Welcome to Subscribe On Youtube
2385. Amount of Time for Binary Tree to Be Infected
Description
You are given the root of a binary tree with unique values, and an integer start. At minute 0, an infection starts from the node with value start.
Each minute, a node becomes infected if:
- The node is currently uninfected.
- The node is adjacent to an infected node.
Return the number of minutes needed for the entire tree to be infected.
Example 1:
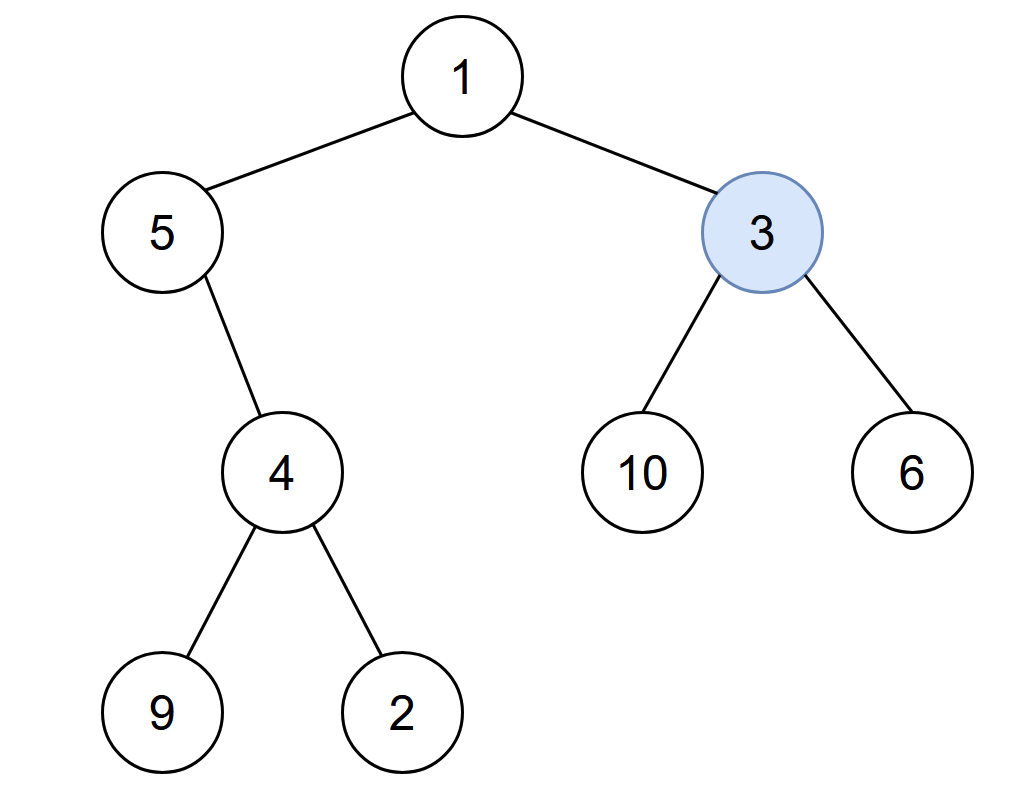
Input: root = [1,5,3,null,4,10,6,9,2], start = 3 Output: 4 Explanation: The following nodes are infected during: - Minute 0: Node 3 - Minute 1: Nodes 1, 10 and 6 - Minute 2: Node 5 - Minute 3: Node 4 - Minute 4: Nodes 9 and 2 It takes 4 minutes for the whole tree to be infected so we return 4.
Example 2:

Input: root = [1], start = 1 Output: 0 Explanation: At minute 0, the only node in the tree is infected so we return 0.
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[1, 105]. 1 <= Node.val <= 105- Each node has a unique value.
- A node with a value of
startexists in the tree.
