Welcome to Subscribe On Youtube
3327. Check if DFS Strings Are Palindromes
Description
You are given a tree rooted at node 0, consisting of n nodes numbered from 0 to n - 1. The tree is represented by an array parent of size n, where parent[i] is the parent of node i. Since node 0 is the root, parent[0] == -1.
You are also given a string s of length n, where s[i] is the character assigned to node i.
Consider an empty string dfsStr, and define a recursive function dfs(int x) that takes a node x as a parameter and performs the following steps in order:
- Iterate over each child
yofxin increasing order of their numbers, and calldfs(y). - Add the character
s[x]to the end of the stringdfsStr.
Note that dfsStr is shared across all recursive calls of dfs.
You need to find a boolean array answer of size n, where for each index i from 0 to n - 1, you do the following:
- Empty the string
dfsStrand calldfs(i). - If the resulting string
dfsStris a palindrome, then setanswer[i]totrue. Otherwise, setanswer[i]tofalse.
Return the array answer.
Example 1:
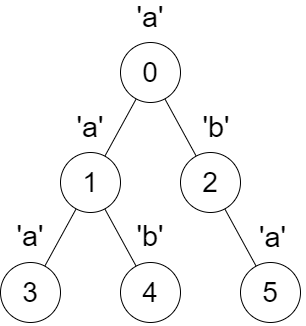
Input: parent = [-1,0,0,1,1,2], s = "aababa"
Output: [true,true,false,true,true,true]
Explanation:
- Calling
dfs(0)results in the stringdfsStr = "abaaba", which is a palindrome. - Calling
dfs(1)results in the stringdfsStr = "aba", which is a palindrome. - Calling
dfs(2)results in the stringdfsStr = "ab", which is not a palindrome. - Calling
dfs(3)results in the stringdfsStr = "a", which is a palindrome. - Calling
dfs(4)results in the stringdfsStr = "b", which is a palindrome. - Calling
dfs(5)results in the stringdfsStr = "a", which is a palindrome.
Example 2:
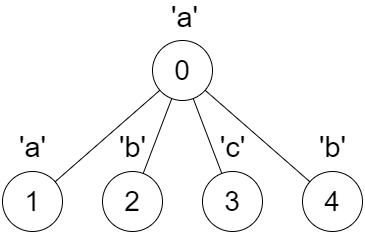
Input: parent = [-1,0,0,0,0], s = "aabcb"
Output: [true,true,true,true,true]
Explanation:
Every call on dfs(x) results in a palindrome string.
Constraints:
n == parent.length == s.length1 <= n <= 1050 <= parent[i] <= n - 1for alli >= 1.parent[0] == -1parentrepresents a valid tree.sconsists only of lowercase English letters.
Solutions
Solution 1: DFS + String Hashing
We can use Depth-First Search (DFS) to traverse the tree and compute the entire $\textit{dfsStr}$, while also determining the interval $[l, r]$ for each node.
Then, we use string hashing to compute the hash values of both $\textit{dfsStr}$ and the reverse of $\textit{dfsStr}$ to check if it is a palindrome.
The time complexity is $O(n)$, and the space complexity is $O(n)$. Here, $n$ is the length of the string $s$.
-
class Hashing { private final long[] p; private final long[] h; private final long mod; public Hashing(String word, long base, int mod) { int n = word.length(); p = new long[n + 1]; h = new long[n + 1]; p[0] = 1; this.mod = mod; for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) { p[i] = p[i - 1] * base % mod; h[i] = (h[i - 1] * base + word.charAt(i - 1)) % mod; } } public long query(int l, int r) { return (h[r] - h[l - 1] * p[r - l + 1] % mod + mod) % mod; } } class Solution { private char[] s; private int[][] pos; private List<Integer>[] g; private StringBuilder dfsStr = new StringBuilder(); public boolean[] findAnswer(int[] parent, String s) { this.s = s.toCharArray(); int n = s.length(); g = new List[n]; pos = new int[n][0]; Arrays.setAll(g, k -> new ArrayList<>()); for (int i = 1; i < n; ++i) { g[parent[i]].add(i); } dfs(0); final int base = 13331; final int mod = 998244353; Hashing h1 = new Hashing(dfsStr.toString(), base, mod); Hashing h2 = new Hashing(new StringBuilder(dfsStr).reverse().toString(), base, mod); boolean[] ans = new boolean[n]; for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) { int l = pos[i][0], r = pos[i][1]; int k = r - l + 1; long v1 = h1.query(l, l + k / 2 - 1); long v2 = h2.query(n + 1 - r, n + 1 - r + k / 2 - 1); ans[i] = v1 == v2; } return ans; } private void dfs(int i) { int l = dfsStr.length() + 1; for (int j : g[i]) { dfs(j); } dfsStr.append(s[i]); int r = dfsStr.length(); pos[i] = new int[] {l, r}; } } -
