Welcome to Subscribe On Youtube
1973. Count Nodes Equal to Sum of Descendants
Description
Given the root of a binary tree, return the number of nodes where the value of the node is equal to the sum of the values of its descendants.
A descendant of a node x is any node that is on the path from node x to some leaf node. The sum is considered to be 0 if the node has no descendants.
Example 1:
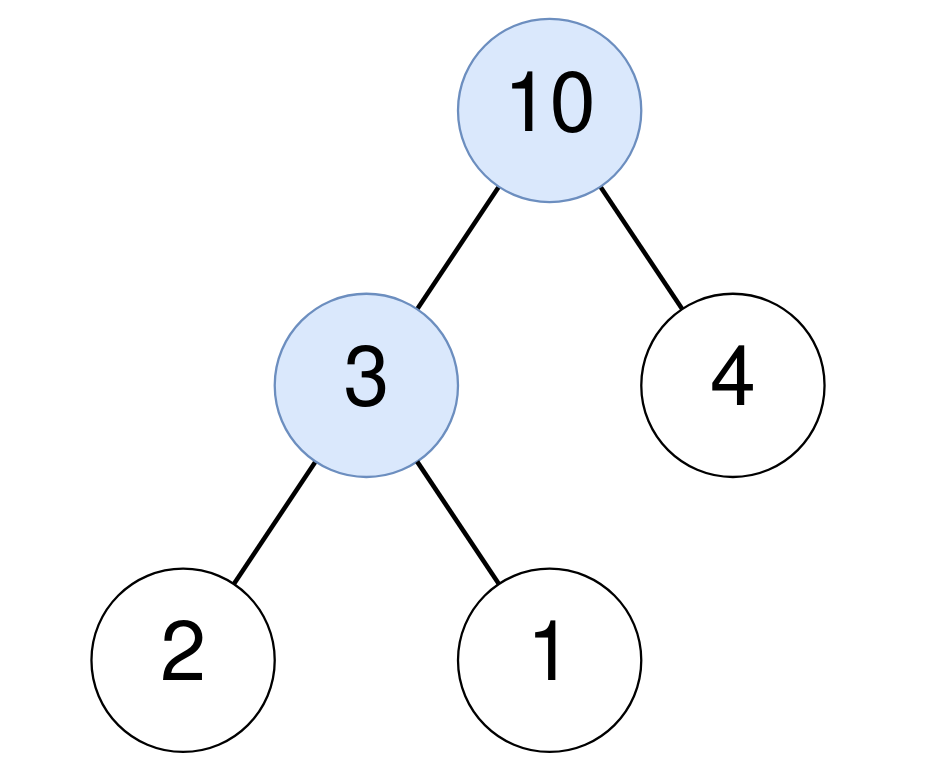
Input: root = [10,3,4,2,1] Output: 2 Explanation: For the node with value 10: The sum of its descendants is 3+4+2+1 = 10. For the node with value 3: The sum of its descendants is 2+1 = 3.
Example 2:
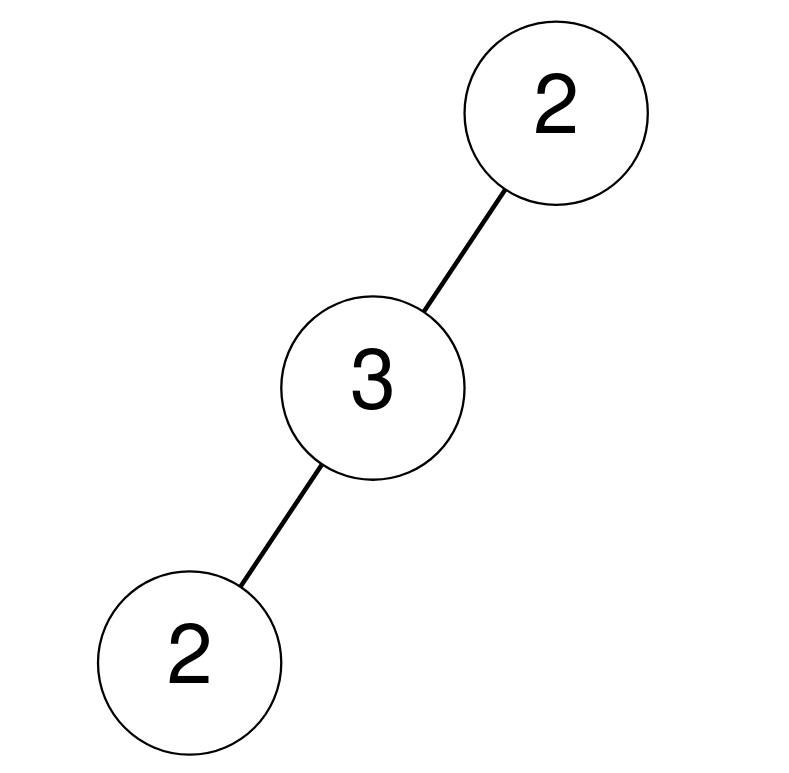
Input: root = [2,3,null,2,null] Output: 0 Explanation: No node has a value that is equal to the sum of its descendants.
Example 3:

Input: root = [0] Output: 1 For the node with value 0: The sum of its descendants is 0 since it has no descendants.
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[1, 105]. 0 <= Node.val <= 105
Solutions
-
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * public class TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode left; * TreeNode right; * TreeNode() {} * TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; } * TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) { * this.val = val; * this.left = left; * this.right = right; * } * } */ class Solution { private int ans; public int equalToDescendants(TreeNode root) { dfs(root); return ans; } private int dfs(TreeNode root) { if (root == null) { return 0; } int l = dfs(root.left); int r = dfs(root.right); if (l + r == root.val) { ++ans; } return root.val + l + r; } } -
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * struct TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode *left; * TreeNode *right; * TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {} * TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {} * TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {} * }; */ class Solution { public: int equalToDescendants(TreeNode* root) { int ans = 0; function<long long(TreeNode*)> dfs = [&](TreeNode* root) -> long long { if (!root) { return 0; } auto l = dfs(root->left); auto r = dfs(root->right); ans += l + r == root->val; return root->val + l + r; }; dfs(root); return ans; } }; -
# Definition for a binary tree node. # class TreeNode: # def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None): # self.val = val # self.left = left # self.right = right class Solution: def equalToDescendants(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> int: def dfs(root): if root is None: return 0 l, r = dfs(root.left), dfs(root.right) if l + r == root.val: nonlocal ans ans += 1 return root.val + l + r ans = 0 dfs(root) return ans -
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * type TreeNode struct { * Val int * Left *TreeNode * Right *TreeNode * } */ func equalToDescendants(root *TreeNode) (ans int) { var dfs func(*TreeNode) int dfs = func(root *TreeNode) int { if root == nil { return 0 } l, r := dfs(root.Left), dfs(root.Right) if l+r == root.Val { ans++ } return root.Val + l + r } dfs(root) return }