Welcome to Subscribe On Youtube
2096. Step-By-Step Directions From a Binary Tree Node to Another
Description
You are given the root of a binary tree with n nodes. Each node is uniquely assigned a value from 1 to n. You are also given an integer startValue representing the value of the start node s, and a different integer destValue representing the value of the destination node t.
Find the shortest path starting from node s and ending at node t. Generate step-by-step directions of such path as a string consisting of only the uppercase letters 'L', 'R', and 'U'. Each letter indicates a specific direction:
'L'means to go from a node to its left child node.'R'means to go from a node to its right child node.'U'means to go from a node to its parent node.
Return the step-by-step directions of the shortest path from node s to node t.
Example 1:
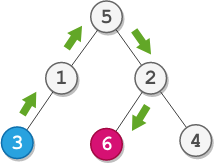
Input: root = [5,1,2,3,null,6,4], startValue = 3, destValue = 6 Output: "UURL" Explanation: The shortest path is: 3 → 1 → 5 → 2 → 6.
Example 2:
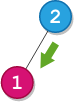
Input: root = [2,1], startValue = 2, destValue = 1 Output: "L" Explanation: The shortest path is: 2 → 1.
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is
n. 2 <= n <= 1051 <= Node.val <= n- All the values in the tree are unique.
1 <= startValue, destValue <= nstartValue != destValue
Solutions
-
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * public class TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode left; * TreeNode right; * TreeNode() {} * TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; } * TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) { * this.val = val; * this.left = left; * this.right = right; * } * } */ class Solution { private Map<Integer, List<List<String>>> edges; private Set<Integer> visited; private String ans; public String getDirections(TreeNode root, int startValue, int destValue) { edges = new HashMap<>(); visited = new HashSet<>(); ans = null; traverse(root); dfs(startValue, destValue, new ArrayList<>()); return ans; } private void traverse(TreeNode root) { if (root == null) { return; } if (root.left != null) { edges.computeIfAbsent(root.val, k -> new ArrayList<>()) .add(Arrays.asList(String.valueOf(root.left.val), "L")); edges.computeIfAbsent(root.left.val, k -> new ArrayList<>()) .add(Arrays.asList(String.valueOf(root.val), "U")); } if (root.right != null) { edges.computeIfAbsent(root.val, k -> new ArrayList<>()) .add(Arrays.asList(String.valueOf(root.right.val), "R")); edges.computeIfAbsent(root.right.val, k -> new ArrayList<>()) .add(Arrays.asList(String.valueOf(root.val), "U")); } traverse(root.left); traverse(root.right); } private void dfs(int start, int dest, List<String> t) { if (visited.contains(start)) { return; } if (start == dest) { if (ans == null || ans.length() > t.size()) { ans = String.join("", t); } return; } visited.add(start); if (edges.containsKey(start)) { for (List<String> item : edges.get(start)) { t.add(item.get(1)); dfs(Integer.parseInt(item.get(0)), dest, t); t.remove(t.size() - 1); } } } } -
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * struct TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode *left; * TreeNode *right; * TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {} * TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {} * TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {} * }; */ class Solution { public: unordered_map<int, vector<pair<int, char>>> edges; unordered_set<int> visited; string ans; string getDirections(TreeNode* root, int startValue, int destValue) { ans = ""; traverse(root); string t = ""; dfs(startValue, destValue, t); return ans; } void traverse(TreeNode* root) { if (!root) return; if (root->left) { edges[root->val].push_back({root->left->val, 'L'}); edges[root->left->val].push_back({root->val, 'U'}); } if (root->right) { edges[root->val].push_back({root->right->val, 'R'}); edges[root->right->val].push_back({root->val, 'U'}); } traverse(root->left); traverse(root->right); } void dfs(int start, int dest, string& t) { if (visited.count(start)) return; if (start == dest) { if (ans == "" || ans.size() > t.size()) ans = t; return; } visited.insert(start); if (edges.count(start)) { for (auto& item : edges[start]) { t += item.second; dfs(item.first, dest, t); t.pop_back(); } } } }; -
