Welcome to Subscribe On Youtube
2133. Check if Every Row and Column Contains All Numbers
Description
An n x n matrix is valid if every row and every column contains all the integers from 1 to n (inclusive).
Given an n x n integer matrix matrix, return true if the matrix is valid. Otherwise, return false.
Example 1:
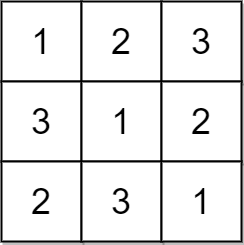
Input: matrix = [[1,2,3],[3,1,2],[2,3,1]] Output: true Explanation: In this case, n = 3, and every row and column contains the numbers 1, 2, and 3. Hence, we return true.
Example 2:
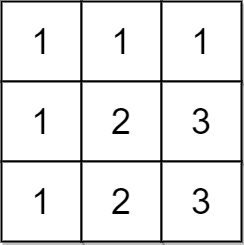
Input: matrix = [[1,1,1],[1,2,3],[1,2,3]] Output: false Explanation: In this case, n = 3, but the first row and the first column do not contain the numbers 2 or 3. Hence, we return false.
Constraints:
n == matrix.length == matrix[i].length1 <= n <= 1001 <= matrix[i][j] <= n
Solutions
-
class Solution { public boolean checkValid(int[][] matrix) { int n = matrix.length; for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) { boolean[] seen = new boolean[n]; for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) { int v = matrix[i][j] - 1; if (seen[v]) { return false; } seen[v] = true; } } for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) { boolean[] seen = new boolean[n]; for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) { int v = matrix[i][j] - 1; if (seen[v]) { return false; } seen[v] = true; } } return true; } } -
class Solution { public: bool checkValid(vector<vector<int>>& matrix) { int n = matrix.size(); for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) { vector<bool> seen(n); for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) { int v = matrix[i][j] - 1; if (seen[v]) return false; seen[v] = true; } } for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) { vector<bool> seen(n); for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) { int v = matrix[i][j] - 1; if (seen[v]) return false; seen[v] = true; } } return true; } }; -
class Solution: def checkValid(self, matrix: List[List[int]]) -> bool: n = len(matrix) for i in range(n): seen = [False] * n for j in range(n): v = matrix[i][j] - 1 if seen[v]: return False seen[v] = True for j in range(n): seen = [False] * n for i in range(n): v = matrix[i][j] - 1 if seen[v]: return False seen[v] = True return True -
func checkValid(matrix [][]int) bool { n := len(matrix) for i := 0; i < n; i++ { seen := make([]bool, n) for j := 0; j < n; j++ { v := matrix[i][j] - 1 if seen[v] { return false } seen[v] = true } } for j := 0; j < n; j++ { seen := make([]bool, n) for i := 0; i < n; i++ { v := matrix[i][j] - 1 if seen[v] { return false } seen[v] = true } } return true } -
function checkValid(matrix: number[][]): boolean { const n = matrix.length; let rows = Array.from({ length: n }, () => new Array(n).fill(false)); let cols = Array.from({ length: n }, () => new Array(n).fill(false)); for (let i = 0; i < n; i++) { for (let j = 0; j < n; j++) { let cur = matrix[i][j]; if (rows[i][cur] || cols[j][cur]) return false; rows[i][cur] = true; cols[j][cur] = true; } } return true; }