Welcome to Subscribe On Youtube
3787. Find Diameter Endpoints of a Tree 🔒
Description
You are given an undirected tree with n nodes, numbered from 0 to n - 1. It is represented by a 2D integer array edges of length n - 1, where edges[i] = [ai, bi] indicates that there is an edge between nodes ai and bi in the tree.
A node is called special if it is an endpoint of any diameter path of the tree.
Return a binary string s of length n, where s[i] = '1' if node i is special, and s[i] = '0' otherwise.
A diameter path of a tree is the longest simple path between any two nodes. A tree may have multiple diameter paths.
An endpoint of a path is the first or last node on that path.
Example 1:
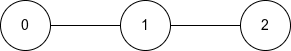
Input: n = 3, edges = [[0,1],[1,2]]
Output: "101"
Explanation:
- The diameter of this tree consists of 2 edges.
- The only diameter path is the path from node 0 to node 2
- The endpoints of this path are nodes 0 and 2, so they are special.
Example 2:
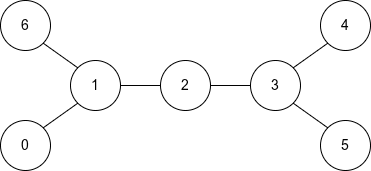
Input: n = 7, edges = [[0,1],[1,2],[2,3],[3,4],[3,5],[1,6]]
Output: "1000111"
Explanation:
The diameter of this tree consists of 4 edges. There are 4 diameter paths:
- The path from node 0 to node 4
- The path from node 0 to node 5
- The path from node 6 to node 4
- The path from node 6 to node 5
The special nodes are nodes 0, 4, 5, 6, as they are endpoints in at least one diameter path.
Example 3:
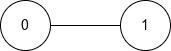
Input: n = 2, edges = [[0,1]]
Output: "11"
Explanation:
- The diameter of this tree consists of 1 edge.
- The only diameter path is the path from node 0 to node 1
- The endpoints of this path are nodes 0 and 1, so they are special.
Constraints:
2 <= n <= 105edges.length == n - 1edges[i] = [ai, bi]0 <= ai, bi < n- The input is generated such that
edgesrepresents a valid tree.
Solutions
Solution 1: BFS
We first convert the array $\text{edges}$ into an adjacency list representation of an undirected graph, where $g[u]$ represents all nodes adjacent to node $u$.
Next, we can use Breadth-First Search (BFS) to find the diameter endpoints of the tree. The specific steps are as follows:
- Starting from any node (e.g., node $0$), use BFS to find the farthest node $a$ from that node.
- Starting from node $a$, use BFS again to find the farthest node $b$ from node $a$, as well as the distance array $\text{dist1}$ from node $a$ to all other nodes.
- Starting from node $b$, use BFS to find the distance array $\text{dist2}$ from node $b$ to all other nodes.
- The diameter length of the tree is $\text{dist1}[b]$. For each node $i$, if $\text{dist1}[i]$ or $\text{dist2}[i]$ equals the diameter length, then node $i$ is a special node.
The time complexity is $O(n)$, and the space complexity is $O(n)$. Where $n$ is the number of nodes.
-
class Solution { public String findSpecialNodes(int n, int[][] edges) { List<Integer>[] g = new ArrayList[n]; Arrays.setAll(g, k -> new ArrayList<>()); for (int[] e : edges) { int a = e[0], b = e[1]; g[a].add(b); g[b].add(a); } record BFSResult(int far, int[] dist) { } IntFunction<BFSResult> bfs = (int start) -> { int[] dist = new int[n]; Arrays.fill(dist, -1); dist[start] = 0; ArrayDeque<Integer> q = new ArrayDeque<>(); q.add(start); int far = start; while (!q.isEmpty()) { int u = q.poll(); if (dist[u] > dist[far]) { far = u; } for (int v : g[u]) { if (dist[v] == -1) { dist[v] = dist[u] + 1; q.add(v); } } } return new BFSResult(far, dist); }; int a = bfs.apply(0).far(); BFSResult r1 = bfs.apply(a); int b = r1.far(); int[] dist1 = r1.dist(); int[] dist2 = bfs.apply(b).dist(); int d = dist1[b]; char[] ans = new char[n]; Arrays.fill(ans, '0'); for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { if (dist1[i] == d || dist2[i] == d) { ans[i] = '1'; } } return new String(ans); } } -
