Welcome to Subscribe On Youtube
2046. Sort Linked List Already Sorted Using Absolute Values
Description
Given the head of a singly linked list that is sorted in non-decreasing order using the absolute values of its nodes, return the list sorted in non-decreasing order using the actual values of its nodes.
Example 1:
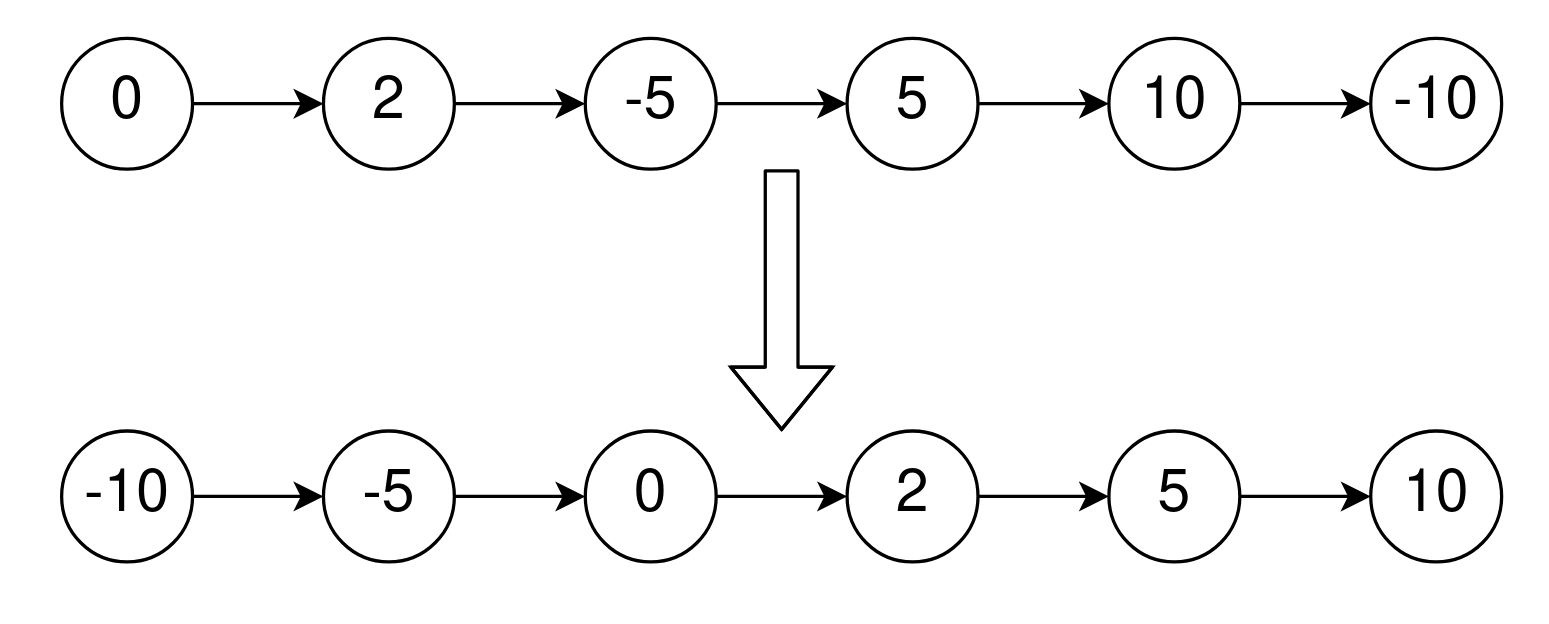
Input: head = [0,2,-5,5,10,-10] Output: [-10,-5,0,2,5,10] Explanation: The list sorted in non-descending order using the absolute values of the nodes is [0,2,-5,5,10,-10]. The list sorted in non-descending order using the actual values is [-10,-5,0,2,5,10].
