Welcome to Subscribe On Youtube
2867. Count Valid Paths in a Tree
Description
There is an undirected tree with n nodes labeled from 1 to n. You are given the integer n and a 2D integer array edges of length n - 1, where edges[i] = [ui, vi] indicates that there is an edge between nodes ui and vi in the tree.
Return the number of valid paths in the tree.
A path (a, b) is valid if there exists exactly one prime number among the node labels in the path from a to b.
Note that:
- The path
(a, b)is a sequence of distinct nodes starting with nodeaand ending with nodebsuch that every two adjacent nodes in the sequence share an edge in the tree. - Path
(a, b)and path(b, a)are considered the same and counted only once.
Example 1:
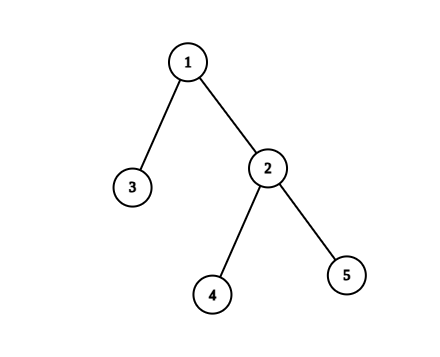
Input: n = 5, edges = [[1,2],[1,3],[2,4],[2,5]] Output: 4 Explanation: The pairs with exactly one prime number on the path between them are: - (1, 2) since the path from 1 to 2 contains prime number 2. - (1, 3) since the path from 1 to 3 contains prime number 3. - (1, 4) since the path from 1 to 4 contains prime number 2. - (2, 4) since the path from 2 to 4 contains prime number 2. It can be shown that there are only 4 valid paths.
Example 2:
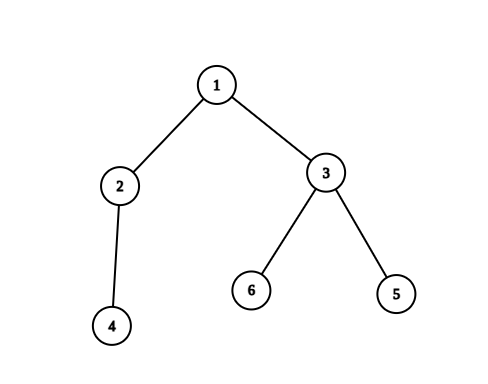
Input: n = 6, edges = [[1,2],[1,3],[2,4],[3,5],[3,6]] Output: 6 Explanation: The pairs with exactly one prime number on the path between them are: - (1, 2) since the path from 1 to 2 contains prime number 2. - (1, 3) since the path from 1 to 3 contains prime number 3. - (1, 4) since the path from 1 to 4 contains prime number 2. - (1, 6) since the path from 1 to 6 contains prime number 3. - (2, 4) since the path from 2 to 4 contains prime number 2. - (3, 6) since the path from 3 to 6 contains prime number 3. It can be shown that there are only 6 valid paths.
Constraints:
1 <= n <= 105edges.length == n - 1edges[i].length == 21 <= ui, vi <= n- The input is generated such that
edgesrepresent a valid tree.
Solutions
Solution 1: Preprocessing + Union-Find + Enumeration
We can preprocess to get all the prime numbers in $[1, n]$, where $prime[i]$ indicates whether $i$ is a prime number.
Next, we build a graph $g$ based on the two-dimensional integer array, where $g[i]$ represents all the neighbor nodes of node $i$. If both nodes of an edge are not prime numbers, we merge these two nodes into the same connected component.
Then, we enumerate all prime numbers $i$ in the range of $[1, n]$, considering all paths that include $i$.
Since $i$ is already a prime number, if $i$ is an endpoint of the path, we only need to accumulate the sizes of all connected components adjacent to node $i$. If $i$ is a middle point on the path, we need to accumulate the product of the sizes of any two adjacent connected components.
The time complexity is $O(n \times \alpha(n))$, and the space complexity is $O(n)$. Here, $n$ is the number of nodes, and $\alpha$ is the inverse function of the Ackermann function.
