Welcome to Subscribe On Youtube
2661. First Completely Painted Row or Column
Description
You are given a 0-indexed integer array arr, and an m x n integer matrix mat. arr and mat both contain all the integers in the range [1, m * n].
Go through each index i in arr starting from index 0 and paint the cell in mat containing the integer arr[i].
Return the smallest index i at which either a row or a column will be completely painted in mat.
Example 1:
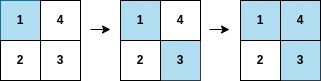
Input: arr = [1,3,4,2], mat = [[1,4],[2,3]] Output: 2 Explanation: The moves are shown in order, and both the first row and second column of the matrix become fully painted at arr[2].
Example 2:
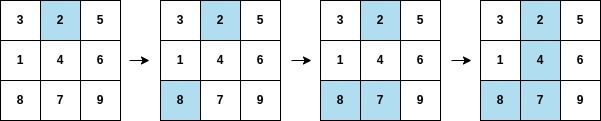
Input: arr = [2,8,7,4,1,3,5,6,9], mat = [[3,2,5],[1,4,6],[8,7,9]] Output: 3 Explanation: The second column becomes fully painted at arr[3].
Constraints:
m == mat.lengthn = mat[i].lengtharr.length == m * n1 <= m, n <= 1051 <= m * n <= 1051 <= arr[i], mat[r][c] <= m * n- All the integers of
arrare unique. - All the integers of
matare unique.
Solutions
Solution 1: Hash Table + Array Counting
We use a hash table $idx$ to record the position of each element in the matrix $mat$, that is $idx[mat[i][j]] = (i, j)$, and define two arrays $row$ and $col$ to record the number of colored elements in each row and each column respectively.
Traverse the array $arr$. For each element $arr[k]$, we find its position $(i, j)$ in the matrix $mat$, and then add $row[i]$ and $col[j]$ by one. If $row[i] = n$ or $col[j] = m$, it means that the $i$-th row or the $j$-th column has been colored, so $arr[k]$ is the element we are looking for, and we return $k$.
The time complexity is $O(m \times n)$, and the space complexity is $O(m \times n)$. Here $m$ and $n$ are the number of rows and columns of the matrix $mat$ respectively.
-
class Solution { public int firstCompleteIndex(int[] arr, int[][] mat) { int m = mat.length, n = mat[0].length; Map<Integer, int[]> idx = new HashMap<>(); for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i) { for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) { idx.put(mat[i][j], new int[] {i, j}); } } int[] row = new int[m]; int[] col = new int[n]; for (int k = 0;; ++k) { var x = idx.get(arr[k]); int i = x[0], j = x[1]; ++row[i]; ++col[j]; if (row[i] == n || col[j] == m) { return k; } } } } -
class Solution { public: int firstCompleteIndex(vector<int>& arr, vector<vector<int>>& mat) { int m = mat.size(), n = mat[0].size(); unordered_map<int, pair<int, int>> idx; for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i) { for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) { idx[mat[i][j]] = {i, j}; } } vector<int> row(m), col(n); for (int k = 0;; ++k) { auto [i, j] = idx[arr[k]]; ++row[i]; ++col[j]; if (row[i] == n || col[j] == m) { return k; } } } }; -
class Solution: def firstCompleteIndex(self, arr: List[int], mat: List[List[int]]) -> int: m, n = len(mat), len(mat[0]) idx = {} for i in range(m): for j in range(n): idx[mat[i][j]] = (i, j) row = [0] * m col = [0] * n for k in range(len(arr)): i, j = idx[arr[k]] row[i] += 1 col[j] += 1 if row[i] == n or col[j] == m: return k -
func firstCompleteIndex(arr []int, mat [][]int) int { m, n := len(mat), len(mat[0]) idx := map[int][2]int{} for i := range mat { for j := range mat[i] { idx[mat[i][j]] = [2]int{i, j} } } row := make([]int, m) col := make([]int, n) for k := 0; ; k++ { x := idx[arr[k]] i, j := x[0], x[1] row[i]++ col[j]++ if row[i] == n || col[j] == m { return k } } } -
function firstCompleteIndex(arr: number[], mat: number[][]): number { const m = mat.length; const n = mat[0].length; const idx: Map<number, number[]> = new Map(); for (let i = 0; i < m; ++i) { for (let j = 0; j < n; ++j) { idx.set(mat[i][j], [i, j]); } } const row: number[] = new Array(m).fill(0); const col: number[] = new Array(n).fill(0); for (let k = 0; ; ++k) { const [i, j] = idx.get(arr[k])!; ++row[i]; ++col[j]; if (row[i] === n || col[j] === m) { return k; } } } -
use std::collections::HashMap; impl Solution { pub fn first_complete_index(arr: Vec<i32>, mat: Vec<Vec<i32>>) -> i32 { let m = mat.len(); let n = mat[0].len(); let mut idx = HashMap::new(); for i in 0..m { for j in 0..n { idx.insert(mat[i][j], [i, j]); } } let mut row = vec![0; m]; let mut col = vec![0; n]; for k in 0..arr.len() { let x = idx.get(&arr[k]).unwrap(); let i = x[0]; let j = x[1]; row[i] += 1; col[j] += 1; if row[i] == n || col[j] == m { return k as i32; } } -1 } }
