Welcome to Subscribe On Youtube
2123. Minimum Operations to Remove Adjacent Ones in Matrix
Description
You are given a 0-indexed binary matrix grid. In one operation, you can flip any 1 in grid to be 0.
A binary matrix is well-isolated if there is no 1 in the matrix that is 4-directionally connected (i.e., horizontal and vertical) to another 1.
Return the minimum number of operations to make grid well-isolated.
Example 1:
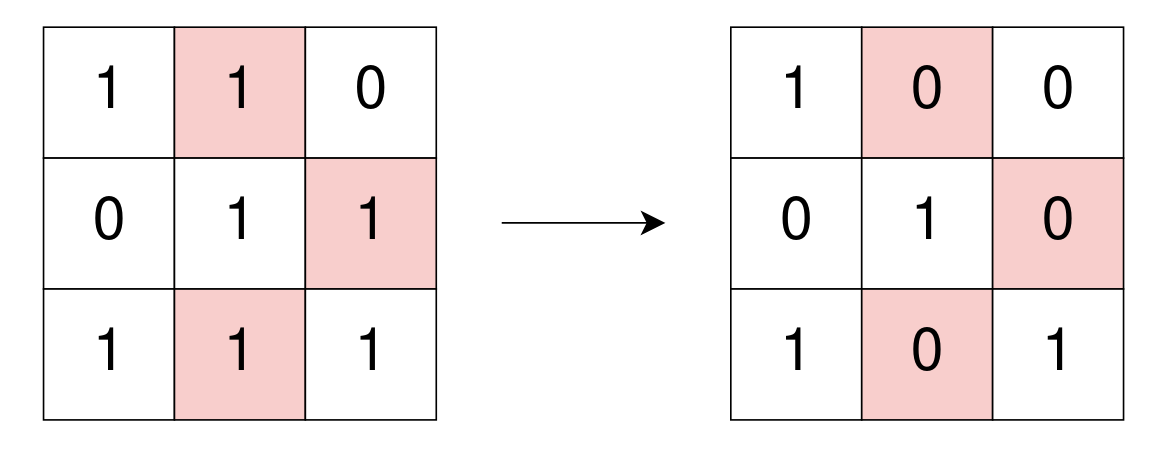
Input: grid = [[1,1,0],[0,1,1],[1,1,1]] Output: 3 Explanation: Use 3 operations to change grid[0][1], grid[1][2], and grid[2][1] to 0. After, no more 1's are 4-directionally connected and grid is well-isolated.
Example 2:
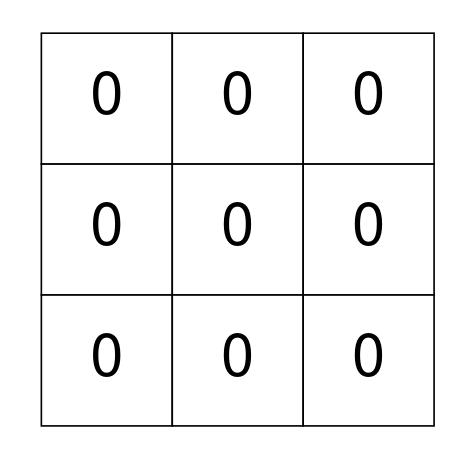
Input: grid = [[0,0,0],[0,0,0],[0,0,0]] Output: 0 Explanation: There are no 1's in grid and it is well-isolated. No operations were done so return 0.
Example 3:
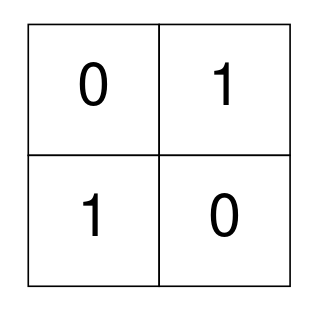
Input: grid = [[0,1],[1,0]] Output: 0 Explanation: None of the 1's are 4-directionally connected and grid is well-isolated. No operations were done so return 0.
Constraints:
m == grid.lengthn == grid[i].length1 <= m, n <= 300grid[i][j]is either0or1.
