Welcome to Subscribe On Youtube
2033. Minimum Operations to Make a Uni-Value Grid
Description
You are given a 2D integer grid of size m x n and an integer x. In one operation, you can add x to or subtract x from any element in the grid.
A uni-value grid is a grid where all the elements of it are equal.
Return the minimum number of operations to make the grid uni-value. If it is not possible, return -1.
Example 1:
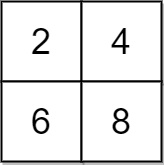
Input: grid = [[2,4],[6,8]], x = 2 Output: 4 Explanation: We can make every element equal to 4 by doing the following: - Add x to 2 once. - Subtract x from 6 once. - Subtract x from 8 twice. A total of 4 operations were used.
Example 2:
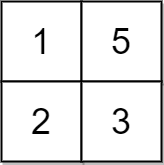
Input: grid = [[1,5],[2,3]], x = 1 Output: 5 Explanation: We can make every element equal to 3.
Example 3:
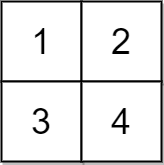
Input: grid = [[1,2],[3,4]], x = 2 Output: -1 Explanation: It is impossible to make every element equal.
Constraints:
m == grid.lengthn == grid[i].length1 <= m, n <= 1051 <= m * n <= 1051 <= x, grid[i][j] <= 104
Solutions
Solution 1: Greedy
Firstly, to make the grid a single-value grid, the remainder of all elements of the grid with $x$ must be the same.
Therefore, we can first traverse the grid to check whether the remainder of all elements with $x$ is the same. If not, return $-1$. Otherwise, we put all elements into an array, sort the array, take the median, then traverse the array, calculate the difference between each element and the median, divide it by $x$, and add all the differences to get the answer.
The time complexity is $O((m \times n) \times \log (m \times n))$, and the space complexity is $O(m \times n)$. Here, $m$ and $n$ are the number of rows and columns of the grid, respectively.
-
class Solution { public int minOperations(int[][] grid, int x) { int m = grid.length, n = grid[0].length; int[] nums = new int[m * n]; int mod = grid[0][0] % x; for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i) { for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) { if (grid[i][j] % x != mod) { return -1; } nums[i * n + j] = grid[i][j]; } } Arrays.sort(nums); int mid = nums[nums.length >> 1]; int ans = 0; for (int v : nums) { ans += Math.abs(v - mid) / x; } return ans; } } -
class Solution { public: int minOperations(vector<vector<int>>& grid, int x) { int m = grid.size(), n = grid[0].size(); int mod = grid[0][0] % x; int nums[m * n]; for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i) { for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) { if (grid[i][j] % x != mod) { return -1; } nums[i * n + j] = grid[i][j]; } } sort(nums, nums + m * n); int mid = nums[(m * n) >> 1]; int ans = 0; for (int v : nums) { ans += abs(v - mid) / x; } return ans; } }; -
class Solution: def minOperations(self, grid: List[List[int]], x: int) -> int: nums = [] mod = grid[0][0] % x for row in grid: for v in row: if v % x != mod: return -1 nums.append(v) nums.sort() mid = nums[len(nums) >> 1] return sum(abs(v - mid) // x for v in nums) -
func minOperations(grid [][]int, x int) int { mod := grid[0][0] % x nums := []int{} for _, row := range grid { for _, v := range row { if v%x != mod { return -1 } nums = append(nums, v) } } sort.Ints(nums) mid := nums[len(nums)>>1] ans := 0 for _, v := range nums { ans += abs(v-mid) / x } return ans } func abs(x int) int { if x < 0 { return -x } return x } -
function minOperations(grid: number[][], x: number): number { const arr = grid.flat(2); arr.sort((a, b) => a - b); const median = arr[Math.floor(arr.length / 2)]; let res = 0; for (const val of arr) { const c = Math.abs(val - median) / x; if (c !== (c | 0)) return -1; res += c; } return res; } -
function minOperations(grid, x) { const arr = grid.flat(2); arr.sort((a, b) => a - b); const median = arr[Math.floor(arr.length / 2)]; let res = 0; for (const val of arr) { const c = Math.abs(val - median) / x; if (c !== (c | 0)) return -1; res += c; } return res; }