class Hashing { private: vector<long long> p; vector<long long> h; long long mod; public: Hashing(string word, long long base, int mod) { int n = word.size(); p.resize(n + 1); h.resize(n + 1); p[0] = 1; this->mod = mod; for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) { p[i] = (p[i - 1] * base) % mod; h[i] = (h[i - 1] * base + word[i - 1] - 'a') % mod; } } long long query(int l, int r) { return (h[r] - h[l - 1] * p[r - l + 1] % mod + mod) % mod; } }; class Solution { public: vector<bool> findAnswer(vector<int>& parent, string s) { int n = s.size(); vector<int> g[n]; for (int i = 1; i < n; ++i) { g[parent[i]].push_back(i); } string dfsStr; vector<pair<int, int>> pos(n); auto dfs = [&](auto&& dfs, int i) -> void { int l = dfsStr.size() + 1; for (int j : g[i]) { dfs(dfs, j); } dfsStr.push_back(s[i]); int r = dfsStr.size(); pos[i] = {l, r}; }; dfs(dfs, 0); const int base = 13331; const int mod = 998244353; Hashing h1(dfsStr, base, mod); reverse(dfsStr.begin(), dfsStr.end()); Hashing h2(dfsStr, base, mod); vector<bool> ans(n); for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) { auto [l, r] = pos[i]; int k = r - l + 1; long long v1 = h1.query(l, l + k / 2 - 1); long long v2 = h2.query(n - r + 1, n - r + 1 + k / 2 - 1); ans[i] = v1 == v2; } return ans; } }; -
class Hashing: __slots__ = ["mod", "h", "p"] def __init__(self, s: List[str], base: int, mod: int): self.mod = mod self.h = [0] * (len(s) + 1) self.p = [1] * (len(s) + 1) for i in range(1, len(s) + 1): self.h[i] = (self.h[i - 1] * base + ord(s[i - 1])) % mod self.p[i] = (self.p[i - 1] * base) % mod def query(self, l: int, r: int) -> int: return (self.h[r] - self.h[l - 1] * self.p[r - l + 1]) % self.mod class Solution: def findAnswer(self, parent: List[int], s: str) -> List[bool]: def dfs(i: int): l = len(dfsStr) + 1 for j in g[i]: dfs(j) dfsStr.append(s[i]) r = len(dfsStr) pos[i] = (l, r) n = len(s) g = [[] for _ in range(n)] for i in range(1, n): g[parent[i]].append(i) dfsStr = [] pos = {} dfs(0) base, mod = 13331, 998244353 h1 = Hashing(dfsStr, base, mod) h2 = Hashing(dfsStr[::-1], base, mod) ans = [] for i in range(n): l, r = pos[i] k = r - l + 1 v1 = h1.query(l, l + k // 2 - 1) v2 = h2.query(n - r + 1, n - r + 1 + k // 2 - 1) ans.append(v1 == v2) return ans -
type Hashing struct { p []int64 h []int64 mod int64 } func NewHashing(word string, base, mod int64) *Hashing { n := len(word) p := make([]int64, n+1) h := make([]int64, n+1) p[0] = 1 for i := 1; i <= n; i++ { p[i] = p[i-1] * base % mod h[i] = (h[i-1]*base + int64(word[i-1])) % mod } return &Hashing{p, h, mod} } func (hs *Hashing) query(l, r int) int64 { return (hs.h[r] - hs.h[l-1]*hs.p[r-l+1]%hs.mod + hs.mod) % hs.mod } func findAnswer(parent []int, s string) (ans []bool) { n := len(s) g := make([][]int, n) for i := 1; i < n; i++ { g[parent[i]] = append(g[parent[i]], i) } dfsStr := []byte{} pos := make([][2]int, n) var dfs func(int) dfs = func(i int) { l := len(dfsStr) + 1 for _, j := range g[i] { dfs(j) } dfsStr = append(dfsStr, s[i]) r := len(dfsStr) pos[i] = [2]int{l, r} } const base = 13331 const mod = 998244353 dfs(0) h1 := NewHashing(string(dfsStr), base, mod) for i, j := 0, len(dfsStr)-1; i < j; i, j = i+1, j-1 { dfsStr[i], dfsStr[j] = dfsStr[j], dfsStr[i] } h2 := NewHashing(string(dfsStr), base, mod) for i := 0; i < n; i++ { l, r := pos[i][0], pos[i][1] k := r - l + 1 v1 := h1.query(l, l+k/2-1) v2 := h2.query(n-r+1, n-r+1+k/2-1) ans = append(ans, v1 == v2) } return }