Welcome to Subscribe On Youtube
2646. Minimize the Total Price of the Trips
Description
There exists an undirected and unrooted tree with n nodes indexed from 0 to n - 1. You are given the integer n and a 2D integer array edges of length n - 1, where edges[i] = [ai, bi] indicates that there is an edge between nodes ai and bi in the tree.
Each node has an associated price. You are given an integer array price, where price[i] is the price of the ith node.
The price sum of a given path is the sum of the prices of all nodes lying on that path.
Additionally, you are given a 2D integer array trips, where trips[i] = [starti, endi] indicates that you start the ith trip from the node starti and travel to the node endi by any path you like.
Before performing your first trip, you can choose some non-adjacent nodes and halve the prices.
Return the minimum total price sum to perform all the given trips.
Example 1:
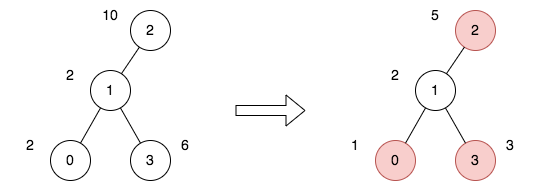
Input: n = 4, edges = [[0,1],[1,2],[1,3]], price = [2,2,10,6], trips = [[0,3],[2,1],[2,3]] Output: 23 Explanation: The diagram above denotes the tree after rooting it at node 2. The first part shows the initial tree and the second part shows the tree after choosing nodes 0, 2, and 3, and making their price half. For the 1st trip, we choose path [0,1,3]. The price sum of that path is 1 + 2 + 3 = 6. For the 2nd trip, we choose path [2,1]. The price sum of that path is 2 + 5 = 7. For the 3rd trip, we choose path [2,1,3]. The price sum of that path is 5 + 2 + 3 = 10. The total price sum of all trips is 6 + 7 + 10 = 23. It can be proven, that 23 is the minimum answer that we can achieve.
Example 2:
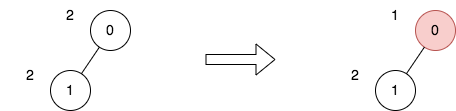
Input: n = 2, edges = [[0,1]], price = [2,2], trips = [[0,0]] Output: 1 Explanation: The diagram above denotes the tree after rooting it at node 0. The first part shows the initial tree and the second part shows the tree after choosing node 0, and making its price half. For the 1st trip, we choose path [0]. The price sum of that path is 1. The total price sum of all trips is 1. It can be proven, that 1 is the minimum answer that we can achieve.
Constraints:
1 <= n <= 50edges.length == n - 10 <= ai, bi <= n - 1edgesrepresents a valid tree.price.length == nprice[i]is an even integer.1 <= price[i] <= 10001 <= trips.length <= 1000 <= starti, endi <= n - 1
Solutions
-
class Solution { private List<Integer>[] g; private int[] price; private int[] cnt; public int minimumTotalPrice(int n, int[][] edges, int[] price, int[][] trips) { this.price = price; cnt = new int[n]; g = new List[n]; Arrays.setAll(g, k -> new ArrayList<>()); for (var e : edges) { int a = e[0], b = e[1]; g[a].add(b); g[b].add(a); } for (var t : trips) { int start = t[0], end = t[1]; dfs(start, -1, end); } int[] ans = dfs2(0, -1); return Math.min(ans[0], ans[1]); } private boolean dfs(int i, int fa, int k) { ++cnt[i]; if (i == k) { return true; } boolean ok = false; for (int j : g[i]) { if (j != fa) { ok = dfs(j, i, k); if (ok) { break; } } } if (!ok) { --cnt[i]; } return ok; } private int[] dfs2(int i, int fa) { int a = cnt[i] * price[i]; int b = a >> 1; for (int j : g[i]) { if (j != fa) { var t = dfs2(j, i); a += Math.min(t[0], t[1]); b += t[0]; } } return new int[] {a, b}; } } -
