Welcome to Subscribe On Youtube
2246. Longest Path With Different Adjacent Characters
Description
You are given a tree (i.e. a connected, undirected graph that has no cycles) rooted at node 0 consisting of n nodes numbered from 0 to n - 1. The tree is represented by a 0-indexed array parent of size n, where parent[i] is the parent of node i. Since node 0 is the root, parent[0] == -1.
You are also given a string s of length n, where s[i] is the character assigned to node i.
Return the length of the longest path in the tree such that no pair of adjacent nodes on the path have the same character assigned to them.
Example 1:
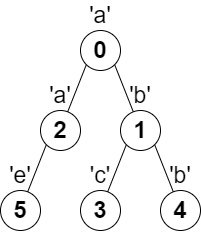
Input: parent = [-1,0,0,1,1,2], s = "abacbe" Output: 3 Explanation: The longest path where each two adjacent nodes have different characters in the tree is the path: 0 -> 1 -> 3. The length of this path is 3, so 3 is returned. It can be proven that there is no longer path that satisfies the conditions.
Example 2:
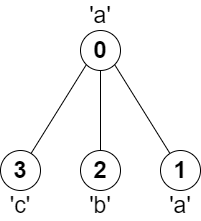
Input: parent = [-1,0,0,0], s = "aabc" Output: 3 Explanation: The longest path where each two adjacent nodes have different characters is the path: 2 -> 0 -> 3. The length of this path is 3, so 3 is returned.
Constraints:
n == parent.length == s.length1 <= n <= 1050 <= parent[i] <= n - 1for alli >= 1parent[0] == -1parentrepresents a valid tree.sconsists of only lowercase English letters.
Solutions
-
class Solution { private List<Integer>[] g; private String s; private int ans; public int longestPath(int[] parent, String s) { int n = parent.length; g = new List[n]; this.s = s; Arrays.setAll(g, k -> new ArrayList<>()); for (int i = 1; i < n; ++i) { g[parent[i]].add(i); } dfs(0); return ans + 1; } private int dfs(int i) { int mx = 0; for (int j : g[i]) { int x = dfs(j) + 1; if (s.charAt(i) != s.charAt(j)) { ans = Math.max(ans, mx + x); mx = Math.max(mx, x); } } return mx; } } -
class Solution { public: int longestPath(vector<int>& parent, string s) { int n = parent.size(); vector<int> g[n]; for (int i = 1; i < n; ++i) { g[parent[i]].push_back(i); } int ans = 0; function<int(int)> dfs = [&](int i) -> int { int mx = 0; for (int j : g[i]) { int x = dfs(j) + 1; if (s[i] != s[j]) { ans = max(ans, mx + x); mx = max(mx, x); } } return mx; }; dfs(0); return ans + 1; } }; -
class Solution: def longestPath(self, parent: List[int], s: str) -> int: def dfs(i: int) -> int: mx = 0 nonlocal ans for j in g[i]: x = dfs(j) + 1 if s[i] != s[j]: ans = max(ans, mx + x) mx = max(mx, x) return mx g = defaultdict(list) for i in range(1, len(parent)): g[parent[i]].append(i) ans = 0 dfs(0) return ans + 1 -
func longestPath(parent []int, s string) int { n := len(parent) g := make([][]int, n) for i := 1; i < n; i++ { g[parent[i]] = append(g[parent[i]], i) } ans := 0 var dfs func(int) int dfs = func(i int) int { mx := 0 for _, j := range g[i] { x := dfs(j) + 1 if s[i] != s[j] { ans = max(ans, x+mx) mx = max(mx, x) } } return mx } dfs(0) return ans + 1 } -
function longestPath(parent: number[], s: string): number { const n = parent.length; const g: number[][] = Array.from({ length: n }, () => []); for (let i = 1; i < n; ++i) { g[parent[i]].push(i); } let ans = 0; const dfs = (i: number): number => { let mx = 0; for (const j of g[i]) { const x = dfs(j) + 1; if (s[i] !== s[j]) { ans = Math.max(ans, mx + x); mx = Math.max(mx, x); } } return mx; }; dfs(0); return ans + 1; }