Welcome to Subscribe On Youtube
Formatted question description: https://leetcode.ca/all/2328.html
2328. Number of Increasing Paths in a Grid
- Difficulty: Hard.
- Related Topics: Array, Dynamic Programming, Depth-First Search, Breadth-First Search, Graph, Topological Sort, Memoization, Matrix.
- Similar Questions: Longest Increasing Path in a Matrix, All Paths From Source to Target.
Problem
You are given an m x n integer matrix grid, where you can move from a cell to any adjacent cell in all 4 directions.
Return the number of **strictly increasing paths in the grid such that you can start from any cell and end at any cell. Since the answer may be very large, return it **modulo 109 + 7.
Two paths are considered different if they do not have exactly the same sequence of visited cells.
Example 1:
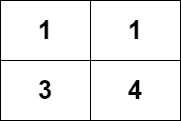
Input: grid = [[1,1],[3,4]]
Output: 8
Explanation: The strictly increasing paths are:
- Paths with length 1: [1], [1], [3], [4].
- Paths with length 2: [1 -> 3], [1 -> 4], [3 -> 4].
- Paths with length 3: [1 -> 3 -> 4].
The total number of paths is 4 + 3 + 1 = 8.
Example 2:
Input: grid = [[1],[2]]
Output: 3
Explanation: The strictly increasing paths are:
- Paths with length 1: [1], [2].
- Paths with length 2: [1 -> 2].
The total number of paths is 2 + 1 = 3.
Constraints:
-
m == grid.length -
n == grid[i].length -
1 <= m, n <= 1000 -
1 <= m * n <= 105 -
1 <= grid[i][j] <= 105
Solution
-
class Solution { private int help(int[][] a, int i, int j, int n, int m, int[][] dp) { if (i < 0 || i >= n || j >= m || j < 0) { return 0; } if (dp[i][j] != 0) { return dp[i][j]; } long res = 0; if (i < n - 1 && a[i + 1][j] > a[i][j]) { res += 1 + help(a, i + 1, j, n, m, dp); } if (i > 0 && a[i - 1][j] > a[i][j]) { res += 1 + help(a, i - 1, j, n, m, dp); } if (j > 0 && a[i][j - 1] > a[i][j]) { res += 1 + help(a, i, j - 1, n, m, dp); } if (j < m - 1 && a[i][j + 1] > a[i][j]) { res += 1 + help(a, i, j + 1, n, m, dp); } dp[i][j] = (int) res % 1000000007; return dp[i][j]; } public int countPaths(int[][] grid) { int n = grid.length; int m = grid[0].length; long ans = (long) n * m; int[][] dp = new int[n][m]; for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) { ans += help(grid, i, j, n, m, dp) % 1000000007; } } ans = ans % 1000000007; return (int) ans; } } ############ class Solution { private int m; private int n; private int[][] g; private int[][] f; private static final int MOD = (int) 1e9 + 7; public int countPaths(int[][] grid) { g = grid; m = g.length; n = g[0].length; f = new int[m][n]; int ans = 0; for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i) { for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) { ans = (ans + dfs(i, j)) % MOD; } } return ans; } private int dfs(int i, int j) { if (f[i][j] != 0) { return f[i][j]; } int res = 1; int[] dirs = {-1, 0, 1, 0, -1}; for (int k = 0; k < 4; ++k) { int x = i + dirs[k], y = j + dirs[k + 1]; if (x >= 0 && x < m && y >= 0 && y < n && g[x][y] > g[i][j]) { res = (res + dfs(x, y)) % MOD; } } f[i][j] = res; return res; } } -
class Solution: def countPaths(self, grid: List[List[int]]) -> int: @cache def dfs(i, j): res = 1 for a, b in [[0, -1], [0, 1], [-1, 0], [1, 0]]: x, y = i + a, j + b if 0 <= x < m and 0 <= y < n and grid[x][y] > grid[i][j]: res += dfs(x, y) return res m, n = len(grid), len(grid[0]) mod = 10**9 + 7 return sum(dfs(i, j) for i in range(m) for j in range(n)) % mod ############ # 2328. Number of Increasing Paths in a Grid # https://leetcode.com/problems/number-of-increasing-paths-in-a-grid/ class Solution: def countPaths(self, grid: List[List[int]]) -> int: rows, cols = len(grid), len(grid[0]) res = 0 M = 10 ** 9 + 7 @cache def go(x, y): count = 1 for dx, dy in [(x + 1, y), (x - 1, y), (x, y + 1), (x, y - 1)]: if 0 <= dx < rows and 0 <= dy < cols and grid[dx][dy] > grid[x][y]: count += go(dx, dy) count % M return count % M for x in range(rows): for y in range(cols): res += go(x, y) res % M return res % M -
class Solution { public: const int mod = 1e9 + 7; int countPaths(vector<vector<int>>& grid) { int ans = 0; vector<vector<int>> f(grid.size(), vector<int>(grid[0].size())); for (int i = 0; i < grid.size(); ++i) for (int j = 0; j < grid[0].size(); ++j) ans = (ans + dfs(i, j, f, grid)) % mod; return ans; } int dfs(int i, int j, vector<vector<int>>& f, vector<vector<int>>& g) { if (f[i][j]) return f[i][j]; int res = 1; vector<int> dirs = {-1, 0, 1, 0, -1}; for (int k = 0; k < 4; ++k) { int x = i + dirs[k], y = j + dirs[k + 1]; if (x >= 0 && x < g.size() && y >= 0 && y < g[0].size() && g[x][y] > g[i][j]) res = (res + dfs(x, y, f, g)) % mod; } f[i][j] = res; return res; } }; -
func countPaths(grid [][]int) int { m, n := len(grid), len(grid[0]) f := make([][]int, m) for i := range f { f[i] = make([]int, n) } mod := int(1e9) + 7 ans := 0 dirs := []int{-1, 0, 1, 0, -1} var dfs func(int, int) int dfs = func(i, j int) int { if f[i][j] > 0 { return f[i][j] } res := 1 for k := 0; k < 4; k++ { x, y := i+dirs[k], j+dirs[k+1] if x >= 0 && x < m && y >= 0 && y < n && grid[x][y] > grid[i][j] { res = (res + dfs(x, y)) % mod } } f[i][j] = res return res } for i, row := range grid { for j := range row { ans = (ans + dfs(i, j)) % mod } } return ans } -
function countPaths(grid: number[][]): number { const mod = BigInt(10 ** 9 + 7); const dirs = [ [0, 1], [1, 0], [0, -1], [-1, 0], ]; const m = grid.length, n = grid[0].length; const dp = Array.from({ length: m }, v => new Array(n).fill(-1n)); function dfs(x, y) { if (dp[x][y] != -1) return dp[x][y]; let count = 1n; for (let [dx, dy] of dirs) { let i = x + dx, j = y + dy; if (i < 0 || i >= m || j < 0 || j >= n || grid[i][j] <= grid[x][y]) continue; count = (count + dfs(i, j)) % mod; } dp[x][y] = count; return count; } let sum = 0n; for (let i = 0; i < m; i++) { for (let j = 0; j < n; j++) { sum = (sum + dfs(i, j)) % mod; } } return Number(sum); }
Explain:
nope.
Complexity:
- Time complexity : O(n).
- Space complexity : O(n).