Welcome to Subscribe On Youtube
3217. Delete Nodes From Linked List Present in Array
Description
You are given an array of integers nums and the head of a linked list. Return the head of the modified linked list after removing all nodes from the linked list that have a value that exists in nums.
Example 1:
Input: nums = [1,2,3], head = [1,2,3,4,5]
Output: [4,5]
Explanation:
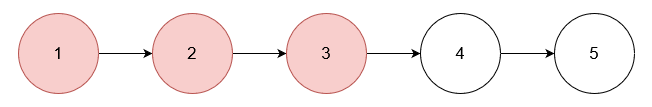
Remove the nodes with values 1, 2, and 3.
Example 2:
Input: nums = [1], head = [1,2,1,2,1,2]
Output: [2,2,2]
Explanation:
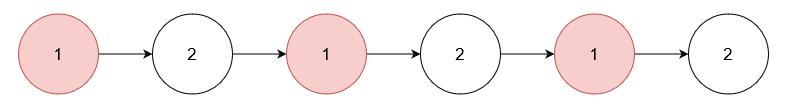
Remove the nodes with value 1.
Example 3:
Input: nums = [5], head = [1,2,3,4]
Output: [1,2,3,4]
Explanation:
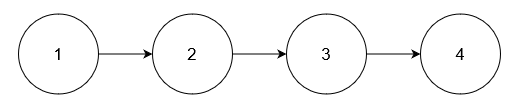
No node has value 5.
Constraints:
1 <= nums.length <= 1051 <= nums[i] <= 105- All elements in
numsare unique. - The number of nodes in the given list is in the range
[1, 105]. 1 <= Node.val <= 105- The input is generated such that there is at least one node in the linked list that has a value not present in
nums.
Solutions
Solution 1: Hash Table
We can use a hash table $\textit{s}$ to store all the elements in the array $\textit{nums}$. Then, we define a dummy node $\textit{dummy}$ and point it to the head node of the list $\textit{head}$.
Next, we traverse the list starting from the dummy node $\textit{dummy}$. If the value of the next node of the current node is in the hash table $\textit{s}$, we make the current node point to the next next node; otherwise, we move the current node pointer to the next node.
Finally, we return the next node of the dummy node $\textit{dummy}$.
The time complexity is $O(n + m)$, and the space complexity is $O(n)$. Here, $n$ is the length of the array $\textit{nums}$, and $m$ is the length of the list $\textit{head}$.
-
/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * public class ListNode { * int val; * ListNode next; * ListNode() {} * ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; } * ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; } * } */ class Solution { public ListNode modifiedList(int[] nums, ListNode head) { Set<Integer> s = new HashSet<>(); for (int x : nums) { s.add(x); } ListNode dummy = new ListNode(0, head); for (ListNode pre = dummy; pre.next != null;) { if (s.contains(pre.next.val)) { pre.next = pre.next.next; } else { pre = pre.next; } } return dummy.next; } } -
/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * struct ListNode { * int val; * ListNode *next; * ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {} * ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {} * ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {} * }; */ class Solution { public: ListNode* modifiedList(vector<int>& nums, ListNode* head) { unordered_set<int> s(nums.begin(), nums.end()); ListNode* dummy = new ListNode(0, head); for (ListNode* pre = dummy; pre->next;) { if (s.count(pre->next->val)) { pre->next = pre->next->next; } else { pre = pre->next; } } return dummy->next; } }; -
# Definition for singly-linked list. # class ListNode: # def __init__(self, val=0, next=None): # self.val = val # self.next = next class Solution: def modifiedList( self, nums: List[int], head: Optional[ListNode] ) -> Optional[ListNode]: s = set(nums) pre = dummy = ListNode(next=head) while pre.next: if pre.next.val in s: pre.next = pre.next.next else: pre = pre.next return dummy.next -
/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * type ListNode struct { * Val int * Next *ListNode * } */ func modifiedList(nums []int, head *ListNode) *ListNode { s := map[int]bool{} for _, x := range nums { s[x] = true } dummy := &ListNode{Next: head} for pre := dummy; pre.Next != nil; { if s[pre.Next.Val] { pre.Next = pre.Next.Next } else { pre = pre.Next } } return dummy.Next } -
/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * class ListNode { * val: number * next: ListNode | null * constructor(val?: number, next?: ListNode | null) { * this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val) * this.next = (next===undefined ? null : next) * } * } */ function modifiedList(nums: number[], head: ListNode | null): ListNode | null { const s: Set<number> = new Set(nums); const dummy = new ListNode(0, head); for (let pre = dummy; pre.next; ) { if (s.has(pre.next.val)) { pre.next = pre.next.next; } else { pre = pre.next; } } return dummy.next; } -
// Definition for singly-linked list. // #[derive(PartialEq, Eq, Clone, Debug)] // pub struct ListNode { // pub val: i32, // pub next: Option<Box<ListNode>> // } // // impl ListNode { // #[inline] // fn new(val: i32) -> Self { // ListNode { // next: None, // val // } // } // } use std::collections::HashSet; impl Solution { pub fn modified_list(nums: Vec<i32>, head: Option<Box<ListNode>>) -> Option<Box<ListNode>> { let s: HashSet<i32> = nums.into_iter().collect(); let mut dummy = Box::new(ListNode { val: 0, next: head }); let mut pre = &mut dummy; while let Some(ref mut node) = pre.next { if s.contains(&node.val) { pre.next = node.next.take(); } else { pre = pre.next.as_mut().unwrap(); } } dummy.next } }