Welcome to Subscribe On Youtube
3446. Sort Matrix by Diagonals
Description
You are given an n x n square matrix of integers grid. Return the matrix such that:
- The diagonals in the bottom-left triangle (including the middle diagonal) are sorted in non-increasing order.
- The diagonals in the top-right triangle are sorted in non-decreasing order.
Example 1:
Input: grid = [[1,7,3],[9,8,2],[4,5,6]]
Output: [[8,2,3],[9,6,7],[4,5,1]]
Explanation:
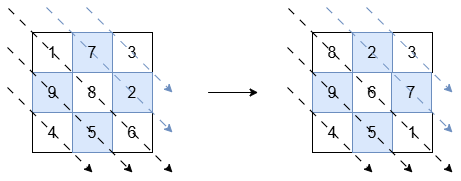
The diagonals with a black arrow (bottom-left triangle) should be sorted in non-increasing order:
[1, 8, 6]becomes[8, 6, 1].[9, 5]and[4]remain unchanged.
The diagonals with a blue arrow (top-right triangle) should be sorted in non-decreasing order:
[7, 2]becomes[2, 7].[3]remains unchanged.
Example 2:
Input: grid = [[0,1],[1,2]]
Output: [[2,1],[1,0]]
Explanation:

The diagonals with a black arrow must be non-increasing, so [0, 2] is changed to [2, 0]. The other diagonals are already in the correct order.
Example 3:
Input: grid = [[1]]
Output: [[1]]
Explanation:
Diagonals with exactly one element are already in order, so no changes are needed.
Constraints:
grid.length == grid[i].length == n1 <= n <= 10-105 <= grid[i][j] <= 105
Solutions
Solution 1: Simulation + Sorting
We can simulate the diagonal sorting process as described in the problem.
First, we sort the diagonals of the lower-left triangle, including the main diagonal, in non-increasing order. Then, we sort the diagonals of the upper-right triangle in non-decreasing order. Finally, we return the sorted matrix.
The time complexity is $O(n^2 \log n)$, and the space complexity is $O(n)$. Here, $n$ is the size of the matrix.
-
class Solution { public int[][] sortMatrix(int[][] grid) { int n = grid.length; for (int k = n - 2; k >= 0; --k) { int i = k, j = 0; List<Integer> t = new ArrayList<>(); while (i < n && j < n) { t.add(grid[i++][j++]); } Collections.sort(t); for (int x : t) { grid[--i][--j] = x; } } for (int k = n - 2; k > 0; --k) { int i = k, j = n - 1; List<Integer> t = new ArrayList<>(); while (i >= 0 && j >= 0) { t.add(grid[i--][j--]); } Collections.sort(t); for (int x : t) { grid[++i][++j] = x; } } return grid; } } -
class Solution { public: vector<vector<int>> sortMatrix(vector<vector<int>>& grid) { int n = grid.size(); for (int k = n - 2; k >= 0; --k) { int i = k, j = 0; vector<int> t; while (i < n && j < n) { t.push_back(grid[i++][j++]); } ranges::sort(t); for (int x : t) { grid[--i][--j] = x; } } for (int k = n - 2; k > 0; --k) { int i = k, j = n - 1; vector<int> t; while (i >= 0 && j >= 0) { t.push_back(grid[i--][j--]); } ranges::sort(t); for (int x : t) { grid[++i][++j] = x; } } return grid; } }; -
class Solution: def sortMatrix(self, grid: List[List[int]]) -> List[List[int]]: n = len(grid) for k in range(n - 2, -1, -1): i, j = k, 0 t = [] while i < n and j < n: t.append(grid[i][j]) i += 1 j += 1 t.sort() i, j = k, 0 while i < n and j < n: grid[i][j] = t.pop() i += 1 j += 1 for k in range(n - 2, 0, -1): i, j = k, n - 1 t = [] while i >= 0 and j >= 0: t.append(grid[i][j]) i -= 1 j -= 1 t.sort() i, j = k, n - 1 while i >= 0 and j >= 0: grid[i][j] = t.pop() i -= 1 j -= 1 return grid -
func sortMatrix(grid [][]int) [][]int { n := len(grid) for k := n - 2; k >= 0; k-- { i, j := k, 0 t := []int{} for ; i < n && j < n; i, j = i+1, j+1 { t = append(t, grid[i][j]) } sort.Ints(t) for _, x := range t { i, j = i-1, j-1 grid[i][j] = x } } for k := n - 2; k > 0; k-- { i, j := k, n-1 t := []int{} for ; i >= 0 && j >= 0; i, j = i-1, j-1 { t = append(t, grid[i][j]) } sort.Ints(t) for _, x := range t { i, j = i+1, j+1 grid[i][j] = x } } return grid } -
function sortMatrix(grid: number[][]): number[][] { const n = grid.length; for (let k = n - 2; k >= 0; --k) { let [i, j] = [k, 0]; const t: number[] = []; while (i < n && j < n) { t.push(grid[i++][j++]); } t.sort((a, b) => a - b); for (const x of t) { grid[--i][--j] = x; } } for (let k = n - 2; k > 0; --k) { let [i, j] = [k, n - 1]; const t: number[] = []; while (i >= 0 && j >= 0) { t.push(grid[i--][j--]); } t.sort((a, b) => a - b); for (const x of t) { grid[++i][++j] = x; } } return grid; } -
/** * @param {number[][]} grid * @return {number[][]} */ var sortMatrix = function (grid) { const n = grid.length; for (let k = n - 2; k >= 0; --k) { let i = k, j = 0; const t = []; while (i < n && j < n) { t.push(grid[i++][j++]); } t.sort((a, b) => a - b); for (const x of t) { grid[--i][--j] = x; } } for (let k = n - 2; k > 0; --k) { let i = k, j = n - 1; const t = []; while (i >= 0 && j >= 0) { t.push(grid[i--][j--]); } t.sort((a, b) => a - b); for (const x of t) { grid[++i][++j] = x; } } return grid; }; -
public class Solution { public int[][] SortMatrix(int[][] grid) { int n = grid.Length; for (int k = n - 2; k >= 0; --k) { int i = k, j = 0; List<int> t = new List<int>(); while (i < n && j < n) { t.Add(grid[i++][j++]); } t.Sort(); foreach (int x in t) { grid[--i][--j] = x; } } for (int k = n - 2; k > 0; --k) { int i = k, j = n - 1; List<int> t = new List<int>(); while (i >= 0 && j >= 0) { t.Add(grid[i--][j--]); } t.Sort(); foreach (int x in t) { grid[++i][++j] = x; } } return grid; } } -
impl Solution { pub fn sort_matrix(mut grid: Vec<Vec<i32>>) -> Vec<Vec<i32>> { let n = grid.len(); if n <= 1 { return grid; } for k in (0..=n - 2).rev() { let mut i = k; let mut j = 0; let mut t = Vec::new(); while i < n && j < n { t.push(grid[i][j]); i += 1; j += 1; } t.sort(); let mut i = k; let mut j = 0; while i < n && j < n { grid[i][j] = t.pop().unwrap(); i += 1; j += 1; } } for k in (1..=n - 2).rev() { let mut i = k; let mut j = n - 1; let mut t = Vec::new(); loop { t.push(grid[i][j]); if i == 0 { break; } i -= 1; j -= 1; } t.sort(); let mut i = k; let mut j = n - 1; loop { grid[i][j] = t.pop().unwrap(); if i == 0 { break; } i -= 1; j -= 1; } } grid } }