class Solution { public: string findSpecialNodes(int n, vector<vector<int>>& edges) { vector<vector<int>> g(n); for (auto& e : edges) { int a = e[0], b = e[1]; g[a].push_back(b); g[b].push_back(a); } auto bfs = [&](int start) -> pair<int, vector<int>> { vector<int> dist(n, -1); dist[start] = 0; deque<int> q; q.push_back(start); int far = start; while (!q.empty()) { int u = q.front(); q.pop_front(); if (dist[u] > dist[far]) { far = u; } for (int v : g[u]) { if (dist[v] == -1) { dist[v] = dist[u] + 1; q.push_back(v); } } } return {far, dist}; }; auto [a, _0] = bfs(0); auto [b, dist1] = bfs(a); auto [_1, dist2] = bfs(b); int d = dist1[b]; string ans(n, '0'); for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { if (dist1[i] == d || dist2[i] == d) { ans[i] = '1'; } } return ans; } }; -
class Solution: def findSpecialNodes(self, n: int, edges: List[List[int]]) -> str: g = [[] for _ in range(n)] for a, b in edges: g[a].append(b) g[b].append(a) def bfs(start: int): dist = [-1] * n dist[start] = 0 q = deque([start]) far = start while q: u = q.popleft() if dist[u] > dist[far]: far = u for v in g[u]: if dist[v] == -1: dist[v] = dist[u] + 1 q.append(v) return far, dist a, _ = bfs(0) b, dist1 = bfs(a) _, dist2 = bfs(b) d = dist1[b] ans = ["0"] * n for i in range(n): if dist1[i] == d or dist2[i] == d: ans[i] = "1" return "".join(ans) -
func findSpecialNodes(n int, edges [][]int) string { g := make([][]int, n) for _, e := range edges { a, b := e[0], e[1] g[a] = append(g[a], b) g[b] = append(g[b], a) } bfs := func(start int) (int, []int) { dist := make([]int, n) for i := range dist { dist[i] = -1 } dist[start] = 0 q := make([]int, 0, n) q = append(q, start) far := start for head := 0; head < len(q); head++ { u := q[head] if dist[u] > dist[far] { far = u } for _, v := range g[u] { if dist[v] == -1 { dist[v] = dist[u] + 1 q = append(q, v) } } } return far, dist } a, _ := bfs(0) b, dist1 := bfs(a) _, dist2 := bfs(b) d := dist1[b] ans := make([]byte, n) for i := range ans { ans[i] = '0' } for i := 0; i < n; i++ { if dist1[i] == d || dist2[i] == d { ans[i] = '1' } } return string(ans) } -
function findSpecialNodes(n: number, edges: number[][]): string { const g: number[][] = Array.from({ length: n }, () => []); for (const [a, b] of edges) { g[a].push(b); g[b].push(a); } const bfs = (start: number): [number, number[]] => { const dist = new Array<number>(n).fill(-1); dist[start] = 0; const q: number[] = [start]; let far = start; for (const u of q) { if (dist[u] > dist[far]) { far = u; } for (const v of g[u]) { if (dist[v] === -1) { dist[v] = dist[u] + 1; q.push(v); } } } return [far, dist]; }; const [a] = bfs(0); const [b, dist1] = bfs(a); const [, dist2] = bfs(b); const d = dist1[b]; const ans: string[] = new Array(n).fill('0'); for (let i = 0; i < n; i++) { if (dist1[i] === d || dist2[i] === d) { ans[i] = '1'; } } return ans.join(''); } -
use std::collections::VecDeque; impl Solution { pub fn find_special_nodes(n: i32, edges: Vec<Vec<i32>>) -> String { let n = n as usize; let mut g: Vec<Vec<usize>> = vec![vec![]; n]; for e in edges { let a = e[0] as usize; let b = e[1] as usize; g[a].push(b); g[b].push(a); } fn bfs(start: usize, g: &Vec<Vec<usize>>) -> (usize, Vec<i32>) { let n = g.len(); let mut dist = vec![-1i32; n]; let mut q: VecDeque<usize> = VecDeque::new(); dist[start] = 0; q.push_back(start); let mut far = start; while let Some(u) = q.pop_front() { if dist[u] > dist[far] { far = u; } for &v in &g[u] { if dist[v] == -1 { dist[v] = dist[u] + 1; q.push_back(v); } } } (far, dist) } let (a, _) = bfs(0, &g); let (b, dist1) = bfs(a, &g); let (_, dist2) = bfs(b, &g); let d = dist1[b]; let mut ans = vec![b'0'; n]; for i in 0..n { if dist1[i] == d || dist2[i] == d { ans[i] = b'1'; } } String::from_utf8(ans).unwrap() } }