Welcome to Subscribe On Youtube
Formatted question description: https://leetcode.ca/all/2374.html
2374. Node With Highest Edge Score
- Difficulty: Medium.
- Related Topics: Hash Table, Graph.
- Similar Questions: Two Sum, Sort Characters By Frequency, Sort Array by Increasing Frequency.
Problem
You are given a directed graph with n nodes labeled from 0 to n - 1, where each node has exactly one outgoing edge.
The graph is represented by a given 0-indexed integer array edges of length n, where edges[i] indicates that there is a directed edge from node i to node edges[i].
The edge score of a node i is defined as the sum of the labels of all the nodes that have an edge pointing to i.
Return the node with the highest **edge score. If multiple nodes have the same **edge score, return the node with the smallest index.
Example 1:
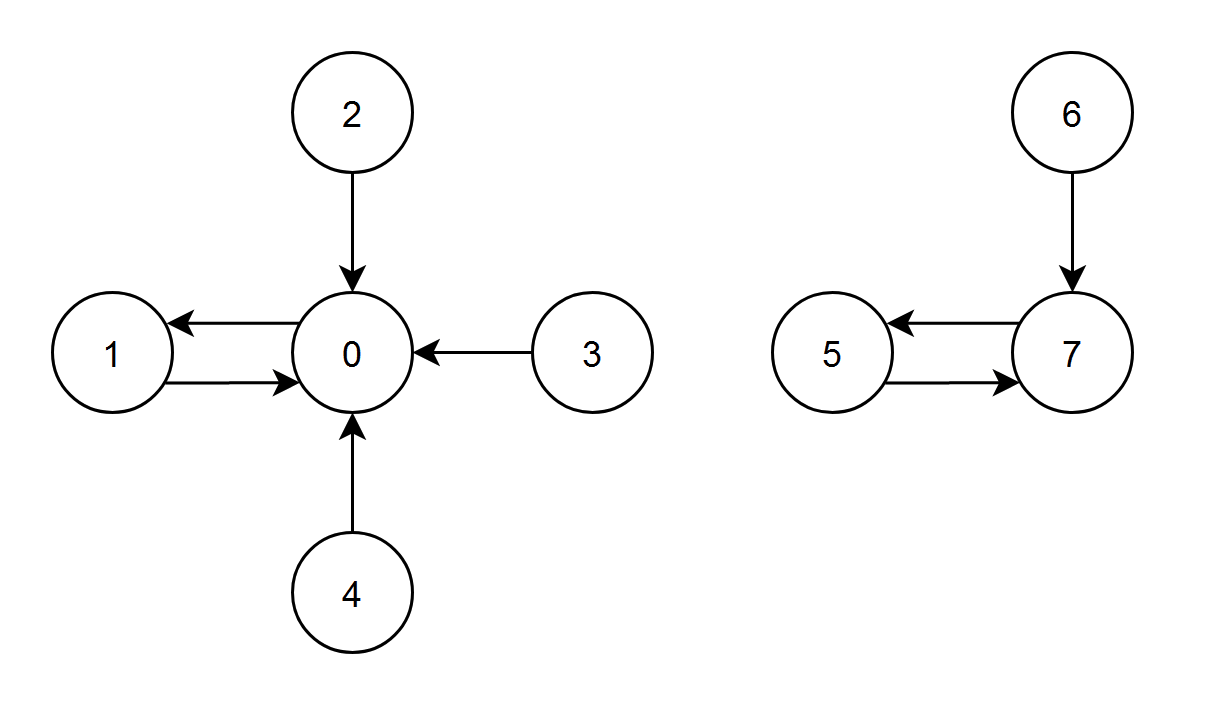
Input: edges = [1,0,0,0,0,7,7,5]
Output: 7
Explanation:
- The nodes 1, 2, 3 and 4 have an edge pointing to node 0. The edge score of node 0 is 1 + 2 + 3 + 4 = 10.
- The node 0 has an edge pointing to node 1. The edge score of node 1 is 0.
- The node 7 has an edge pointing to node 5. The edge score of node 5 is 7.
- The nodes 5 and 6 have an edge pointing to node 7. The edge score of node 7 is 5 + 6 = 11.
Node 7 has the highest edge score so return 7.
