Welcome to Subscribe On Youtube
Formatted question description: https://leetcode.ca/all/1819.html
1819. Number of Different Subsequences GCDs
Level
Hard
Description
You are given an array nums that consists of positive integers.
The GCD of a sequence of numbers is defined as the greatest integer that divides all the numbers in the sequence evenly.
- For example, the GCD of the sequence
[4,6,16]is2.
A subsequence of an array is a sequence that can be formed by removing some elements (possibly none) of the array.
- For example,
[2,5,10]is a subsequence of[1,2,1,2,4,1,5,10].
Return the number of different GCDs among all non-empty subsequences of nums.
Example 1:
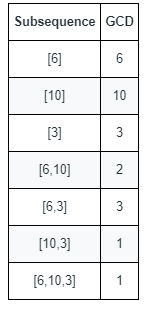
Input: nums = [6,10,3]
Output: 5
Explanation: The figure shows all the non-empty subsequences and their GCDs.
The different GCDs are 6, 10, 3, 2, and 1.
Example 2:
Input: nums = [5,15,40,5,6]
Output: 7
Constraints:
1 <= nums.length <= 10^51 <= nums[i] <= 2 * 10^5
Solution
For each num in nums, obtain all the factors of num. Count the number of each factor from 1 to max(nums). For each i such that 1 <= i <= max(nums), let counts[i] be the number of factor i that occurs in nums. If i is in nums, or counts[i] > 0 and there does not exist any j such that j > i and j % i == 0, then i is the GCD of a subsequence of nums. Finally, return the number of different subsequences GCDs.
-
class Solution { public int countDifferentSubsequenceGCDs(int[] nums) { Set<Integer> set = new HashSet<Integer>(); int max = 0; for (int num : nums) { set.add(num); max = Math.max(max, num); } int[] counts = new int[max + 1]; for (int num : set) { for (int i = 1; i * i <= num; i++) { if (num % i == 0) { counts[i]++; if (i * i != num) counts[num / i]++; } } } int count = 0; for (int i = 1; i <= max; i++) { if (set.contains(i)) count++; else if (counts[i] > 0) { boolean flag = true; for (int j = i * 2; j <= max; j += i) { if (counts[j] == counts[i]) { flag = false; break; } } if (flag) count++; } } return count; } } ############ class Solution { public int countDifferentSubsequenceGCDs(int[] nums) { int mx = Arrays.stream(nums).max().getAsInt(); boolean[] vis = new boolean[mx + 1]; for (int x : nums) { vis[x] = true; } int ans = 0; for (int x = 1; x <= mx; ++x) { int g = 0; for (int y = x; y <= mx; y += x) { if (vis[y]) { g = gcd(g, y); if (x == g) { ++ans; break; } } } } return ans; } private int gcd(int a, int b) { return b == 0 ? a : gcd(b, a % b); } } -
// OJ: https://leetcode.com/problems/number-of-different-subsequences-gcds/ // Time: O(NlogN) // Space: O(N) class Solution { public: int countDifferentSubsequenceGCDs(vector<int>& A) { const int N = 2e5; int ans = 0; bool seen[N + 1] = {}; for (int n : A) seen[n] = true; for (int i = 1; i <= N; ++i) { int div = 0; for (int j = i; j <= N; j += i) { if (seen[j]) div = gcd(div, j); } if (div == i) ++ans; } return ans; } }; -
class Solution: def countDifferentSubsequenceGCDs(self, nums: List[int]) -> int: mx = max(nums) vis = set(nums) ans = 0 for x in range(1, mx + 1): g = 0 for y in range(x, mx + 1, x): if y in vis: g = gcd(g, y) if g == x: ans += 1 break return ans -
func countDifferentSubsequenceGCDs(nums []int) (ans int) { mx := 0 for _, x := range nums { mx = max(mx, x) } vis := make([]bool, mx+1) for _, x := range nums { vis[x] = true } for x := 1; x <= mx; x++ { g := 0 for y := x; y <= mx; y += x { if vis[y] { g = gcd(g, y) if g == x { ans++ break } } } } return } func max(a, b int) int { if a > b { return a } return b } func gcd(a, b int) int { if b == 0 { return a } return gcd(b, a%b) }