Welcome to Subscribe On Youtube
2146. K Highest Ranked Items Within a Price Range
Description
You are given a 0-indexed 2D integer array grid of size m x n that represents a map of the items in a shop. The integers in the grid represent the following:
0represents a wall that you cannot pass through.1represents an empty cell that you can freely move to and from.- All other positive integers represent the price of an item in that cell. You may also freely move to and from these item cells.
It takes 1 step to travel between adjacent grid cells.
You are also given integer arrays pricing and start where pricing = [low, high] and start = [row, col] indicates that you start at the position (row, col) and are interested only in items with a price in the range of [low, high] (inclusive). You are further given an integer k.
You are interested in the positions of the k highest-ranked items whose prices are within the given price range. The rank is determined by the first of these criteria that is different:
- Distance, defined as the length of the shortest path from the
start(shorter distance has a higher rank). - Price (lower price has a higher rank, but it must be in the price range).
- The row number (smaller row number has a higher rank).
- The column number (smaller column number has a higher rank).
Return the k highest-ranked items within the price range sorted by their rank (highest to lowest). If there are fewer than k reachable items within the price range, return all of them.
Example 1:
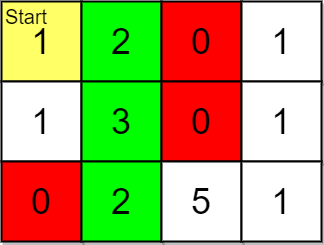
Input: grid = [[1,2,0,1],[1,3,0,1],[0,2,5,1]], pricing = [2,5], start = [0,0], k = 3 Output: [[0,1],[1,1],[2,1]] Explanation: You start at (0,0). With a price range of [2,5], we can take items from (0,1), (1,1), (2,1) and (2,2). The ranks of these items are: - (0,1) with distance 1 - (1,1) with distance 2 - (2,1) with distance 3 - (2,2) with distance 4 Thus, the 3 highest ranked items in the price range are (0,1), (1,1), and (2,1).
Example 2:
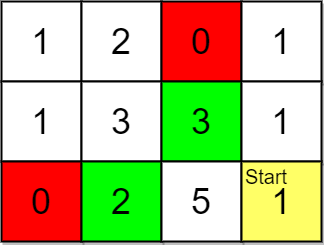
Input: grid = [[1,2,0,1],[1,3,3,1],[0,2,5,1]], pricing = [2,3], start = [2,3], k = 2 Output: [[2,1],[1,2]] Explanation: You start at (2,3). With a price range of [2,3], we can take items from (0,1), (1,1), (1,2) and (2,1). The ranks of these items are: - (2,1) with distance 2, price 2 - (1,2) with distance 2, price 3 - (1,1) with distance 3 - (0,1) with distance 4 Thus, the 2 highest ranked items in the price range are (2,1) and (1,2).
Example 3:
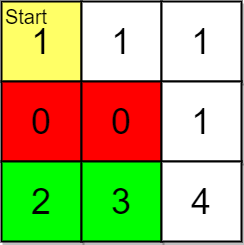
Input: grid = [[1,1,1],[0,0,1],[2,3,4]], pricing = [2,3], start = [0,0], k = 3 Output: [[2,1],[2,0]] Explanation: You start at (0,0). With a price range of [2,3], we can take items from (2,0) and (2,1). The ranks of these items are: - (2,1) with distance 5 - (2,0) with distance 6 Thus, the 2 highest ranked items in the price range are (2,1) and (2,0). Note that k = 3 but there are only 2 reachable items within the price range.
Constraints:
m == grid.lengthn == grid[i].length1 <= m, n <= 1051 <= m * n <= 1050 <= grid[i][j] <= 105pricing.length == 22 <= low <= high <= 105start.length == 20 <= row <= m - 10 <= col <= n - 1grid[row][col] > 01 <= k <= m * n
Solutions
BFS.