Solutions
-
class Solution { private Map<Integer, List<Integer>> g = new HashMap<>(); private Set<Integer> vis = new HashSet<>(); private int[] match; public int minimumOperations(int[][] grid) { int m = grid.length, n = grid[0].length; for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i) { for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) { if ((i + j) % 2 == 1 && grid[i][j] == 1) { int x = i * n + j; if (i < m - 1 && grid[i + 1][j] == 1) { g.computeIfAbsent(x, z -> new ArrayList<>()).add(x + n); } if (i > 0 && grid[i - 1][j] == 1) { g.computeIfAbsent(x, z -> new ArrayList<>()).add(x - n); } if (j < n - 1 && grid[i][j + 1] == 1) { g.computeIfAbsent(x, z -> new ArrayList<>()).add(x + 1); } if (j > 0 && grid[i][j - 1] == 1) { g.computeIfAbsent(x, z -> new ArrayList<>()).add(x - 1); } } } } match = new int[m * n]; Arrays.fill(match, -1); int ans = 0; for (int i : g.keySet()) { ans += find(i); vis.clear(); } return ans; } private int find(int i) { for (int j : g.get(i)) { if (vis.add(j)) { if (match[j] == -1 || find(match[j]) == 1) { match[j] = i; return 1; } } } return 0; } } -
class Solution { public: int minimumOperations(vector<vector<int>>& grid) { int m = grid.size(), n = grid[0].size(); vector<int> match(m * n, -1); unordered_set<int> vis; unordered_map<int, vector<int>> g; for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i) { for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) { if ((i + j) % 2 && grid[i][j]) { int x = i * n + j; if (i < m - 1 && grid[i + 1][j]) { g[x].push_back(x + n); } if (i && grid[i - 1][j]) { g[x].push_back(x - n); } if (j < n - 1 && grid[i][j + 1]) { g[x].push_back(x + 1); } if (j && grid[i][j - 1]) { g[x].push_back(x - 1); } } } } int ans = 0; function<int(int)> find = [&](int i) -> int { for (int& j : g[i]) { if (!vis.count(j)) { vis.insert(j); if (match[j] == -1 || find(match[j])) { match[j] = i; return 1; } } } return 0; }; for (auto& [i, _] : g) { ans += find(i); vis.clear(); } return ans; } }; -
class Solution: def minimumOperations(self, grid: List[List[int]]) -> int: def find(i: int) -> int: for j in g[i]: if j not in vis: vis.add(j) if match[j] == -1 or find(match[j]): match[j] = i return 1 return 0 g = defaultdict(list) m, n = len(grid), len(grid[0]) for i, row in enumerate(grid): for j, v in enumerate(row): if (i + j) % 2 and v: x = i * n + j if i < m - 1 and grid[i + 1][j]: g[x].append(x + n) if i and grid[i - 1][j]: g[x].append(x - n) if j < n - 1 and grid[i][j + 1]: g[x].append(x + 1) if j and grid[i][j - 1]: g[x].append(x - 1) match = [-1] * (m * n) ans = 0 for i in g.keys(): vis = set() ans += find(i) return ans -
func minimumOperations(grid [][]int) (ans int) { m, n := len(grid), len(grid[0]) vis := map[int]bool{} match := make([]int, m*n) for i := range match { match[i] = -1 } g := map[int][]int{} for i, row := range grid { for j, v := range row { if (i+j)&1 == 1 && v == 1 { x := i*n + j if i < m-1 && grid[i+1][j] == 1 { g[x] = append(g[x], x+n) } if i > 0 && grid[i-1][j] == 1 { g[x] = append(g[x], x-n) } if j < n-1 && grid[i][j+1] == 1 { g[x] = append(g[x], x+1) } if j > 0 && grid[i][j-1] == 1 { g[x] = append(g[x], x-1) } } } } var find func(int) int find = func(i int) int { for _, j := range g[i] { if !vis[j] { vis[j] = true if match[j] == -1 || find(match[j]) == 1 { match[j] = i return 1 } } } return 0 } for i := range g { ans += find(i) vis = map[int]bool{} } return } -
function minimumOperations(grid: number[][]): number { const m = grid.length; const n = grid[0].length; const match: number[] = Array(m * n).fill(-1); const vis: Set<number> = new Set(); const g: Map<number, number[]> = new Map(); for (let i = 0; i < m; ++i) { for (let j = 0; j < n; ++j) { if ((i + j) % 2 && grid[i][j]) { const x = i * n + j; g.set(x, []); if (i < m - 1 && grid[i + 1][j]) { g.get(x)!.push(x + n); } if (i && grid[i - 1][j]) { g.get(x)!.push(x - n); } if (j < n - 1 && grid[i][j + 1]) { g.get(x)!.push(x + 1); } if (j && grid[i][j - 1]) { g.get(x)!.push(x - 1); } } } } const find = (i: number): number => { for (const j of g.get(i)!) { if (!vis.has(j)) { vis.add(j); if (match[j] === -1 || find(match[j])) { match[j] = i; return 1; } } } return 0; }; let ans = 0; for (const i of g.keys()) { ans += find(i); vis.clear(); } return ans; }