Welcome to Subscribe On Youtube
Formatted question description: https://leetcode.ca/all/2035.html
2035. Partition Array Into Two Arrays to Minimize Sum Difference (Hard)
You are given an integer array nums of 2 * n integers. You need to partition nums into two arrays of length n to minimize the absolute difference of the sums of the arrays. To partition nums, put each element of nums into one of the two arrays.
Return the minimum possible absolute difference.
Example 1:
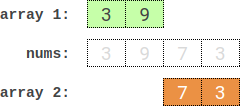
Input: nums = [3,9,7,3] Output: 2 Explanation: One optimal partition is: [3,9] and [7,3]. The absolute difference between the sums of the arrays is abs((3 + 9) - (7 + 3)) = 2.
Example 2:
Input: nums = [-36,36] Output: 72 Explanation: One optimal partition is: [-36] and [36]. The absolute difference between the sums of the arrays is abs((-36) - (36)) = 72.
Example 3:
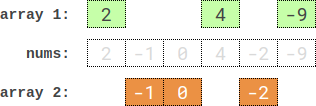
Input: nums = [2,-1,0,4,-2,-9] Output: 0 Explanation: One optimal partition is: [2,4,-9] and [-1,0,-2]. The absolute difference between the sums of the arrays is abs((2 + 4 + -9) - (-1 + 0 + -2)) = 0.
Constraints:
1 <= n <= 15nums.length == 2 * n-107 <= nums[i] <= 107
Similar Questions:
- Partition Equal Subset Sum (Medium)
- Split Array With Same Average (Hard)
- Tallest Billboard (Hard)
- Last Stone Weight II (Medium)
- Closest Subsequence Sum (Hard)
Solution 1. Meet in the Middle
We select k elements from the first half (left part) whose sum is a and N - k elements from the right part whose sum is b. These total N elements have sum a + b, and the complement N elements have sum sum(A) - a - b. Since we want to minimize abs(a + b - (sum(A) - a - b)) = abs(sum(A) - 2 * (a + b)), for a given a, the optimal b = (sum(A) - 2 * a) / 2.
We can enumerate each possible a of a left subset of size k, and binary search the closest value to the optimal b of a right subset of size N - k.
// OJ: https://leetcode.com/problems/partition-array-into-two-arrays-to-minimize-sum-difference/
// Time: O(2^N * N)
// Space: O(2^N)
class Solution {
public:
int minimumDifference(vector<int>& A) {
int N = A.size() / 2, sum = accumulate(begin(A), end(A), 0);
vector<vector<int>> left(N + 1), right(N + 1); // left[k] is an array of all sums of left subsets of size `k`.
for (int mask = 0; mask < 1 << N; ++mask) { // fill all the left and right sum arrays
int k = __builtin_popcount(mask), L = 0, R = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < N; ++i) {
if (mask >> i & 1) {
L += A[i];
R += A[i + N];
}
}
left[k].push_back(L);
right[k].push_back(R);
}
for (int k = 0; k <= N; ++k) sort(begin(right[k]), end(right[k])); // sort right[k] for binsary search
int ans = min(abs(sum - 2 * left[N][0]), abs(sum - 2 * right[N][0])); // If we pick all N elements from first half or second half
for (int k = 1; k <= N; ++k) {
auto &v = right[N - k];
for (int a : left[k]) {
int b = (sum - 2 * a) / 2;
auto it = lower_bound(begin(v), end(v), b);
if (it != end(v)) ans = min(ans, abs(sum - 2 * (a + *it)));
if (it != begin(v)) ans = min(ans, abs(sum - 2 * (a + *prev(it))));
}
}
return ans;
}
};
NOTE
Similar to 1755. Closest Subsequence Sum (Hard)