Welcome to Subscribe On Youtube
2316. Count Unreachable Pairs of Nodes in an Undirected Graph
Description
You are given an integer n. There is an undirected graph with n nodes, numbered from 0 to n - 1. You are given a 2D integer array edges where edges[i] = [ai, bi] denotes that there exists an undirected edge connecting nodes ai and bi.
Return the number of pairs of different nodes that are unreachable from each other.
Example 1:
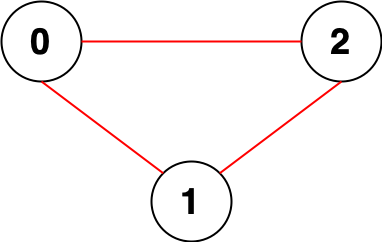
Input: n = 3, edges = [[0,1],[0,2],[1,2]] Output: 0 Explanation: There are no pairs of nodes that are unreachable from each other. Therefore, we return 0.
Example 2:
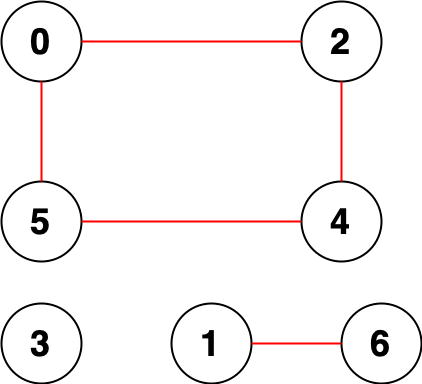
Input: n = 7, edges = [[0,2],[0,5],[2,4],[1,6],[5,4]] Output: 14 Explanation: There are 14 pairs of nodes that are unreachable from each other: [[0,1],[0,3],[0,6],[1,2],[1,3],[1,4],[1,5],[2,3],[2,6],[3,4],[3,5],[3,6],[4,6],[5,6]]. Therefore, we return 14.
Constraints:
1 <= n <= 1050 <= edges.length <= 2 * 105edges[i].length == 20 <= ai, bi < nai != bi- There are no repeated edges.
Solutions
Solution 1: DFS
For any two nodes in an undirected graph, if there is a path between them, then they are mutually reachable.
Therefore, we can use depth-first search to find the number of nodes $t$ in each connected component, and then multiply the current number of nodes $t$ in the connected component by the number of nodes $s$ in all previous connected components to obtain the number of unreachable node pairs in the current connected component, which is $s \times t$. Then, we add $t$ to $s$ and continue to search for the next connected component until all connected components have been searched, and we can obtain the final answer.
The time complexity is $O(n + m)$, and the space complexity is $O(n + m)$. Here, $n$ and $m$ are the number of nodes and edges, respectively.
-
class Solution { private List<Integer>[] g; private boolean[] vis; public long countPairs(int n, int[][] edges) { g = new List[n]; vis = new boolean[n]; Arrays.setAll(g, i -> new ArrayList<>()); for (var e : edges) { int a = e[0], b = e[1]; g[a].add(b); g[b].add(a); } long ans = 0, s = 0; for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) { int t = dfs(i); ans += s * t; s += t; } return ans; } private int dfs(int i) { if (vis[i]) { return 0; } vis[i] = true; int cnt = 1; for (int j : g[i]) { cnt += dfs(j); } return cnt; } } -
class Solution { public: long long countPairs(int n, vector<vector<int>>& edges) { vector<int> g[n]; for (auto& e : edges) { int a = e[0], b = e[1]; g[a].push_back(b); g[b].push_back(a); } bool vis[n]; memset(vis, 0, sizeof(vis)); function<int(int)> dfs = [&](int i) { if (vis[i]) { return 0; } vis[i] = true; int cnt = 1; for (int j : g[i]) { cnt += dfs(j); } return cnt; }; long long ans = 0, s = 0; for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) { int t = dfs(i); ans += s * t; s += t; } return ans; } }; -
class Solution: def countPairs(self, n: int, edges: List[List[int]]) -> int: def dfs(i: int) -> int: if vis[i]: return 0 vis[i] = True return 1 + sum(dfs(j) for j in g[i]) g = [[] for _ in range(n)] for a, b in edges: g[a].append(b) g[b].append(a) vis = [False] * n ans = s = 0 for i in range(n): t = dfs(i) ans += s * t s += t return ans -
func countPairs(n int, edges [][]int) (ans int64) { g := make([][]int, n) for _, e := range edges { a, b := e[0], e[1] g[a] = append(g[a], b) g[b] = append(g[b], a) } vis := make([]bool, n) var dfs func(int) int dfs = func(i int) int { if vis[i] { return 0 } vis[i] = true cnt := 1 for _, j := range g[i] { cnt += dfs(j) } return cnt } var s int64 for i := 0; i < n; i++ { t := int64(dfs(i)) ans += s * t s += t } return } -
function countPairs(n: number, edges: number[][]): number { const g: number[][] = Array.from({ length: n }, () => []); for (const [a, b] of edges) { g[a].push(b); g[b].push(a); } const vis: boolean[] = Array(n).fill(false); const dfs = (i: number): number => { if (vis[i]) { return 0; } vis[i] = true; let cnt = 1; for (const j of g[i]) { cnt += dfs(j); } return cnt; }; let [ans, s] = [0, 0]; for (let i = 0; i < n; ++i) { const t = dfs(i); ans += s * t; s += t; } return ans; } -
impl Solution { pub fn count_pairs(n: i32, edges: Vec<Vec<i32>>) -> i64 { let n = n as usize; let mut g = vec![vec![]; n]; let mut vis = vec![false; n]; for e in edges { let u = e[0] as usize; let v = e[1] as usize; g[u].push(v); g[v].push(u); } fn dfs(g: &Vec<Vec<usize>>, vis: &mut Vec<bool>, u: usize) -> i64 { if vis[u] { return 0; } vis[u] = true; let mut cnt = 1; for &v in &g[u] { cnt += dfs(g, vis, v); } cnt } let mut ans = 0; let mut s = 0; for u in 0..n { let t = dfs(&g, &mut vis, u); ans += t * s; s += t; } ans } }