Example 2:
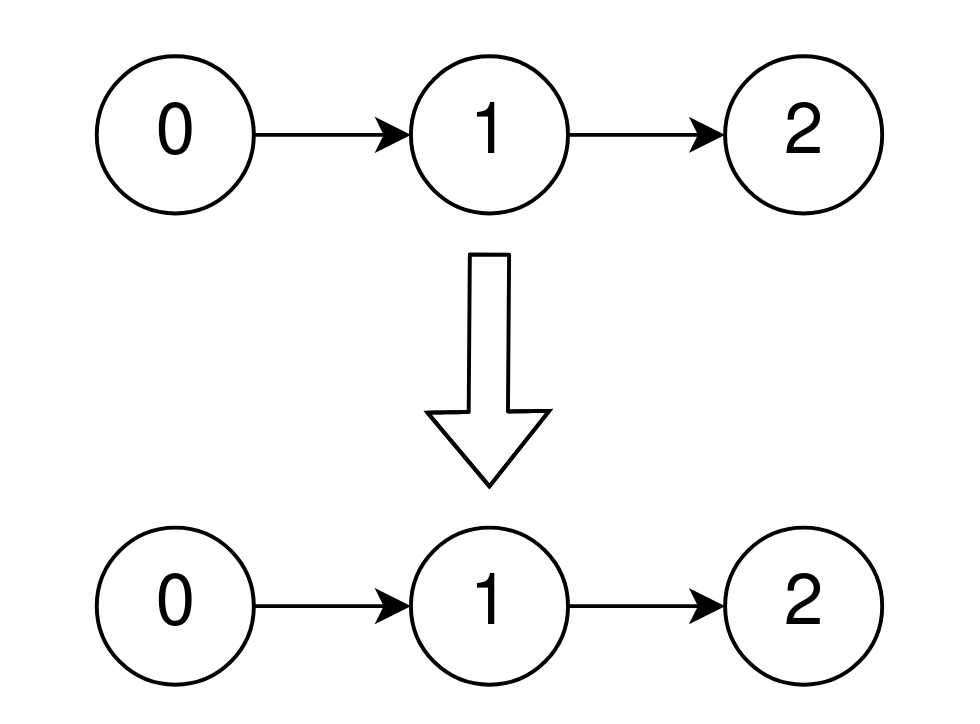
Input: head = [0,1,2] Output: [0,1,2] Explanation: The linked list is already sorted in non-decreasing order.
Example 3:
Input: head = [1] Output: [1] Explanation: The linked list is already sorted in non-decreasing order.
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the list is the range
[1, 105]. -5000 <= Node.val <= 5000headis sorted in non-decreasing order using the absolute value of its nodes.
Follow up:
- Can you think of a solution with
O(n)time complexity?
Solutions
-
/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * public class ListNode { * int val; * ListNode next; * ListNode() {} * ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; } * ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; } * } */ class Solution { public ListNode sortLinkedList(ListNode head) { ListNode prev = head, curr = head.next; while (curr != null) { if (curr.val < 0) { ListNode t = curr.next; prev.next = t; curr.next = head; head = curr; curr = t; } else { prev = curr; curr = curr.next; } } return head; } } -
/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * struct ListNode { * int val; * ListNode *next; * ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {} * ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {} * ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {} * }; */ class Solution { public: ListNode* sortLinkedList(ListNode* head) { ListNode* prev = head; ListNode* curr = head->next; while (curr) { if (curr->val < 0) { auto t = curr->next; prev->next = t; curr->next = head; head = curr; curr = t; } else { prev = curr; curr = curr->next; } } return head; } }; -
# Definition for singly-linked list. # class ListNode: # def __init__(self, val=0, next=None): # self.val = val # self.next = next class Solution: def sortLinkedList(self, head: Optional[ListNode]) -> Optional[ListNode]: prev, curr = head, head.next while curr: if curr.val < 0: t = curr.next prev.next = t curr.next = head head = curr curr = t else: prev, curr = curr, curr.next return head -
/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * type ListNode struct { * Val int * Next *ListNode * } */ func sortLinkedList(head *ListNode) *ListNode { prev, curr := head, head.Next for curr != nil { if curr.Val < 0 { t := curr.Next prev.Next = t curr.Next = head head = curr curr = t } else { prev, curr = curr, curr.Next } } return head } -
/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * class ListNode { * val: number * next: ListNode | null * constructor(val?: number, next?: ListNode | null) { * this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val) * this.next = (next===undefined ? null : next) * } * } */ function sortLinkedList(head: ListNode | null): ListNode | null { let [prev, curr] = [head, head.next]; while (curr !== null) { if (curr.val < 0) { const t = curr.next; prev.next = t; curr.next = head; head = curr; curr = t; } else { [prev, curr] = [curr, curr.next]; } } return head; }