class Solution { public: int minimumTotalPrice(int n, vector<vector<int>>& edges, vector<int>& price, vector<vector<int>>& trips) { vector<vector<int>> g(n); vector<int> cnt(n); for (auto& e : edges) { int a = e[0], b = e[1]; g[a].push_back(b); g[b].push_back(a); } function<bool(int, int, int)> dfs = [&](int i, int fa, int k) -> bool { ++cnt[i]; if (i == k) { return true; } bool ok = false; for (int j : g[i]) { if (j != fa) { ok = dfs(j, i, k); if (ok) { break; } } } if (!ok) { --cnt[i]; } return ok; }; function<pair<int, int>(int, int)> dfs2 = [&](int i, int fa) -> pair<int, int> { int a = cnt[i] * price[i]; int b = a >> 1; for (int j : g[i]) { if (j != fa) { auto [x, y] = dfs2(j, i); a += min(x, y); b += x; } } return {a, b}; }; for (auto& t : trips) { int start = t[0], end = t[1]; dfs(start, -1, end); } auto [a, b] = dfs2(0, -1); return min(a, b); } }; -
class Solution: def minimumTotalPrice( self, n: int, edges: List[List[int]], price: List[int], trips: List[List[int]] ) -> int: def dfs(i: int, fa: int, k: int) -> bool: cnt[i] += 1 if i == k: return True ok = any(j != fa and dfs(j, i, k) for j in g[i]) if not ok: cnt[i] -= 1 return ok def dfs2(i: int, fa: int) -> (int, int): a = cnt[i] * price[i] b = a // 2 for j in g[i]: if j != fa: x, y = dfs2(j, i) a += min(x, y) b += x return a, b g = [[] for _ in range(n)] for a, b in edges: g[a].append(b) g[b].append(a) cnt = Counter() for start, end in trips: dfs(start, -1, end) return min(dfs2(0, -1)) -
func minimumTotalPrice(n int, edges [][]int, price []int, trips [][]int) int { g := make([][]int, n) for _, e := range edges { a, b := e[0], e[1] g[a] = append(g[a], b) g[b] = append(g[b], a) } cnt := make([]int, n) var dfs func(int, int, int) bool dfs = func(i, fa, k int) bool { cnt[i]++ if i == k { return true } ok := false for _, j := range g[i] { if j != fa { ok = dfs(j, i, k) if ok { break } } } if !ok { cnt[i]-- } return ok } for _, t := range trips { start, end := t[0], t[1] dfs(start, -1, end) } var dfs2 func(int, int) (int, int) dfs2 = func(i, fa int) (int, int) { a := price[i] * cnt[i] b := a >> 1 for _, j := range g[i] { if j != fa { x, y := dfs2(j, i) a += min(x, y) b += x } } return a, b } a, b := dfs2(0, -1) return min(a, b) } -
function minimumTotalPrice( n: number, edges: number[][], price: number[], trips: number[][], ): number { const g: number[][] = Array.from({ length: n }, () => []); for (const [a, b] of edges) { g[a].push(b); g[b].push(a); } const cnt: number[] = new Array(n).fill(0); const dfs = (i: number, fa: number, k: number): boolean => { ++cnt[i]; if (i === k) { return true; } let ok = false; for (const j of g[i]) { if (j !== fa) { ok = dfs(j, i, k); if (ok) { break; } } } if (!ok) { --cnt[i]; } return ok; }; for (const [start, end] of trips) { dfs(start, -1, end); } const dfs2 = (i: number, fa: number): number[] => { let a: number = price[i] * cnt[i]; let b: number = a >> 1; for (const j of g[i]) { if (j !== fa) { const [x, y] = dfs2(j, i); a += Math.min(x, y); b += x; } } return [a, b]; }; const [a, b] = dfs2(0, -1); return Math.min(a, b); }