Welcome to Subscribe On Youtube
3650. Minimum Cost Path with Edge Reversals
Description
You are given a directed, weighted graph with n nodes labeled from 0 to n - 1, and an array edges where edges[i] = [ui, vi, wi] represents a directed edge from node ui to node vi with cost wi.
Each node ui has a switch that can be used at most once: when you arrive at ui and have not yet used its switch, you may activate it on one of its incoming edges vi → ui reverse that edge to ui → vi and immediately traverse it.
The reversal is only valid for that single move, and using a reversed edge costs 2 * wi.
Return the minimum total cost to travel from node 0 to node n - 1. If it is not possible, return -1.
Example 1:
Input: n = 4, edges = [[0,1,3],[3,1,1],[2,3,4],[0,2,2]]
Output: 5
Explanation:
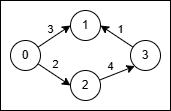
- Use the path
0 → 1(cost 3). - At node 1 reverse the original edge
3 → 1into1 → 3and traverse it at cost2 * 1 = 2. - Total cost is
3 + 2 = 5.
Example 2:
Input: n = 4, edges = [[0,2,1],[2,1,1],[1,3,1],[2,3,3]]
Output: 3
Explanation:
- No reversal is needed. Take the path
0 → 2(cost 1), then2 → 1(cost 1), then1 → 3(cost 1). - Total cost is
1 + 1 + 1 = 3.
Constraints:
2 <= n <= 5 * 1041 <= edges.length <= 105edges[i] = [ui, vi, wi]0 <= ui, vi <= n - 11 <= wi <= 1000
Solutions
Solution 1
-
class Solution { public int minCost(int n, int[][] edges) { List<int[]>[] g = new ArrayList[n]; Arrays.setAll(g, k -> new ArrayList<>()); for (int[] e : edges) { int u = e[0], v = e[1], w = e[2]; g[u].add(new int[] {v, w}); g[v].add(new int[] {u, w * 2}); } final int inf = Integer.MAX_VALUE / 2; int[] dist = new int[n]; Arrays.fill(dist, inf); dist[0] = 0; PriorityQueue<int[]> pq = new PriorityQueue<>(Comparator.comparingInt(a -> a[0])); pq.offer(new int[] {0, 0}); while (!pq.isEmpty()) { int[] cur = pq.poll(); int d = cur[0], u = cur[1]; if (d > dist[u]) { continue; } if (u == n - 1) { return d; } for (int[] nei : g[u]) { int v = nei[0], w = nei[1]; int nd = d + w; if (nd < dist[v]) { dist[v] = nd; pq.offer(new int[] {nd, v}); } } } return -1; } } -
class Solution { public: int minCost(int n, vector<vector<int>>& edges) { using pii = pair<int, int>; vector<vector<pii>> g(n); for (auto& e : edges) { int u = e[0], v = e[1], w = e[2]; g[u].push_back({v, w}); g[v].push_back({u, w * 2}); } const int inf = INT_MAX / 2; vector<int> dist(n, inf); dist[0] = 0; priority_queue<pii, vector<pii>, greater<pii>> pq; pq.push({0, 0}); while (!pq.empty()) { auto [d, u] = pq.top(); pq.pop(); if (d > dist[u]) { continue; } if (u == n - 1) { return d; } for (auto& [v, w] : g[u]) { int nd = d + w; if (nd < dist[v]) { dist[v] = nd; pq.push({nd, v}); } } } return -1; } }; -
class Solution: def minCost(self, n: int, edges: List[List[int]]) -> int: g = [[] for _ in range(n)] for u, v, w in edges: g[u].append((v, w)) g[v].append((u, w * 2)) pq = [(0, 0)] dist = [inf] * n dist[0] = 0 while pq: d, u = heappop(pq) if d > dist[u]: continue if u == n - 1: return d for v, w in g[u]: nd = d + w if nd < dist[v]: dist[v] = nd heappush(pq, (nd, v)) return -1 -
func minCost(n int, edges [][]int) int { g := make([][][2]int, n) for _, e := range edges { u, v, w := e[0], e[1], e[2] g[u] = append(g[u], [2]int{v, w}) g[v] = append(g[v], [2]int{u, w * 2}) } inf := math.MaxInt / 2 dist := make([]int, n) for i := range dist { dist[i] = inf } dist[0] = 0 pq := &hp{} heap.Init(pq) heap.Push(pq, pair{0, 0}) for pq.Len() > 0 { cur := heap.Pop(pq).(pair) d, u := cur.x, cur.i if d > dist[u] { continue } if u == n-1 { return d } for _, ne := range g[u] { v, w := ne[0], ne[1] if nd := d + w; nd < dist[v] { dist[v] = nd heap.Push(pq, pair{nd, v}) } } } return -1 } type pair struct{ x, i int } type hp []pair func (h hp) Len() int { return len(h) } func (h hp) Less(i, j int) bool { return h[i].x < h[j].x } func (h hp) Swap(i, j int) { h[i], h[j] = h[j], h[i] } func (h *hp) Push(x any) { *h = append(*h, x.(pair)) } func (h *hp) Pop() (x any) { a := *h x = a[len(a)-1] *h = a[:len(a)-1] return } -
function minCost(n: number, edges: number[][]): number { const g: number[][][] = Array.from({ length: n }, () => []); for (const [u, v, w] of edges) { g[u].push([v, w]); g[v].push([u, w * 2]); } const dist: number[] = Array(n).fill(Infinity); dist[0] = 0; const pq = new PriorityQueue<number[]>((a, b) => a[0] - b[0]); pq.enqueue([0, 0]); while (!pq.isEmpty()) { const [d, u] = pq.dequeue(); if (d > dist[u]) { continue; } if (u === n - 1) { return d; } for (const [v, w] of g[u]) { const nd = d + w; if (nd < dist[v]) { dist[v] = nd; pq.enqueue([nd, v]); } } } return -1; }