-
class PrimeTable { private final boolean[] prime; public PrimeTable(int n) { prime = new boolean[n + 1]; Arrays.fill(prime, true); prime[0] = false; prime[1] = false; for (int i = 2; i <= n; ++i) { if (prime[i]) { for (int j = i + i; j <= n; j += i) { prime[j] = false; } } } } public boolean isPrime(int x) { return prime[x]; } } class UnionFind { private final int[] p; private final int[] size; public UnionFind(int n) { p = new int[n]; size = new int[n]; for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) { p[i] = i; size[i] = 1; } } public int find(int x) { if (p[x] != x) { p[x] = find(p[x]); } return p[x]; } public boolean union(int a, int b) { int pa = find(a), pb = find(b); if (pa == pb) { return false; } if (size[pa] > size[pb]) { p[pb] = pa; size[pa] += size[pb]; } else { p[pa] = pb; size[pb] += size[pa]; } return true; } public int size(int x) { return size[find(x)]; } } class Solution { private static final PrimeTable PT = new PrimeTable(100010); public long countPaths(int n, int[][] edges) { List<Integer>[] g = new List[n + 1]; Arrays.setAll(g, i -> new ArrayList<>()); UnionFind uf = new UnionFind(n + 1); for (int[] e : edges) { int u = e[0], v = e[1]; g[u].add(v); g[v].add(u); if (!PT.isPrime(u) && !PT.isPrime(v)) { uf.union(u, v); } } long ans = 0; for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) { if (PT.isPrime(i)) { long t = 0; for (int j : g[i]) { if (!PT.isPrime(j)) { long cnt = uf.size(j); ans += cnt; ans += cnt * t; t += cnt; } } } } return ans; } } -
const int mx = 1e5 + 10; bool prime[mx + 1]; int init = []() { for (int i = 2; i <= mx; ++i) prime[i] = true; for (int i = 2; i <= mx; ++i) { if (prime[i]) { for (int j = i + i; j <= mx; j += i) { prime[j] = false; } } } return 0; }(); class UnionFind { public: UnionFind(int n) { p = vector<int>(n); size = vector<int>(n, 1); iota(p.begin(), p.end(), 0); } bool unite(int a, int b) { int pa = find(a), pb = find(b); if (pa == pb) { return false; } if (size[pa] > size[pb]) { p[pb] = pa; size[pa] += size[pb]; } else { p[pa] = pb; size[pb] += size[pa]; } return true; } int find(int x) { if (p[x] != x) { p[x] = find(p[x]); } return p[x]; } int getSize(int x) { return size[find(x)]; } private: vector<int> p, size; }; class Solution { public: long long countPaths(int n, vector<vector<int>>& edges) { vector<int> g[n + 1]; UnionFind uf(n + 1); for (auto& e : edges) { int u = e[0], v = e[1]; g[u].push_back(v); g[v].push_back(u); if (!prime[u] && !prime[v]) { uf.unite(u, v); } } long long ans = 0; for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) { if (prime[i]) { long long t = 0; for (int j : g[i]) { if (!prime[j]) { long long cnt = uf.getSize(j); ans += cnt; ans += cnt * t; t += cnt; } } } } return ans; } }; -
class UnionFind: def __init__(self, n): self.p = list(range(n)) self.size = [1] * n def find(self, x): if self.p[x] != x: self.p[x] = self.find(self.p[x]) return self.p[x] def union(self, a, b): pa, pb = self.find(a), self.find(b) if pa == pb: return False if self.size[pa] > self.size[pb]: self.p[pb] = pa self.size[pa] += self.size[pb] else: self.p[pa] = pb self.size[pb] += self.size[pa] return True mx = 10**5 + 10 prime = [True] * (mx + 1) prime[0] = prime[1] = False for i in range(2, mx + 1): if prime[i]: for j in range(i * i, mx + 1, i): prime[j] = False class Solution: def countPaths(self, n: int, edges: List[List[int]]) -> int: g = [[] for _ in range(n + 1)] uf = UnionFind(n + 1) for u, v in edges: g[u].append(v) g[v].append(u) if prime[u] + prime[v] == 0: uf.union(u, v) ans = 0 for i in range(1, n + 1): if prime[i]: t = 0 for j in g[i]: if not prime[j]: cnt = uf.size[uf.find(j)] ans += cnt ans += t * cnt t += cnt return ans -
const mx int = 1e5 + 10 var prime [mx]bool func init() { for i := 2; i < mx; i++ { prime[i] = true } for i := 2; i < mx; i++ { if prime[i] { for j := i + i; j < mx; j += i { prime[j] = false } } } } type unionFind struct { p, size []int } func newUnionFind(n int) *unionFind { p := make([]int, n) size := make([]int, n) for i := range p { p[i] = i size[i] = 1 } return &unionFind{p, size} } func (uf *unionFind) find(x int) int { if uf.p[x] != x { uf.p[x] = uf.find(uf.p[x]) } return uf.p[x] } func (uf *unionFind) union(a, b int) bool { pa, pb := uf.find(a), uf.find(b) if pa == pb { return false } if uf.size[pa] > uf.size[pb] { uf.p[pb] = pa uf.size[pa] += uf.size[pb] } else { uf.p[pa] = pb uf.size[pb] += uf.size[pa] } return true } func (uf *unionFind) getSize(x int) int { return uf.size[uf.find(x)] } func countPaths(n int, edges [][]int) (ans int64) { uf := newUnionFind(n + 1) g := make([][]int, n+1) for _, e := range edges { u, v := e[0], e[1] g[u] = append(g[u], v) g[v] = append(g[v], u) if !prime[u] && !prime[v] { uf.union(u, v) } } for i := 1; i <= n; i++ { if prime[i] { t := 0 for _, j := range g[i] { if !prime[j] { cnt := uf.getSize(j) ans += int64(cnt + cnt*t) t += cnt } } } } return } -
const mx = 100010; const prime = Array(mx).fill(true); prime[0] = prime[1] = false; for (let i = 2; i <= mx; ++i) { if (prime[i]) { for (let j = i + i; j <= mx; j += i) { prime[j] = false; } } } class UnionFind { p: number[]; size: number[]; constructor(n: number) { this.p = Array(n) .fill(0) .map((_, i) => i); this.size = Array(n).fill(1); } find(x: number): number { if (this.p[x] !== x) { this.p[x] = this.find(this.p[x]); } return this.p[x]; } union(a: number, b: number): boolean { const [pa, pb] = [this.find(a), this.find(b)]; if (pa === pb) { return false; } if (this.size[pa] > this.size[pb]) { this.p[pb] = pa; this.size[pa] += this.size[pb]; } else { this.p[pa] = pb; this.size[pb] += this.size[pa]; } return true; } getSize(x: number): number { return this.size[this.find(x)]; } } function countPaths(n: number, edges: number[][]): number { const uf = new UnionFind(n + 1); const g: number[][] = Array(n + 1) .fill(0) .map(() => []); for (const [u, v] of edges) { g[u].push(v); g[v].push(u); if (!prime[u] && !prime[v]) { uf.union(u, v); } } let ans = 0; for (let i = 1; i <= n; ++i) { if (prime[i]) { let t = 0; for (let j of g[i]) { if (!prime[j]) { const cnt = uf.getSize(j); ans += cnt + t * cnt; t += cnt; } } } } return ans; }