Welcome to Subscribe On Youtube
Formatted question description: https://leetcode.ca/all/2265.html
2265. Count Nodes Equal to Average of Subtree
- Difficulty: Medium.
- Related Topics: Tree, Depth-First Search, Binary Tree.
- Similar Questions: Maximum Average Subtree, Insufficient Nodes in Root to Leaf Paths, Count Nodes Equal to Sum of Descendants.
Problem
Given the root of a binary tree, return the number of nodes where the value of the node is equal to the **average of the values in its subtree**.
Note:
-
The average of
nelements is the sum of thenelements divided bynand rounded down to the nearest integer. -
A subtree of
rootis a tree consisting ofrootand all of its descendants.
Example 1:
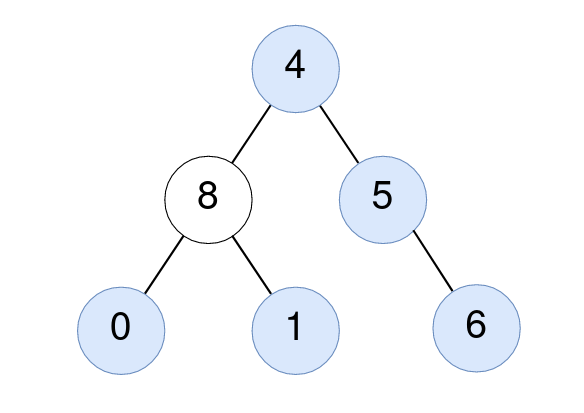
Input: root = [4,8,5,0,1,null,6]
Output: 5
Explanation:
For the node with value 4: The average of its subtree is (4 + 8 + 5 + 0 + 1 + 6) / 6 = 24 / 6 = 4.
For the node with value 5: The average of its subtree is (5 + 6) / 2 = 11 / 2 = 5.
For the node with value 0: The average of its subtree is 0 / 1 = 0.
For the node with value 1: The average of its subtree is 1 / 1 = 1.
For the node with value 6: The average of its subtree is 6 / 1 = 6.
Example 2:

Input: root = [1]
Output: 1
Explanation: For the node with value 1: The average of its subtree is 1 / 1 = 1.
Constraints:
-
The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[1, 1000]. -
0 <= Node.val <= 1000
Solution (Java, C++, Python)
-
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * public class TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode left; * TreeNode right; * TreeNode() {} * TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; } * TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) { * this.val = val; * this.left = left; * this.right = right; * } * } */ class Solution { private int ans = 0; public int averageOfSubtree(TreeNode root) { dfs(root); return ans; } private int[] dfs(TreeNode node) { if (node == null) { return new int[] {0, 0}; } int[] left = dfs(node.left); int[] right = dfs(node.right); int currsum = left[0] + right[0] + node.val; int currcount = left[1] + right[1] + 1; if (currsum / currcount == node.val) { ++ans; } return new int[] {currsum, currcount}; } } ############ /** * Definition for a binary tree node. * public class TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode left; * TreeNode right; * TreeNode() {} * TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; } * TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) { * this.val = val; * this.left = left; * this.right = right; * } * } */ class Solution { private int ans; public int averageOfSubtree(TreeNode root) { ans = 0; dfs(root); return ans; } private int[] dfs(TreeNode root) { if (root == null) { return new int[] {0, 0}; } int[] l = dfs(root.left); int[] r = dfs(root.right); int s = l[0] + r[0] + root.val; int n = l[1] + r[1] + 1; if (s / n == root.val) { ++ans; } return new int[] {s, n}; } } -
# Definition for a binary tree node. # class TreeNode: # def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None): # self.val = val # self.left = left # self.right = right class Solution: def averageOfSubtree(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> int: def dfs(root): if root is None: return 0, 0 ls, ln = dfs(root.left) rs, rn = dfs(root.right) s = ls + rs + root.val n = ln + rn + 1 if s // n == root.val: nonlocal ans ans += 1 return s, n ans = 0 dfs(root) return ans ############ # 2265. Count Nodes Equal to Average of Subtree # https://leetcode.com/problems/count-nodes-equal-to-average-of-subtree/ # Definition for a binary tree node. # class TreeNode: # def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None): # self.val = val # self.left = left # self.right = right class Solution: def averageOfSubtree(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> int: res = 0 def go(node): if not node: return (0, 0) lCount, lValues = go(node.left) rCount, rValues = go(node.right) nodeCount, nodeValues = 1 + lCount + rCount, node.val + lValues + rValues average = nodeValues // nodeCount if node.val == average: nonlocal res res += 1 return (nodeCount, nodeValues) go(root) return res -
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * struct TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode *left; * TreeNode *right; * TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {} * TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {} * TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {} * }; */ class Solution { public: int ans; int averageOfSubtree(TreeNode* root) { ans = 0; dfs(root); return ans; } vector<int> dfs(TreeNode* root) { if (!root) return {0, 0}; auto l = dfs(root->left); auto r = dfs(root->right); int s = l[0] + r[0] + root->val; int n = l[1] + r[1] + 1; if (s / n == root->val) ++ans; return {s, n}; } }; -
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * type TreeNode struct { * Val int * Left *TreeNode * Right *TreeNode * } */ func averageOfSubtree(root *TreeNode) int { ans := 0 var dfs func(*TreeNode) (int, int) dfs = func(root *TreeNode) (int, int) { if root == nil { return 0, 0 } ls, ln := dfs(root.Left) rs, rn := dfs(root.Right) s := ls + rs + root.Val n := ln + rn + 1 if s/n == root.Val { ans++ } return s, n } dfs(root) return ans }
Explain:
nope.
Complexity:
- Time complexity : O(n).
- Space complexity : O(n).