Welcome to Subscribe On Youtube
Formatted question description: https://leetcode.ca/all/2054.html
2054. Two Best Non-Overlapping Events (Medium)
You are given a 0-indexed 2D integer array of events where events[i] = [startTimei, endTimei, valuei]. The ith event starts at startTimei and ends at endTimei, and if you attend this event, you will receive a value of valuei. You can choose at most two non-overlapping events to attend such that the sum of their values is maximized.
Return this maximum sum.
Note that the start time and end time is inclusive: that is, you cannot attend two events where one of them starts and the other ends at the same time. More specifically, if you attend an event with end time t, the next event must start at or after t + 1.
Example 1:
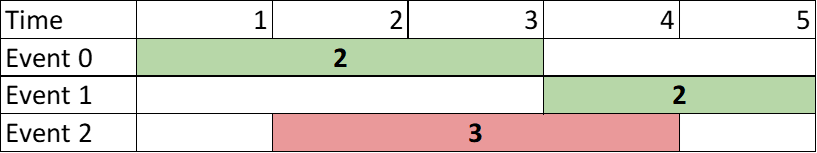
Input: events = [[1,3,2],[4,5,2],[2,4,3]] Output: 4 Explanation: Choose the green events, 0 and 1 for a sum of 2 + 2 = 4.
Example 2:
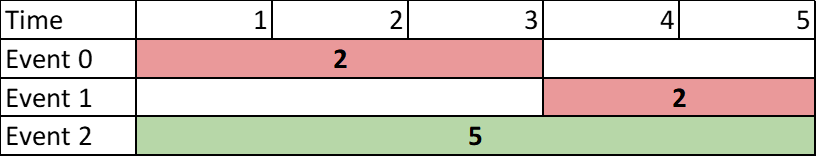
Input: events = [[1,3,2],[4,5,2],[1,5,5]] Output: 5 Explanation: Choose event 2 for a sum of 5.
Example 3:

Input: events = [[1,5,3],[1,5,1],[6,6,5]] Output: 8 Explanation: Choose events 0 and 2 for a sum of 3 + 5 = 8.
Constraints:
2 <= events.length <= 105events[i].length == 31 <= startTimei <= endTimei <= 1091 <= valuei <= 106
Companies:
razorpay
Related Topics:
Array, Binary Search, Dynamic Programming, Sorting, Heap (Priority Queue)
Similar Questions:
Solution 1. Mono-stack
// OJ: https://leetcode.com/problems/two-best-non-overlapping-events/
// Time: O(NlogN)
// Space: O(N)
class Solution {
public:
int maxTwoEvents(vector<vector<int>>& A) {
sort(begin(A), end(A));
int N = A.size(), ans = 0, mx = 0;
stack<pair<int, int>> s; // startTime, val
for (int i = N - 1; i >= 0; --i) {
if (s.empty() || s.top().second < A[i][2]) s.emplace(A[i][0], A[i][2]);
ans = max(ans, A[i][2]);
}
sort(begin(A), end(A), [](auto &a, auto &b) { return a[1] < b[1]; });
for (int i = 0; i < N && s.size(); ++i) {
while (s.size() && s.top().first <= A[i][1]) s.pop();
mx = max(mx, A[i][2]);
if (s.size()) ans = max(ans, mx + s.top().second);
}
return ans;
}
};
Solution 2. Map + Binary Search
// OJ: https://leetcode.com/problems/two-best-non-overlapping-events/
// Time: O(NlogN)
// Space: O(N)
class Solution {
public:
int maxTwoEvents(vector<vector<int>>& A) {
sort(begin(A), end(A));
int N = A.size(), ans = 0;
map<int, int> m;
for (int i = N - 1, mx = 0; i >= 0; --i) {
m[A[i][0]] = (mx = max(mx, A[i][2]));
ans = max(ans, A[i][2]);
}
sort(begin(A), end(A), [](auto &a, auto &b) { return a[1] < b[1]; });
for (int i = 0, mx = 0; i < N; ++i) {
mx = max(mx, A[i][2]);
auto it = m.upper_bound(A[i][1]);
if (it != m.end()) ans = max(ans, mx + it->second);
}
return ans;
}
};
Solution 3. Map + Binary Search
// OJ: https://leetcode.com/problems/two-best-non-overlapping-events/
// Time: O(NlogN)
// Space: O(N)
class Solution {
public:
int maxTwoEvents(vector<vector<int>>& A) {
sort(begin(A), end(A));
int N = A.size(), ans = 0, mx = 0;
map<int, int> m; // startTime -> maxVal
for (int i = N - 1; i >= 0; --i) {
mx = max(mx, A[i][2]);
auto it = m.upper_bound(A[i][1]);
if (it != m.end()) ans = max(ans, A[i][2] + it->second);
m[A[i][0]] = mx;
}
return max(ans, mx);
}
};
Solution 4. Line Sweep
// OJ: https://leetcode.com/problems/two-best-non-overlapping-events/
// Time: O(NlogN)
// Space: O(N)
// Ref: https://leetcode.com/problems/two-best-non-overlapping-events/discuss/1552570/Very-Simple-sort-%2B-greedy%3A-No-DP-no-Binary-Search-no-HeapPQBST
class Solution {
public:
int maxTwoEvents(vector<vector<int>>& A) {
vector<array<int, 3>> B; // time, isStart, value
for (auto &e : A) {
B.push_back({ e[0], 1, e[2] });
B.push_back({ e[1] + 1, 0, e[2] });
}
sort(begin(B), end(B));
int ans = 0, maxEndValue = 0;
for (auto &[time, isStart, value] : B) {
if (isStart) ans = max(ans, value + maxEndValue);
else maxEndValue = max(maxEndValue, value);
}
return ans;
}
};