-
class Solution { public List<List<Integer>> highestRankedKItems( int[][] grid, int[] pricing, int[] start, int k) { int m = grid.length, n = grid[0].length; int row = start[0], col = start[1]; int low = pricing[0], high = pricing[1]; List<int[]> items = new ArrayList<>(); if (low <= grid[row][col] && grid[row][col] <= high) { items.add(new int[] {0, grid[row][col], row, col}); } grid[row][col] = 0; Deque<int[]> q = new ArrayDeque<>(); q.offer(new int[] {row, col, 0}); int[] dirs = {-1, 0, 1, 0, -1}; while (!q.isEmpty()) { int[] p = q.poll(); int i = p[0], j = p[1], d = p[2]; for (int l = 0; l < 4; ++l) { int x = i + dirs[l], y = j + dirs[l + 1]; if (x >= 0 && x < m && y >= 0 && y < n && grid[x][y] > 0) { if (low <= grid[x][y] && grid[x][y] <= high) { items.add(new int[] {d + 1, grid[x][y], x, y}); } grid[x][y] = 0; q.offer(new int[] {x, y, d + 1}); } } } items.sort((a, b) -> { if (a[0] != b[0]) { return a[0] - b[0]; } if (a[1] != b[1]) { return a[1] - b[1]; } if (a[2] != b[2]) { return a[2] - b[2]; } return a[3] - b[3]; }); List<List<Integer>> ans = new ArrayList<>(); for (int i = 0; i < items.size() && i < k; ++i) { int[] p = items.get(i); ans.add(Arrays.asList(p[2], p[3])); } return ans; } } -
class Solution { public: vector<vector<int>> highestRankedKItems(vector<vector<int>>& grid, vector<int>& pricing, vector<int>& start, int k) { int m = grid.size(), n = grid[0].size(); int row = start[0], col = start[1]; int low = pricing[0], high = pricing[1]; vector<tuple<int, int, int, int>> items; if (low <= grid[row][col] && grid[row][col] <= high) items.emplace_back(0, grid[row][col], row, col); queue<tuple<int, int, int>> q; q.emplace(row, col, 0); grid[row][col] = 0; vector<int> dirs = {-1, 0, 1, 0, -1}; while (!q.empty()) { auto [i, j, d] = q.front(); q.pop(); for (int l = 0; l < 4; ++l) { int x = i + dirs[l], y = j + dirs[l + 1]; if (x >= 0 && x < m && y >= 0 && y < n && grid[x][y]) { if (low <= grid[x][y] && grid[x][y] <= high) items.emplace_back(d + 1, grid[x][y], x, y); grid[x][y] = 0; q.emplace(x, y, d + 1); } } } sort(items.begin(), items.end()); vector<vector<int>> ans; for (int i = 0; i < items.size() && i < k; ++i) { auto [d, p, x, y] = items[i]; ans.push_back({x, y}); } return ans; } }; -
class Solution: def highestRankedKItems( self, grid: List[List[int]], pricing: List[int], start: List[int], k: int ) -> List[List[int]]: m, n = len(grid), len(grid[0]) row, col, low, high = start + pricing items = [] if low <= grid[row][col] <= high: items.append([0, grid[row][col], row, col]) q = deque([(row, col, 0)]) grid[row][col] = 0 while q: i, j, d = q.popleft() for a, b in [[0, 1], [0, -1], [1, 0], [-1, 0]]: x, y = i + a, j + b if 0 <= x < m and 0 <= y < n and grid[x][y]: if low <= grid[x][y] <= high: items.append([d + 1, grid[x][y], x, y]) q.append((x, y, d + 1)) grid[x][y] = 0 items.sort() return [item[2:] for item in items][:k] -
func highestRankedKItems(grid [][]int, pricing []int, start []int, k int) [][]int { m, n := len(grid), len(grid[0]) row, col := start[0], start[1] low, high := pricing[0], pricing[1] var items [][]int if low <= grid[row][col] && grid[row][col] <= high { items = append(items, []int{0, grid[row][col], row, col}) } q := [][]int{ {row, col, 0} } grid[row][col] = 0 dirs := []int{-1, 0, 1, 0, -1} for len(q) > 0 { p := q[0] q = q[1:] i, j, d := p[0], p[1], p[2] for l := 0; l < 4; l++ { x, y := i+dirs[l], j+dirs[l+1] if x >= 0 && x < m && y >= 0 && y < n && grid[x][y] > 0 { if low <= grid[x][y] && grid[x][y] <= high { items = append(items, []int{d + 1, grid[x][y], x, y}) } grid[x][y] = 0 q = append(q, []int{x, y, d + 1}) } } } sort.Slice(items, func(i, j int) bool { a, b := items[i], items[j] if a[0] != b[0] { return a[0] < b[0] } if a[1] != b[1] { return a[1] < b[1] } if a[2] != b[2] { return a[2] < b[2] } return a[3] < b[3] }) var ans [][]int for i := 0; i < len(items) && i < k; i++ { ans = append(ans, items[i][2:]) } return ans } -
function highestRankedKItems( grid: number[][], pricing: number[], start: number[], k: number, ): number[][] { const [m, n] = [grid.length, grid[0].length]; const [row, col] = start; const [low, high] = pricing; let q: [number, number][] = [[row, col]]; const pq: [number, number, number, number][] = []; if (low <= grid[row][col] && grid[row][col] <= high) { pq.push([0, grid[row][col], row, col]); } grid[row][col] = 0; const dirs = [-1, 0, 1, 0, -1]; for (let step = 1; q.length > 0; ++step) { const nq: [number, number][] = []; for (const [x, y] of q) { for (let j = 0; j < 4; j++) { const nx = x + dirs[j]; const ny = y + dirs[j + 1]; if (nx >= 0 && nx < m && ny >= 0 && ny < n && grid[nx][ny] > 0) { if (low <= grid[nx][ny] && grid[nx][ny] <= high) { pq.push([step, grid[nx][ny], nx, ny]); } grid[nx][ny] = 0; nq.push([nx, ny]); } } } q = nq; } pq.sort((a, b) => { if (a[0] !== b[0]) return a[0] - b[0]; if (a[1] !== b[1]) return a[1] - b[1]; if (a[2] !== b[2]) return a[2] - b[2]; return a[3] - b[3]; }); const ans: number[][] = []; for (let i = 0; i < Math.min(k, pq.length); i++) { ans.push([pq[i][2], pq[i][3]]); } return ans; }