Example 2:
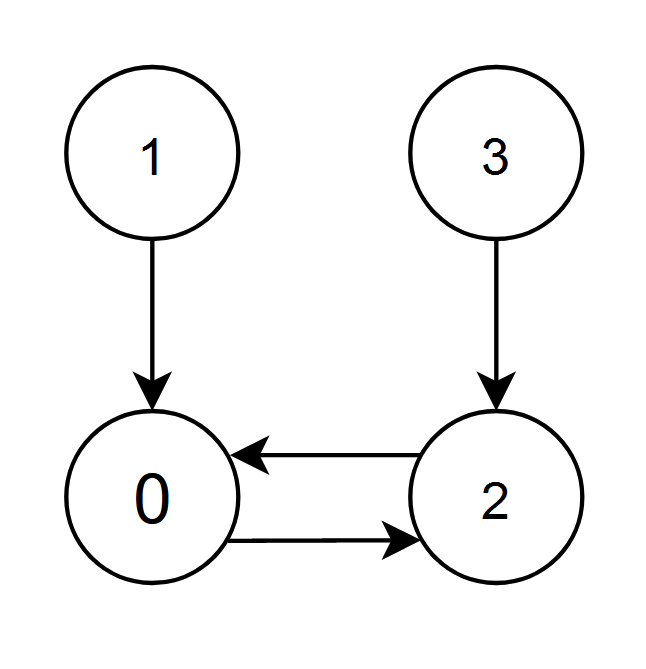
Input: edges = [2,0,0,2]
Output: 0
Explanation:
- The nodes 1 and 2 have an edge pointing to node 0. The edge score of node 0 is 1 + 2 = 3.
- The nodes 0 and 3 have an edge pointing to node 2. The edge score of node 2 is 0 + 3 = 3.
Nodes 0 and 2 both have an edge score of 3. Since node 0 has a smaller index, we return 0.
Constraints:
-
n == edges.length -
2 <= n <= 105 -
0 <= edges[i] < n -
edges[i] != i
Solution (Java, C++, Python)
-
class Solution { public int edgeScore(int[] edges) { int n = edges.length; int[] score = new int[n]; int maxScore = 0; int node = 0; for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { score[edges[i]] += i; if (score[edges[i]] >= maxScore) { if (score[edges[i]] == maxScore) { node = Math.min(node, edges[i]); } else { node = edges[i]; } maxScore = score[edges[i]]; } } return node; } } ############ class Solution { public int edgeScore(int[] edges) { int n = edges.length; long[] cnt = new long[n]; for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) { cnt[edges[i]] += i; } int ans = 0; for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) { if (cnt[ans] < cnt[i]) { ans = i; } } return ans; } } -
class Solution: def edgeScore(self, edges: List[int]) -> int: cnt = Counter() for i, v in enumerate(edges): cnt[v] += i ans = 0 for i in range(len(edges)): if cnt[ans] < cnt[i]: ans = i return ans ############ # 2374. Node With Highest Edge Score # https://leetcode.com/problems/node-with-highest-edge-score/ class Solution: def edgeScore(self, edges: List[int]) -> int: n = len(edges) scores = [0] * n for node, out in enumerate(edges): scores[out] += node res = maxScore = -1 for node, score in enumerate(scores): if score > maxScore: maxScore = score res = node return res -
class Solution { public: int edgeScore(vector<int>& edges) { int n = edges.size(); vector<long long> cnt(n); for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) { cnt[edges[i]] += i; } int ans = 0; for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) { if (cnt[ans] < cnt[i]) { ans = i; } } return ans; } }; -
func edgeScore(edges []int) int { n := len(edges) cnt := make([]int, n) for i, v := range edges { cnt[v] += i } ans := 0 for i, v := range cnt { if cnt[ans] < v { ans = i } } return ans } -
function edgeScore(edges: number[]): number { const n = edges.length; const sum = new Array(n).fill(0); for (let i = 0; i < n; i++) { sum[edges[i]] += i; } let res = 0; for (let i = 0; i < n; i++) { if (sum[res] < sum[i]) { res = i; } } return res; }
Explain:
nope.
Complexity:
- Time complexity : O(n).
- Space complexity : O(n).