# Definition for a binary tree node. # class TreeNode: # def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None): # self.val = val # self.left = left # self.right = right class Solution: def getDirections( self, root: Optional[TreeNode], startValue: int, destValue: int ) -> str: edges = defaultdict(list) ans = None visited = set() def traverse(root): if not root: return if root.left: edges[root.val].append([root.left.val, 'L']) edges[root.left.val].append([root.val, 'U']) if root.right: edges[root.val].append([root.right.val, 'R']) edges[root.right.val].append([root.val, 'U']) traverse(root.left) traverse(root.right) def dfs(start, dest, t): nonlocal ans if start in visited: return if start == dest: if ans is None or len(ans) > len(t): ans = ''.join(t) return visited.add(start) for d, k in edges[start]: t.append(k) dfs(d, dest, t) t.pop() traverse(root) dfs(startValue, destValue, []) return ans -
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * type TreeNode struct { * Val int * Left *TreeNode * Right *TreeNode * } */ func getDirections(root *TreeNode, startValue int, destValue int) string { var lca func(node *TreeNode, p, q int) *TreeNode lca = func(node *TreeNode, p, q int) *TreeNode { if node == nil || node.Val == p || node.Val == q { return node } left := lca(node.Left, p, q) right := lca(node.Right, p, q) if left != nil && right != nil { return node } if left != nil { return left } return right } var dfs func(node *TreeNode, x int, path *[]byte) bool dfs = func(node *TreeNode, x int, path *[]byte) bool { if node == nil { return false } if node.Val == x { return true } *path = append(*path, 'L') if dfs(node.Left, x, path) { return true } (*path)[len(*path)-1] = 'R' if dfs(node.Right, x, path) { return true } *path = (*path)[:len(*path)-1] return false } node := lca(root, startValue, destValue) pathToStart := []byte{} pathToDest := []byte{} dfs(node, startValue, &pathToStart) dfs(node, destValue, &pathToDest) return string(bytes.Repeat([]byte{'U'}, len(pathToStart))) + string(pathToDest) } -
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * class TreeNode { * val: number * left: TreeNode | null * right: TreeNode | null * constructor(val?: number, left?: TreeNode | null, right?: TreeNode | null) { * this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val) * this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left) * this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right) * } * } */ function getDirections(root: TreeNode | null, startValue: number, destValue: number): string { const lca = (node: TreeNode | null, p: number, q: number): TreeNode | null => { if (node === null || node.val === p || node.val === q) { return node; } const left = lca(node.left, p, q); const right = lca(node.right, p, q); if (left !== null && right !== null) { return node; } return left !== null ? left : right; }; const dfs = (node: TreeNode | null, x: number, path: string[]): boolean => { if (node === null) { return false; } if (node.val === x) { return true; } path.push('L'); if (dfs(node.left, x, path)) { return true; } path[path.length - 1] = 'R'; if (dfs(node.right, x, path)) { return true; } path.pop(); return false; }; const node = lca(root, startValue, destValue); const pathToStart: string[] = []; const pathToDest: string[] = []; dfs(node, startValue, pathToStart); dfs(node, destValue, pathToDest); return 'U'.repeat(pathToStart.length) + pathToDest.join(''); } -
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * function TreeNode(val, left, right) { * this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val) * this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left) * this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right) * } */ /** * @param {TreeNode} root * @param {number} startValue * @param {number} destValue * @return {string} */ var getDirections = function (root, startValue, destValue) { const lca = (node, p, q) => { if (node === null || [p, q].includes(node.val)) { return node; } const left = lca(node.left, p, q); const right = lca(node.right, p, q); return left && right ? node : left ?? right; }; const dfs = (node, x, path) => { if (node === null) { return false; } if (node.val === x) { return true; } path.push('L'); if (dfs(node.left, x, path)) { return true; } path[path.length - 1] = 'R'; if (dfs(node.right, x, path)) { return true; } path.pop(); return false; }; const node = lca(root, startValue, destValue); const pathToStart = []; const pathToDest = []; dfs(node, startValue, pathToStart); dfs(node, destValue, pathToDest); return 'U'.repeat(pathToStart.length) + pathToDest.join(''); };