Solutions
-
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * public class TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode left; * TreeNode right; * TreeNode() {} * TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; } * TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) { * this.val = val; * this.left = left; * this.right = right; * } * } */ class Solution { private Map<Integer, List<Integer>> g = new HashMap<>(); public int amountOfTime(TreeNode root, int start) { dfs(root); Deque<Integer> q = new ArrayDeque<>(); Set<Integer> vis = new HashSet<>(); q.offer(start); int ans = -1; while (!q.isEmpty()) { ++ans; for (int n = q.size(); n > 0; --n) { int i = q.pollFirst(); vis.add(i); if (g.containsKey(i)) { for (int j : g.get(i)) { if (!vis.contains(j)) { q.offer(j); } } } } } return ans; } private void dfs(TreeNode root) { if (root == null) { return; } if (root.left != null) { g.computeIfAbsent(root.val, k -> new ArrayList<>()).add(root.left.val); g.computeIfAbsent(root.left.val, k -> new ArrayList<>()).add(root.val); } if (root.right != null) { g.computeIfAbsent(root.val, k -> new ArrayList<>()).add(root.right.val); g.computeIfAbsent(root.right.val, k -> new ArrayList<>()).add(root.val); } dfs(root.left); dfs(root.right); } } -
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * struct TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode *left; * TreeNode *right; * TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {} * TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {} * TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {} * }; */ class Solution { public: unordered_map<int, vector<int>> g; int amountOfTime(TreeNode* root, int start) { dfs(root); queue<int> q{ {start} }; unordered_set<int> vis; int ans = -1; while (q.size()) { ++ans; for (int n = q.size(); n; --n) { int i = q.front(); q.pop(); vis.insert(i); for (int j : g[i]) { if (!vis.count(j)) { q.push(j); } } } } return ans; } void dfs(TreeNode* root) { if (!root) return; if (root->left) { g[root->val].push_back(root->left->val); g[root->left->val].push_back(root->val); } if (root->right) { g[root->val].push_back(root->right->val); g[root->right->val].push_back(root->val); } dfs(root->left); dfs(root->right); } }; -
# Definition for a binary tree node. # class TreeNode: # def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None): # self.val = val # self.left = left # self.right = right class Solution: def amountOfTime(self, root: Optional[TreeNode], start: int) -> int: def dfs(root): if root is None: return if root.left: g[root.val].append(root.left.val) g[root.left.val].append(root.val) if root.right: g[root.val].append(root.right.val) g[root.right.val].append(root.val) dfs(root.left) dfs(root.right) g = defaultdict(list) dfs(root) vis = set() q = deque([start]) ans = -1 while q: ans += 1 for _ in range(len(q)): i = q.popleft() vis.add(i) for j in g[i]: if j not in vis: q.append(j) return ans -
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * type TreeNode struct { * Val int * Left *TreeNode * Right *TreeNode * } */ func amountOfTime(root *TreeNode, start int) int { g := map[int][]int{} var dfs func(*TreeNode) dfs = func(root *TreeNode) { if root == nil { return } if root.Left != nil { g[root.Val] = append(g[root.Val], root.Left.Val) g[root.Left.Val] = append(g[root.Left.Val], root.Val) } if root.Right != nil { g[root.Val] = append(g[root.Val], root.Right.Val) g[root.Right.Val] = append(g[root.Right.Val], root.Val) } dfs(root.Left) dfs(root.Right) } dfs(root) q := []int{start} ans := -1 vis := map[int]bool{} for len(q) > 0 { ans++ for n := len(q); n > 0; n-- { i := q[0] q = q[1:] vis[i] = true for _, j := range g[i] { if !vis[j] { q = append(q, j) } } } } return ans } -
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * class TreeNode { * val: number * left: TreeNode | null * right: TreeNode | null * constructor(val?: number, left?: TreeNode | null, right?: TreeNode | null) { * this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val) * this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left) * this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right) * } * } */ function amountOfTime(root: TreeNode | null, start: number): number { const map = new Map<number, number[]>(); const create = ({ val, left, right }: TreeNode) => { if (left != null) { map.set(val, [...(map.get(val) ?? []), left.val]); map.set(left.val, [...(map.get(left.val) ?? []), val]); create(left); } if (right != null) { map.set(val, [...(map.get(val) ?? []), right.val]); map.set(right.val, [...(map.get(right.val) ?? []), val]); create(right); } }; create(root); const dfs = (st: number, fa: number) => { let res = 0; for (const v of map.get(st) ?? []) { if (v !== fa) { res = Math.max(res, dfs(v, st) + 1); } } return res; }; return dfs(start, -1); }