Welcome to Subscribe On Youtube
3044. Most Frequent Prime
Description
You are given a m x n 0-indexed 2D matrix mat. From every cell, you can create numbers in the following way:
- There could be at most
8paths from the cells namely: east, south-east, south, south-west, west, north-west, north, and north-east. - Select a path from them and append digits in this path to the number being formed by traveling in this direction.
- Note that numbers are generated at every step, for example, if the digits along the path are
1, 9, 1, then there will be three numbers generated along the way:1, 19, 191.
Return the most frequent prime number greater than 10 out of all the numbers created by traversing the matrix or -1 if no such prime number exists. If there are multiple prime numbers with the highest frequency, then return the largest among them.
Note: It is invalid to change the direction during the move.
Example 1:
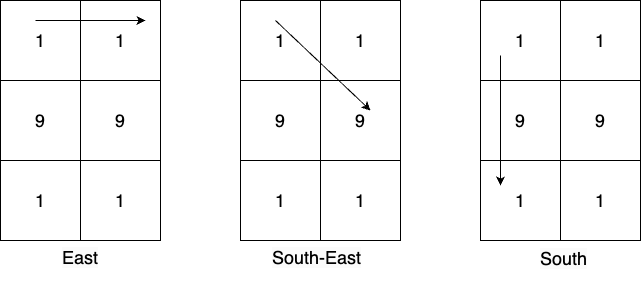
Input: mat = [[1,1],[9,9],[1,1]] Output: 19 Explanation: From cell (0,0) there are 3 possible directions and the numbers greater than 10 which can be created in those directions are: East: [11], South-East: [19], South: [19,191]. Numbers greater than 10 created from the cell (0,1) in all possible directions are: [19,191,19,11]. Numbers greater than 10 created from the cell (1,0) in all possible directions are: [99,91,91,91,91]. Numbers greater than 10 created from the cell (1,1) in all possible directions are: [91,91,99,91,91]. Numbers greater than 10 created from the cell (2,0) in all possible directions are: [11,19,191,19]. Numbers greater than 10 created from the cell (2,1) in all possible directions are: [11,19,19,191]. The most frequent prime number among all the created numbers is 19.
Example 2:
Input: mat = [[7]] Output: -1 Explanation: The only number which can be formed is 7. It is a prime number however it is not greater than 10, so return -1.
Example 3:
Input: mat = [[9,7,8],[4,6,5],[2,8,6]] Output: 97 Explanation: Numbers greater than 10 created from the cell (0,0) in all possible directions are: [97,978,96,966,94,942]. Numbers greater than 10 created from the cell (0,1) in all possible directions are: [78,75,76,768,74,79]. Numbers greater than 10 created from the cell (0,2) in all possible directions are: [85,856,86,862,87,879]. Numbers greater than 10 created from the cell (1,0) in all possible directions are: [46,465,48,42,49,47]. Numbers greater than 10 created from the cell (1,1) in all possible directions are: [65,66,68,62,64,69,67,68]. Numbers greater than 10 created from the cell (1,2) in all possible directions are: [56,58,56,564,57,58]. Numbers greater than 10 created from the cell (2,0) in all possible directions are: [28,286,24,249,26,268]. Numbers greater than 10 created from the cell (2,1) in all possible directions are: [86,82,84,86,867,85]. Numbers greater than 10 created from the cell (2,2) in all possible directions are: [68,682,66,669,65,658]. The most frequent prime number among all the created numbers is 97.
Constraints:
m == mat.lengthn == mat[i].length1 <= m, n <= 61 <= mat[i][j] <= 9
Solutions
Solution 1: Hash Table + Enumeration
We can use a hash table to count the frequency of each prime number greater than 10.
For each cell, we can start from it, generate a number along one of the 8 directions, and then determine whether the generated number is a prime number greater than 10. If it is, we add it to the hash table.
Finally, we traverse the hash table to find the prime number with the highest frequency. If there are multiple prime numbers with the highest frequency, we return the largest one.
The time complexity is $O(m \times n \times \max(m, n) \times {10}^{\frac{\max(m, n)}{2}})$, and the space complexity is $O(m \times n \times \max(m, n))$. Here, $m$ and $n$ are the number of rows and columns of mat, respectively.
