Welcome to Subscribe On Youtube
Formatted question description: https://leetcode.ca/all/2428.html
2428. Maximum Sum of an Hourglass
- Difficulty: Medium.
- Related Topics: .
- Similar Questions: Matrix Block Sum.
Problem
You are given an m x n integer matrix grid.
We define an hourglass as a part of the matrix with the following form:
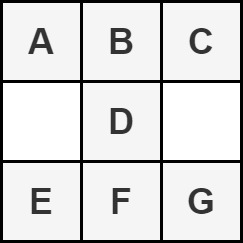
Return the **maximum sum of the elements of an hourglass**.
Note that an hourglass cannot be rotated and must be entirely contained within the matrix.
Example 1:
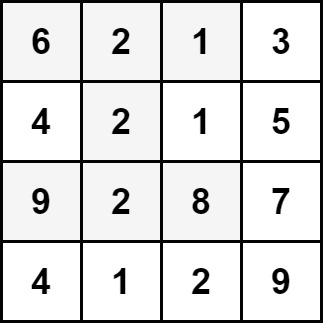
Input: grid = [[6,2,1,3],[4,2,1,5],[9,2,8,7],[4,1,2,9]]
Output: 30
Explanation: The cells shown above represent the hourglass with the maximum sum: 6 + 2 + 1 + 2 + 9 + 2 + 8 = 30.
Example 2:
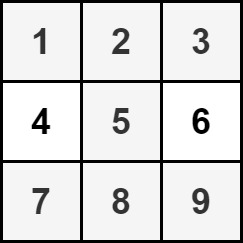
Input: grid = [[1,2,3],[4,5,6],[7,8,9]]
Output: 35
Explanation: There is only one hourglass in the matrix, with the sum: 1 + 2 + 3 + 5 + 7 + 8 + 9 = 35.
Constraints:
-
m == grid.length -
n == grid[i].length -
3 <= m, n <= 150 -
0 <= grid[i][j] <= 10^6
Solution (Java, C++, Python)
-
class Solution { public int maxSum(int[][] grid) { int m = grid.length, n = grid[0].length; int ans = 0; for (int i = 1; i < m - 1; ++i) { for (int j = 1; j < n - 1; ++j) { int t = 0; for (int x = i - 1; x <= i + 1; ++x) { for (int y = j - 1; y <= j + 1; ++y) { t += grid[x][y]; } } t -= grid[i][j - 1]; t -= grid[i][j + 1]; ans = Math.max(ans, t); } } return ans; } } -
class Solution { public: int maxSum(vector<vector<int>>& grid) { int m = grid.size(), n = grid[0].size(); int ans = 0; for (int i = 1; i < m - 1; ++i) { for (int j = 1; j < n - 1; ++j) { int t = 0; for (int x = i - 1; x <= i + 1; ++x) { for (int y = j - 1; y <= j + 1; ++y) { t += grid[x][y]; } } t -= grid[i][j - 1]; t -= grid[i][j + 1]; ans = max(ans, t); } } return ans; } }; -
class Solution: def maxSum(self, grid: List[List[int]]) -> int: m, n = len(grid), len(grid[0]) ans = 0 for i in range(1, m - 1): for j in range(1, n - 1): t = 0 for x in [i - 1, i, i + 1]: for y in [j - 1, j, j + 1]: t += grid[x][y] t -= grid[i][j - 1] t -= grid[i][j + 1] ans = max(ans, t) return ans -
func maxSum(grid [][]int) int { m, n := len(grid), len(grid[0]) ans := 0 for i := 1; i < m-1; i++ { for j := 1; j < n-1; j++ { t := 0 for x := i - 1; x <= i+1; x++ { for y := j - 1; y <= j+1; y++ { t += grid[x][y] } } t -= grid[i][j-1] t -= grid[i][j+1] ans = max(ans, t) } } return ans } func max(a, b int) int { if a > b { return a } return b } -
function maxSum(grid: number[][]): number { const m = grid.length, n = grid[0].length; let threeSum = Array.from({ length: m }, () => new Array(n - 2).fill(0)); for (let i = 0; i < m; i++) { for (let j = 1; j < n - 1; j++) { threeSum[i][j - 1] = grid[i][j - 1] + grid[i][j] + grid[i][j + 1]; } } let ans = 0; for (let i = 1; i < m - 1; i++) { for (let j = 1; j < n - 1; j++) { ans = Math.max( ans, threeSum[i - 1][j - 1] + grid[i][j] + threeSum[i + 1][j - 1], ); } } return ans; }
Explain:
nope.
Complexity:
- Time complexity : O(n).
- Space complexity : O(n).