Welcome to Subscribe On Youtube
Formatted question description: https://leetcode.ca/all/2492.html
2492. Minimum Score of a Path Between Two Cities
- Difficulty: Medium.
- Related Topics: .
- Similar Questions: Checking Existence of Edge Length Limited Paths, Checking Existence of Edge Length Limited Paths II.
Problem
You are given a positive integer n representing n cities numbered from 1 to n. You are also given a 2D array roads where roads[i] = [ai, bi, distancei] indicates that there is a **bidirectional **road between cities ai and bi with a distance equal to distancei. The cities graph is not necessarily connected.
The score of a path between two cities is defined as the **minimum **distance of a road in this path.
Return the **minimum **possible score of a path between cities **1 and **n.
Note:
-
A path is a sequence of roads between two cities.
-
It is allowed for a path to contain the same road multiple times, and you can visit cities
1andnmultiple times along the path. -
The test cases are generated such that there is at least one path between
1andn.
Example 1:
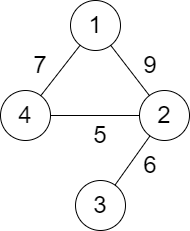
Input: n = 4, roads = [[1,2,9],[2,3,6],[2,4,5],[1,4,7]]
Output: 5
Explanation: The path from city 1 to 4 with the minimum score is: 1 -> 2 -> 4. The score of this path is min(9,5) = 5.
It can be shown that no other path has less score.
Example 2:
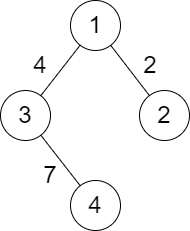
Input: n = 4, roads = [[1,2,2],[1,3,4],[3,4,7]]
Output: 2
Explanation: The path from city 1 to 4 with the minimum score is: 1 -> 2 -> 1 -> 3 -> 4. The score of this path is min(2,2,4,7) = 2.
Constraints:
-
2 <= n <= 105 -
1 <= roads.length <= 105 -
roads[i].length == 3 -
1 <= ai, bi <= n -
ai != bi -
1 <= distancei <= 104 -
There are no repeated edges.
-
There is at least one path between
1andn.
Solution (Java, C++, Python)
-
class Solution { private List<int[]>[] g; private boolean[] vis; private int ans = 1 << 30; public int minScore(int n, int[][] roads) { g = new List[n]; vis = new boolean[n]; Arrays.setAll(g, k -> new ArrayList<>()); for (var e : roads) { int a = e[0] - 1, b = e[1] - 1, d = e[2]; g[a].add(new int[] {b, d}); g[b].add(new int[] {a, d}); } dfs(0); return ans; } private void dfs(int i) { for (var nxt : g[i]) { int j = nxt[0], d = nxt[1]; ans = Math.min(ans, d); if (!vis[j]) { vis[j] = true; dfs(j); } } } } -
class Solution { public: int minScore(int n, vector<vector<int>>& roads) { vector<vector<pair<int, int>>> g(n); bool vis[n]; memset(vis, 0, sizeof vis); for (auto& e : roads) { int a = e[0] - 1, b = e[1] - 1, d = e[2]; g[a].emplace_back(b, d); g[b].emplace_back(a, d); } int ans = INT_MAX; function<void(int)> dfs = [&](int i) { for (auto [j, d] : g[i]) { ans = min(ans, d); if (!vis[j]) { vis[j] = true; dfs(j); } } }; dfs(0); return ans; } }; -
class Solution: def minScore(self, n: int, roads: List[List[int]]) -> int: def dfs(i): nonlocal ans for j, d in g[i]: ans = min(ans, d) if not vis[j]: vis[j] = True dfs(j) g = defaultdict(list) for a, b, d in roads: g[a].append((b, d)) g[b].append((a, d)) vis = [False] * (n + 1) ans = inf dfs(1) return ans -
func minScore(n int, roads [][]int) int { type pair struct{ i, v int } g := make([][]pair, n) for _, e := range roads { a, b, d := e[0]-1, e[1]-1, e[2] g[a] = append(g[a], pair{b, d}) g[b] = append(g[b], pair{a, d}) } vis := make([]bool, n) ans := 1 << 30 var dfs func(int) dfs = func(i int) { for _, nxt := range g[i] { j, d := nxt.i, nxt.v ans = min(ans, d) if !vis[j] { vis[j] = true dfs(j) } } } dfs(0) return ans } func min(a, b int) int { if a < b { return a } return b } -
function minScore(n: number, roads: number[][]): number { const vis = new Array(n + 1).fill(false); const g = Array.from({ length: n + 1 }, () => []); for (const [a, b, v] of roads) { g[a].push([b, v]); g[b].push([a, v]); } let ans = Infinity; const dfs = (i: number) => { if (vis[i]) { return; } vis[i] = true; for (const [j, v] of g[i]) { ans = Math.min(ans, v); dfs(j); } }; dfs(1); return ans; } -
var minScore = function (n, roads) { // 构建点到点的映射表 const graph = Array.from({ length: n + 1 }, () => new Map()); for (let [u, v, w] of roads) { graph[u].set(v, w); graph[v].set(u, w); } // DFS const vis = new Array(n).fill(false); let ans = Infinity; var dfs = function (u) { vis[u] = true; for (const [v, w] of graph[u]) { ans = Math.min(ans, w); if (!vis[v]) dfs(v); } }; dfs(1); return ans; }; -
impl Solution { fn dfs(i: usize, mut ans: i32, g: &Vec<Vec<(usize, i32)>>, vis: &mut Vec<bool>) -> i32 { if vis[i] { return ans; } vis[i] = true; for (j, v) in g[i].iter() { ans = ans.min(*v.min(&Self::dfs(*j, ans, g, vis))); } ans } pub fn min_score(n: i32, roads: Vec<Vec<i32>>) -> i32 { let n = n as usize; let mut vis = vec![false; n + 1]; let mut g = vec![Vec::new(); n + 1]; for road in roads.iter() { let a = road[0] as usize; let b = road[1] as usize; let v = road[2]; g[a].push((b, v)); g[b].push((a, v)); } Self::dfs(1, i32::MAX, &g, &mut vis) } }
Explain:
nope.
Complexity:
- Time complexity : O(n).
- Space complexity : O(n).