-
class Solution { public int mostFrequentPrime(int[][] mat) { int m = mat.length, n = mat[0].length; Map<Integer, Integer> cnt = new HashMap<>(); for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i) { for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) { for (int a = -1; a <= 1; ++a) { for (int b = -1; b <= 1; ++b) { if (a == 0 && b == 0) { continue; } int x = i + a, y = j + b, v = mat[i][j]; while (x >= 0 && x < m && y >= 0 && y < n) { v = v * 10 + mat[x][y]; if (isPrime(v)) { cnt.merge(v, 1, Integer::sum); } x += a; y += b; } } } } } int ans = -1, mx = 0; for (var e : cnt.entrySet()) { int v = e.getKey(), x = e.getValue(); if (mx < x || (mx == x && ans < v)) { mx = x; ans = v; } } return ans; } private boolean isPrime(int n) { for (int i = 2; i <= n / i; ++i) { if (n % i == 0) { return false; } } return true; } } -
class Solution { public: int mostFrequentPrime(vector<vector<int>>& mat) { int m = mat.size(), n = mat[0].size(); unordered_map<int, int> cnt; for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i) { for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) { for (int a = -1; a <= 1; ++a) { for (int b = -1; b <= 1; ++b) { if (a == 0 && b == 0) { continue; } int x = i + a, y = j + b, v = mat[i][j]; while (x >= 0 && x < m && y >= 0 && y < n) { v = v * 10 + mat[x][y]; if (isPrime(v)) { cnt[v]++; } x += a; y += b; } } } } } int ans = -1, mx = 0; for (auto& [v, x] : cnt) { if (mx < x || (mx == x && ans < v)) { mx = x; ans = v; } } return ans; } private: bool isPrime(int n) { for (int i = 2; i <= n / i; ++i) { if (n % i == 0) { return false; } } return true; } }; -
class Solution: def mostFrequentPrime(self, mat: List[List[int]]) -> int: def is_prime(x: int) -> int: return all(x % i != 0 for i in range(2, isqrt(x) + 1)) m, n = len(mat), len(mat[0]) cnt = Counter() for i in range(m): for j in range(n): for a in range(-1, 2): for b in range(-1, 2): if a == 0 and b == 0: continue x, y, v = i + a, j + b, mat[i][j] while 0 <= x < m and 0 <= y < n: v = v * 10 + mat[x][y] if is_prime(v): cnt[v] += 1 x, y = x + a, y + b ans, mx = -1, 0 for v, x in cnt.items(): if mx < x: mx = x ans = v elif mx == x: ans = max(ans, v) return ans -
func mostFrequentPrime(mat [][]int) int { m, n := len(mat), len(mat[0]) cnt := make(map[int]int) for i := 0; i < m; i++ { for j := 0; j < n; j++ { for a := -1; a <= 1; a++ { for b := -1; b <= 1; b++ { if a == 0 && b == 0 { continue } x, y, v := i+a, j+b, mat[i][j] for x >= 0 && x < m && y >= 0 && y < n { v = v*10 + mat[x][y] if isPrime(v) { cnt[v]++ } x += a y += b } } } } } ans, mx := -1, 0 for v, x := range cnt { if mx < x || (mx == x && ans < v) { mx = x ans = v } } return ans } func isPrime(n int) bool { for i := 2; i <= n/i; i++ { if n%i == 0 { return false } } return true } -
function mostFrequentPrime(mat: number[][]): number { const m: number = mat.length; const n: number = mat[0].length; const cnt: Map<number, number> = new Map(); const isPrime = (x: number): boolean => { for (let i = 2; i <= x / i; ++i) { if (x % i === 0) { return false; } } return true; }; for (let i = 0; i < m; ++i) { for (let j = 0; j < n; ++j) { for (let a = -1; a <= 1; ++a) { for (let b = -1; b <= 1; ++b) { if (a === 0 && b === 0) { continue; } let [x, y, v] = [i + a, j + b, mat[i][j]]; while (x >= 0 && x < m && y >= 0 && y < n) { v = v * 10 + mat[x][y]; if (isPrime(v)) { cnt.set(v, (cnt.get(v) || 0) + 1); } x += a; y += b; } } } } } let [ans, mx] = [-1, 0]; cnt.forEach((x, v) => { if (mx < x || (mx === x && ans < v)) { mx = x; ans = v; } }); return ans; }