Welcome to Subscribe On Youtube
2218. Maximum Value of K Coins From Piles
Description
There are n piles of coins on a table. Each pile consists of a positive number of coins of assorted denominations.
In one move, you can choose any coin on top of any pile, remove it, and add it to your wallet.
Given a list piles, where piles[i] is a list of integers denoting the composition of the ith pile from top to bottom, and a positive integer k, return the maximum total value of coins you can have in your wallet if you choose exactly k coins optimally.
Example 1:
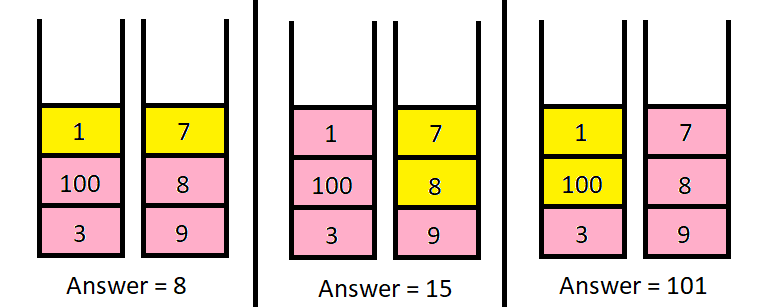
Input: piles = [[1,100,3],[7,8,9]], k = 2 Output: 101 Explanation: The above diagram shows the different ways we can choose k coins. The maximum total we can obtain is 101.
Example 2:
Input: piles = [[100],[100],[100],[100],[100],[100],[1,1,1,1,1,1,700]], k = 7 Output: 706 Explanation: The maximum total can be obtained if we choose all coins from the last pile.
Constraints:
n == piles.length1 <= n <= 10001 <= piles[i][j] <= 1051 <= k <= sum(piles[i].length) <= 2000
Solutions
-
class Solution { public int maxValueOfCoins(List<List<Integer>> piles, int k) { int n = piles.size(); List<int[]> presum = new ArrayList<>(); for (List<Integer> p : piles) { int m = p.size(); int[] s = new int[m + 1]; for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i) { s[i + 1] = s[i] + p.get(i); } presum.add(s); } int[] dp = new int[k + 1]; for (int[] s : presum) { for (int j = k; j >= 0; --j) { for (int idx = 0; idx < s.length; ++idx) { if (j >= idx) { dp[j] = Math.max(dp[j], dp[j - idx] + s[idx]); } } } } return dp[k]; } } -
class Solution { public: int maxValueOfCoins(vector<vector<int>>& piles, int k) { vector<vector<int>> presum; for (auto& p : piles) { int m = p.size(); vector<int> s(m + 1); for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i) s[i + 1] = s[i] + p[i]; presum.push_back(s); } vector<int> dp(k + 1); for (auto& s : presum) { for (int j = k; ~j; --j) { for (int idx = 0; idx < s.size(); ++idx) { if (j >= idx) dp[j] = max(dp[j], dp[j - idx] + s[idx]); } } } return dp[k]; } }; -
class Solution: def maxValueOfCoins(self, piles: List[List[int]], k: int) -> int: presum = [list(accumulate(p, initial=0)) for p in piles] n = len(piles) dp = [[0] * (k + 1) for _ in range(n + 1)] for i, s in enumerate(presum, 1): for j in range(k + 1): for idx, v in enumerate(s): if j >= idx: dp[i][j] = max(dp[i][j], dp[i - 1][j - idx] + v) return dp[-1][-1] -
func maxValueOfCoins(piles [][]int, k int) int { var presum [][]int for _, p := range piles { m := len(p) s := make([]int, m+1) for i, v := range p { s[i+1] = s[i] + v } presum = append(presum, s) } dp := make([]int, k+1) for _, s := range presum { for j := k; j >= 0; j-- { for idx, v := range s { if j >= idx { dp[j] = max(dp[j], dp[j-idx]+v) } } } } return dp[k] } -
function maxValueOfCoins(piles: number[][], k: number): number { const n = piles.length; const f: number[][] = Array.from({ length: n + 1 }, () => Array(k + 1).fill(0)); for (let i = 1; i <= n; i++) { const nums = piles[i - 1]; const s = Array(nums.length + 1).fill(0); for (let j = 1; j <= nums.length; j++) { s[j] = s[j - 1] + nums[j - 1]; } for (let j = 0; j <= k; j++) { for (let h = 0; h < s.length && h <= j; h++) { f[i][j] = Math.max(f[i][j], f[i - 1][j - h] + s[h]); } } } return f[n][k]; }