Welcome to Subscribe On Youtube
Formatted question description: https://leetcode.ca/all/2285.html
2285. Maximum Total Importance of Roads
- Difficulty: Medium.
- Related Topics: Greedy, Graph, Sorting, Heap (Priority Queue).
- Similar Questions: .
Problem
You are given an integer n denoting the number of cities in a country. The cities are numbered from 0 to n - 1.
You are also given a 2D integer array roads where roads[i] = [ai, bi] denotes that there exists a bidirectional road connecting cities ai and bi.
You need to assign each city with an integer value from 1 to n, where each value can only be used once. The importance of a road is then defined as the sum of the values of the two cities it connects.
Return the **maximum total importance of all roads possible after assigning the values optimally.**
Example 1:
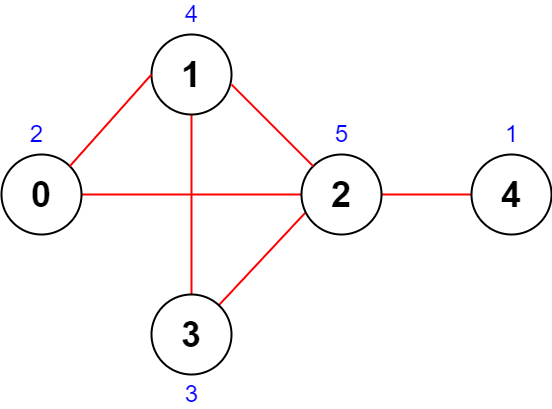
Input: n = 5, roads = [[0,1],[1,2],[2,3],[0,2],[1,3],[2,4]]
Output: 43
Explanation: The figure above shows the country and the assigned values of [2,4,5,3,1].
- The road (0,1) has an importance of 2 + 4 = 6.
- The road (1,2) has an importance of 4 + 5 = 9.
- The road (2,3) has an importance of 5 + 3 = 8.
- The road (0,2) has an importance of 2 + 5 = 7.
- The road (1,3) has an importance of 4 + 3 = 7.
- The road (2,4) has an importance of 5 + 1 = 6.
The total importance of all roads is 6 + 9 + 8 + 7 + 7 + 6 = 43.
It can be shown that we cannot obtain a greater total importance than 43.
Example 2:
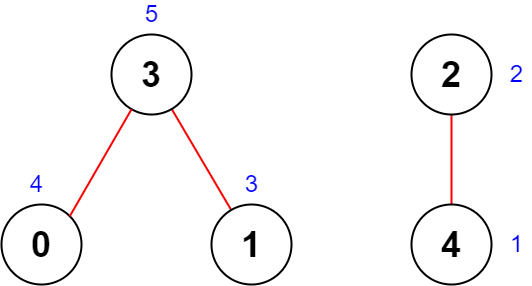
Input: n = 5, roads = [[0,3],[2,4],[1,3]]
Output: 20
Explanation: The figure above shows the country and the assigned values of [4,3,2,5,1].
- The road (0,3) has an importance of 4 + 5 = 9.
- The road (2,4) has an importance of 2 + 1 = 3.
- The road (1,3) has an importance of 3 + 5 = 8.
The total importance of all roads is 9 + 3 + 8 = 20.
It can be shown that we cannot obtain a greater total importance than 20.
Constraints:
-
2 <= n <= 5 * 104 -
1 <= roads.length <= 5 * 104 -
roads[i].length == 2 -
0 <= ai, bi <= n - 1 -
ai != bi -
There are no duplicate roads.
Solution (Java, C++, Python)
-
class Solution { public long maximumImportance(int n, int[][] roads) { int[] degree = new int[n]; int maxdegree = 0; for (int[] r : roads) { degree[r[0]]++; degree[r[1]]++; maxdegree = Math.max(maxdegree, Math.max(degree[r[0]], degree[r[1]])); } Map<Integer, Integer> rank = new HashMap<>(); int i = n; while (i > 0) { for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) { if (degree[j] == maxdegree) { rank.put(j, i--); degree[j] = Integer.MIN_VALUE; } } maxdegree = 0; for (int d : degree) { maxdegree = Math.max(maxdegree, d); } } long res = 0; for (int[] r : roads) { res += rank.get(r[0]) + rank.get(r[1]); } return res; } } ############ class Solution { public long maximumImportance(int n, int[][] roads) { int[] deg = new int[n]; for (int[] r : roads) { ++deg[r[0]]; ++deg[r[1]]; } Arrays.sort(deg); long ans = 0; for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) { ans += (long) (i + 1) * deg[i]; } return ans; } } -
class Solution: def maximumImportance(self, n: int, roads: List[List[int]]) -> int: deg = [0] * n for a, b in roads: deg[a] += 1 deg[b] += 1 deg.sort() return sum(i * v for i, v in enumerate(deg, 1)) ############ # 2285. Maximum Total Importance of Roads # https://leetcode.com/problems/maximum-total-importance-of-roads/ class Solution: def maximumImportance(self, n: int, roads: List[List[int]]) -> int: count = defaultdict(int) for a, b in roads: count[a] += 1 count[b] += 1 scores = defaultdict(int) v = sorted(count.items(), key = lambda x:-x[1]) for k, cnt in v: scores[k] = n n -= 1 res = 0 for a, b in roads: res += scores[a] + scores[b] return res -
class Solution { public: long long maximumImportance(int n, vector<vector<int>>& roads) { vector<int> deg(n); for (auto& r : roads) { ++deg[r[0]]; ++deg[r[1]]; } sort(deg.begin(), deg.end()); long long ans = 0; for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) ans += 1ll * (i + 1) * deg[i]; return ans; } }; -
func maximumImportance(n int, roads [][]int) int64 { deg := make([]int, n) for _, r := range roads { deg[r[0]]++ deg[r[1]]++ } sort.Ints(deg) var ans int64 for i := 0; i < n; i++ { ans += int64((i + 1) * deg[i]) } return ans }
Explain:
nope.
Complexity:
- Time complexity : O(n).
- Space complexity : O(n).