Welcome to Subscribe On Youtube
2608. Shortest Cycle in a Graph
Description
There is a bi-directional graph with n vertices, where each vertex is labeled from 0 to n - 1. The edges in the graph are represented by a given 2D integer array edges, where edges[i] = [ui, vi] denotes an edge between vertex ui and vertex vi. Every vertex pair is connected by at most one edge, and no vertex has an edge to itself.
Return the length of the shortest cycle in the graph. If no cycle exists, return -1.
A cycle is a path that starts and ends at the same node, and each edge in the path is used only once.
Example 1:
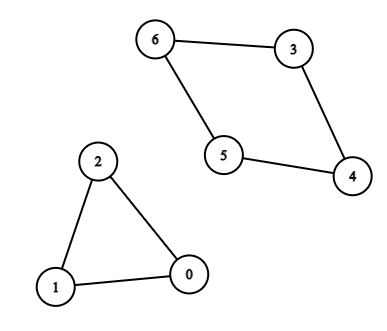
Input: n = 7, edges = [[0,1],[1,2],[2,0],[3,4],[4,5],[5,6],[6,3]] Output: 3 Explanation: The cycle with the smallest length is : 0 -> 1 -> 2 -> 0
Example 2:
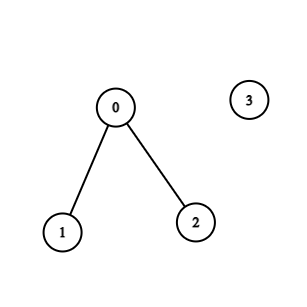
Input: n = 4, edges = [[0,1],[0,2]] Output: -1 Explanation: There are no cycles in this graph.
Constraints:
2 <= n <= 10001 <= edges.length <= 1000edges[i].length == 20 <= ui, vi < nui != vi- There are no repeated edges.
Solutions
Solution 1: Enumerate edges + BFS
We first construct the adjacency list $g$ of the graph according to the array $edges$, where $g[u]$ represents all the adjacent vertices of vertex $u$.
Then we enumerate the two-directional edge $(u, v)$, if the path from vertex $u$ to vertex $v$ still exists after deleting this edge, then the length of the shortest cycle containing this edge is $dist[v] + 1$, where $dist[v]$ represents the shortest path length from vertex $u$ to vertex $v$. We take the minimum of all these cycles.
The time complexity is $O(m^2)$ and the space complexity is $O(m + n)$, where $m$ and $n$ are the length of the array $edges$ and the number of vertices.
Solution 2: Enumerate points + BFS
Similar to Solution 1, we first construct the adjacency list $g$ of the graph according to the array $edges$, where $g[u]$ represents all the adjacent vertices of vertex $u$.
Then we enumerate the vertex $u$, if there are two paths from vertex $u$ to vertex $v$, then we currently find a cycle, the length is the sum of the length of the two paths. We take the minimum of all these cycles.
The time complexity is $O(m \times n)$ and the space complexity is $O(m + n)$, where $m$ and $n$ are the length of the array $edges$ and the number of vertices.
-
class Solution { private List<Integer>[] g; private final int inf = 1 << 30; public int findShortestCycle(int n, int[][] edges) { g = new List[n]; Arrays.setAll(g, k -> new ArrayList<>()); for (var e : edges) { int u = e[0], v = e[1]; g[u].add(v); g[v].add(u); } int ans = inf; for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) { ans = Math.min(ans, bfs(i)); } return ans < inf ? ans : -1; } private int bfs(int u) { int[] dist = new int[g.length]; Arrays.fill(dist, -1); dist[u] = 0; Deque<int[]> q = new ArrayDeque<>(); q.offer(new int[] {u, -1}); int ans = inf; while (!q.isEmpty()) { var p = q.poll(); u = p[0]; int fa = p[1]; for (int v : g[u]) { if (dist[v] < 0) { dist[v] = dist[u] + 1; q.offer(new int[] {v, u}); } else if (v != fa) { ans = Math.min(ans, dist[u] + dist[v] + 1); } } } return ans; } } -
class Solution { public: int findShortestCycle(int n, vector<vector<int>>& edges) { vector<vector<int>> g(n); for (auto& e : edges) { int u = e[0], v = e[1]; g[u].push_back(v); g[v].push_back(u); } const int inf = 1 << 30; auto bfs = [&](int u) -> int { int dist[n]; memset(dist, -1, sizeof(dist)); dist[u] = 0; queue<pair<int, int>> q; q.emplace(u, -1); int ans = inf; while (!q.empty()) { auto p = q.front(); u = p.first; int fa = p.second; q.pop(); for (int v : g[u]) { if (dist[v] < 0) { dist[v] = dist[u] + 1; q.emplace(v, u); } else if (v != fa) { ans = min(ans, dist[u] + dist[v] + 1); } } } return ans; }; int ans = inf; for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) { ans = min(ans, bfs(i)); } return ans < inf ? ans : -1; } }; -
class Solution: def findShortestCycle(self, n: int, edges: List[List[int]]) -> int: def bfs(u: int) -> int: dist = [-1] * n dist[u] = 0 q = deque([(u, -1)]) ans = inf while q: u, fa = q.popleft() for v in g[u]: if dist[v] < 0: dist[v] = dist[u] + 1 q.append((v, u)) elif v != fa: ans = min(ans, dist[u] + dist[v] + 1) return ans g = defaultdict(list) for u, v in edges: g[u].append(v) g[v].append(u) ans = min(bfs(i) for i in range(n)) return ans if ans < inf else -1 -
func findShortestCycle(n int, edges [][]int) int { g := make([][]int, n) for _, e := range edges { u, v := e[0], e[1] g[u] = append(g[u], v) g[v] = append(g[v], u) } const inf = 1 << 30 bfs := func(u int) int { dist := make([]int, n) for i := range dist { dist[i] = -1 } dist[u] = 0 q := [][2]int{ {u, -1} } ans := inf for len(q) > 0 { p := q[0] u = p[0] fa := p[1] q = q[1:] for _, v := range g[u] { if dist[v] < 0 { dist[v] = dist[u] + 1 q = append(q, [2]int{v, u}) } else if v != fa { ans = min(ans, dist[u]+dist[v]+1) } } } return ans } ans := inf for i := 0; i < n; i++ { ans = min(ans, bfs(i)) } if ans < inf { return ans } return -1 } func min(a, b int) int { if a < b { return a } return b } -
function findShortestCycle(n: number, edges: number[][]): number { const g: number[][] = new Array(n).fill(0).map(() => []); for (const [u, v] of edges) { g[u].push(v); g[v].push(u); } const inf = 1 << 30; let ans = inf; const bfs = (u: number) => { const dist: number[] = new Array(n).fill(-1); dist[u] = 0; const q: number[][] = [[u, -1]]; let ans = inf; while (q.length) { const p = q.shift()!; u = p[0]; const fa = p[1]; for (const v of g[u]) { if (dist[v] < 0) { dist[v] = dist[u] + 1; q.push([v, u]); } else if (v !== fa) { ans = Math.min(ans, dist[u] + dist[v] + 1); } } } return ans; }; for (let i = 0; i < n; ++i) { ans = Math.min(ans, bfs(i)); } return ans < inf ? ans : -1; }