Welcome to Subscribe On Youtube
Formatted question description: https://leetcode.ca/all/2096.html
2096. Step-By-Step Directions From a Binary Tree Node to Another (Medium)
You are given the root of a binary tree with n nodes. Each node is uniquely assigned a value from 1 to n. You are also given an integer startValue representing the value of the start node s, and a different integer destValue representing the value of the destination node t.
Find the shortest path starting from node s and ending at node t. Generate step-by-step directions of such path as a string consisting of only the uppercase letters 'L', 'R', and 'U'. Each letter indicates a specific direction:
'L'means to go from a node to its left child node.'R'means to go from a node to its right child node.'U'means to go from a node to its parent node.
Return the step-by-step directions of the shortest path from node s to node t.
Example 1:
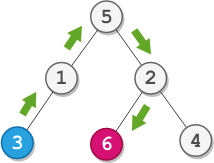
Input: root = [5,1,2,3,null,6,4], startValue = 3, destValue = 6 Output: "UURL" Explanation: The shortest path is: 3 → 1 → 5 → 2 → 6.
Example 2:
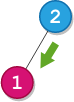
Input: root = [2,1], startValue = 2, destValue = 1 Output: "L" Explanation: The shortest path is: 2 → 1.
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is
n. 2 <= n <= 1051 <= Node.val <= n- All the values in the tree are unique.
1 <= startValue, destValue <= nstartValue != destValue
Companies:
Google
Related Topics:
String, Tree, Depth-First Search, Binary Tree
Similar Questions:
- Path Sum II (Medium)
- Lowest Common Ancestor of a Binary Tree (Medium)
- Binary Tree Paths (Easy)
- Find Distance in a Binary Tree (Medium)
Solution 1. DFS
// OJ: https://leetcode.com/problems/step-by-step-directions-from-a-binary-tree-node-to-another/
// Time: O(N)
// Space: O(H)
class Solution {
public:
string getDirections(TreeNode* root, int s, int d) {
bool sm = false, dm = false; // `sm` = source node met
int cnt = 0;
string ans;
function<void(TreeNode*, bool)> dfs = [&](TreeNode *root, bool isLeftChild) {
if (cnt == 2 || !root) return; // If we've seen both nodes or the current node is NULL, skip
int init = cnt;
if (sm) ans += isLeftChild ? "L" : "R";
else if (dm) ans += "U";
if (root->val == s) {
sm = true;
++cnt;
} else if (root->val == d) {
dm = true;
++cnt;
}
dfs(root->left, true);
dfs(root->right, false);
// When backtracking
if (init == 0 && cnt == 1) { // If we met the first node
if (sm) ans += "U"; // If it's source, add `U`
else ans += isLeftChild ? "L" : "R"; // If it's dest, add `L/R`
} else if (cnt == init && ans.size()) ans.pop_back(); // If the `cnt` doesn't change, the operation we did for this node is not useful.
};
dfs(root, false);
if (ans.back() == 'U') reverse(begin(ans), end(ans));
return ans;
}
};
Solution 2. DFS
// OJ: https://leetcode.com/problems/step-by-step-directions-from-a-binary-tree-node-to-another/
// Time: O(N)
// Space: O(H)
class Solution {
bool getPath(TreeNode *root, int val, string &ans) {
if (!root) return false;
if (root->val == val) return true;
ans += 'L';
if (getPath(root->left, val, ans)) return true;
ans.back() = 'R';
if (getPath(root->right, val, ans)) return true;
ans.pop_back();
return false;
}
public:
string getDirections(TreeNode* root, int s, int d) {
string a, b;
getPath(root, s, a);
getPath(root, d, b);
int i = 0;
while (i < a.size() && i < b.size() && a[i] == b[i]) ++i;
return string(a.size() - i, 'U') + b.substr(i);
}
};