Welcome to Subscribe On Youtube
3068. Find the Maximum Sum of Node Values
Description
There exists an undirected tree with n nodes numbered 0 to n - 1. You are given a 0-indexed 2D integer array edges of length n - 1, where edges[i] = [ui, vi] indicates that there is an edge between nodes ui and vi in the tree. You are also given a positive integer k, and a 0-indexed array of non-negative integers nums of length n, where nums[i] represents the value of the node numbered i.
Alice wants the sum of values of tree nodes to be maximum, for which Alice can perform the following operation any number of times (including zero) on the tree:
- Choose any edge
[u, v]connecting the nodesuandv, and update their values as follows:nums[u] = nums[u] XOR knums[v] = nums[v] XOR k
Return the maximum possible sum of the values Alice can achieve by performing the operation any number of times.
Example 1:
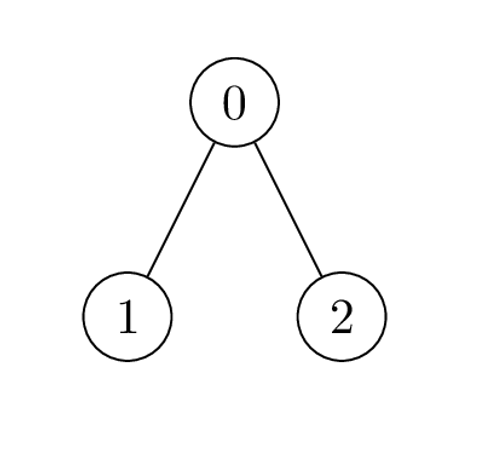
Input: nums = [1,2,1], k = 3, edges = [[0,1],[0,2]] Output: 6 Explanation: Alice can achieve the maximum sum of 6 using a single operation: - Choose the edge [0,2]. nums[0] and nums[2] become: 1 XOR 3 = 2, and the array nums becomes: [1,2,1] -> [2,2,2]. The total sum of values is 2 + 2 + 2 = 6. It can be shown that 6 is the maximum achievable sum of values.
Example 2:
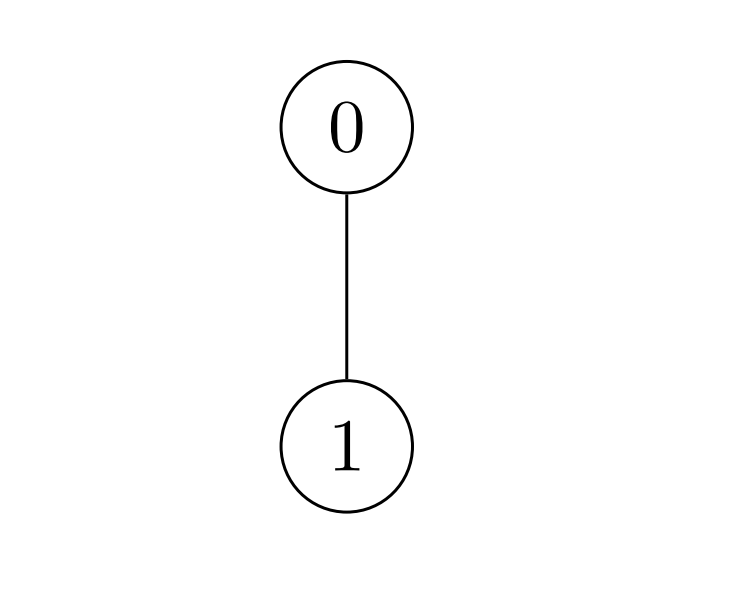
Input: nums = [2,3], k = 7, edges = [[0,1]] Output: 9 Explanation: Alice can achieve the maximum sum of 9 using a single operation: - Choose the edge [0,1]. nums[0] becomes: 2 XOR 7 = 5 and nums[1] become: 3 XOR 7 = 4, and the array nums becomes: [2,3] -> [5,4]. The total sum of values is 5 + 4 = 9. It can be shown that 9 is the maximum achievable sum of values.
Example 3:

Input: nums = [7,7,7,7,7,7], k = 3, edges = [[0,1],[0,2],[0,3],[0,4],[0,5]] Output: 42 Explanation: The maximum achievable sum is 42 which can be achieved by Alice performing no operations.
Constraints:
2 <= n == nums.length <= 2 * 1041 <= k <= 1090 <= nums[i] <= 109edges.length == n - 1edges[i].length == 20 <= edges[i][0], edges[i][1] <= n - 1- The input is generated such that
edgesrepresent a valid tree.
Solutions
Solution 1
-
class Solution { public: long long maximumValueSum(vector<int>& nums, int k, vector<vector<int>>& edges) { long long totalSum = 0; int count = 0; int positiveMin = INT_MAX; int negativeMax = INT_MIN; for (int nodeValue : nums) { int nodeValAfterOperation = nodeValue ^ k; totalSum += nodeValue; int netChange = nodeValAfterOperation - nodeValue; if (netChange > 0) { positiveMin = min(positiveMin, netChange); totalSum += netChange; count += 1; } else { negativeMax = max(negativeMax, netChange); } } if (count % 2 == 0) { return totalSum; } return max(totalSum - positiveMin, totalSum + negativeMax); } }; -
class Solution { public long maximumValueSum(int[] nums, int k, int[][] edges) { long f0 = 0, f1 = -0x3f3f3f3f; for (int x : nums) { long tmp = f0; f0 = Math.max(f0 + x, f1 + (x ^ k)); f1 = Math.max(f1 + x, tmp + (x ^ k)); } return f0; } } -
class Solution: def maximumValueSum(self, nums: List[int], k: int, edges: List[List[int]]) -> int: f0, f1 = 0, -inf for x in nums: f0, f1 = max(f0 + x, f1 + (x ^ k)), max(f1 + x, f0 + (x ^ k)) return f0 -
func maximumValueSum(nums []int, k int, edges [][]int) int64 { f0, f1 := 0, -0x3f3f3f3f for _, x := range nums { f0, f1 = max(f0+x, f1+(x^k)), max(f1+x, f0+(x^k)) } return int64(f0) } -
function maximumValueSum(nums: number[], k: number, edges: number[][]): number { let [f0, f1] = [0, -Infinity]; for (const x of nums) { [f0, f1] = [Math.max(f0 + x, f1 + (x ^ k)), Math.max(f1 + x, f0 + (x ^ k))]; } return f0; } -
public class Solution { public long MaximumValueSum(int[] nums, int k, int[][] edges) { long f0 = 0, f1 = -0x3f3f3f3f; foreach (int x in nums) { long tmp = f0; f0 = Math.Max(f0 + x, f1 + (x ^ k)); f1 = Math.Max(f1 + x, tmp + (x ^ k)); } return f0; } } -
impl Solution { pub fn maximum_value_sum(nums: Vec<i32>, k: i32, edges: Vec<Vec<i32>>) -> i64 { let mut f0: i64 = 0; let mut f1: i64 = i64::MIN; for &x in &nums { let tmp = f0; f0 = std::cmp::max(f0 + x as i64, f1 + (x ^ k) as i64); f1 = std::cmp::max(f1 + x as i64, tmp + (x ^ k) as i64); } f0 } }