()) result = aggregate var list1: SinglyLinkedList[int] var list2: SinglyLinkedList[int] for i in @[2, 4, 3]: list1.append(i) for i in @[5, 6, 4]: list2.append(i) echo(preview(list1)) echo(preview(list2)) echo(preview(addTwoNumbers(list1, list2))) -
// Definition for singly-linked list. // #[derive(PartialEq, Eq, Clone, Debug)] // pub struct ListNode { // pub val: i32, // pub next: Option<Box<ListNode>> // } // // impl ListNode { // #[inline] // fn new(val: i32) -> Self { // ListNode { // next: None, // val // } // } // } impl Solution { pub fn add_two_numbers( mut l1: Option<Box<ListNode>>, mut l2: Option<Box<ListNode>> ) -> Option<Box<ListNode>> { let mut dummy = Some(Box::new(ListNode::new(0))); let mut cur = &mut dummy; let mut sum = 0; while l1.is_some() || l2.is_some() || sum != 0 { if let Some(node) = l1 { sum += node.val; l1 = node.next; } if let Some(node) = l2 { sum += node.val; l2 = node.next; } cur.as_mut().unwrap().next = Some(Box::new(ListNode::new(sum % 10))); cur = &mut cur.as_mut().unwrap().next; sum /= 10; } dummy.unwrap().next.take() } } -
/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * public class ListNode { * public var val: Int * public var next: ListNode? * public init() { self.val = 0; self.next = nil; } * public init(_ val: Int) { self.val = val; self.next = nil; } * public init(_ val: Int, _ next: ListNode?) { self.val = val; self.next = next; } * } */ class Solution { func addTwoNumbers(_ l1: ListNode?, _ l2: ListNode?) -> ListNode? { var dummy = ListNode.init() var carry = 0 var l1 = l1 var l2 = l2 var cur = dummy while l1 != nil || l2 != nil || carry != 0 { let s = (l1?.val ?? 0) + (l2?.val ?? 0) + carry carry = s / 10 cur.next = ListNode.init(s % 10) cur = cur.next! l1 = l1?.next l2 = l2?.next } return dummy.next } }