Welcome to Subscribe On Youtube
Formatted question description: https://leetcode.ca/all/1766.html
1766. Tree of Coprimes
Level
Hard
Description
There is a tree (i.e., a connected, undirected graph that has no cycles) consisting of n nodes numbered from 0 to n - 1 and exactly n - 1 edges. Each node has a value associated with it, and the root of the tree is node 0.
To represent this tree, you are given an integer array nums and a 2D array edges. Each nums[i] represents the i-th node’s value, and each edges[j] = [u_j, v_j] represents an edge between nodes u_j and v_j in the tree.
Two values x and y are coprime if gcd(x, y) == 1 where gcd(x, y) is the greatest common divisor of x and y.
An ancestor of a node i is any other node on the shortest path from node i to the root. A node is not considered an ancestor of itself.
Return an array ans of size n, where ans[i] is the closest ancestor to node i such that nums[i] and nums[ans[i]] are coprime, or -1 if there is no such ancestor.
Example 1:
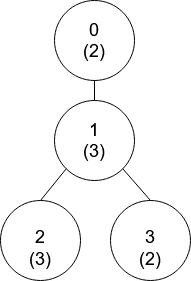
Input: nums = [2,3,3,2], edges = [[0,1],[1,2],[1,3]]
Output: [-1,0,0,1]
Explanation: In the above figure, each node’s value is in parentheses.
- Node 0 has no coprime ancestors.
- Node 1 has only one ancestor, node 0. Their values are coprime (gcd(2,3) == 1).
- Node 2 has two ancestors, nodes 1 and 0. Node 1’s value is not coprime (gcd(3,3) == 3), but node 0’s value is (gcd(2,3) == 1), so node 0 is the closest valid ancestor.
- Node 3 has two ancestors, nodes 1 and 0. It is coprime with node 1 (gcd(3,2) == 1), so node 1 is its closest valid ancestor.
Example 2:
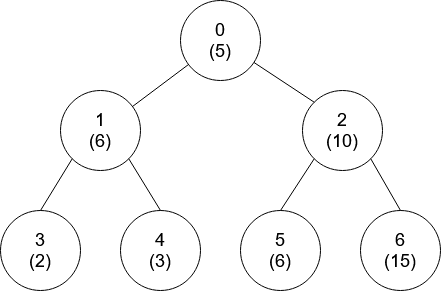
Input: nums = [5,6,10,2,3,6,15], edges = [[0,1],[0,2],[1,3],[1,4],[2,5],[2,6]]
Output: [-1,0,-1,0,0,0,-1]
Constraints:
nums.length == n1 <= nums[i] <= 501 <= n <= 10^5edges.length == n - 1edges[j].length == 20 <= u_j, v_j < nu_j != v_j
Solution
First, store each node’s adjacent nodes. Next, preprocess the numbers from 1 to 50 and find coprimes for each number. Then, do depth first search starting from root node 0 and fimd the nearest coprime node for each node.
-
class Solution { int[] ans; Map<Integer, List<Integer>> edgesMap = new HashMap<Integer, List<Integer>>(); Map<Integer, List<Integer>> coprimesMap = new HashMap<Integer, List<Integer>>(); int[] depths; int[] pos = new int[51]; public int[] getCoprimes(int[] nums, int[][] edges) { int n = nums.length; ans = new int[n]; depths = new int[n]; Arrays.fill(ans, -1); Arrays.fill(pos, -1); for (int[] edge : edges) { int node0 = edge[0], node1 = edge[1]; List<Integer> list0 = edgesMap.getOrDefault(node0, new ArrayList<Integer>()); List<Integer> list1 = edgesMap.getOrDefault(node1, new ArrayList<Integer>()); list0.add(node1); list1.add(node0); edgesMap.put(node0, list0); edgesMap.put(node1, list1); } for (int i = 1; i <= 50; i++) { for (int j = 1; j <= 50; j++) { if (gcd(i, j) == 1) { List<Integer> list = coprimesMap.getOrDefault(i, new ArrayList<Integer>()); list.add(j); coprimesMap.put(i, list); } } } depthFirstSearch(nums, 0, -1); return ans; } public void depthFirstSearch(int[] nums, int u, int form) { int t = nums[u]; for (int v : coprimesMap.get(t)) { if (pos[v] != -1) { if (ans[u] == -1 || depths[ans[u]] < depths[pos[v]]) ans[u] = pos[v]; } } int p = pos[t]; pos[t] = u; for (int i : edgesMap.get(u)) { if (i != form) { depths[i] = depths[u] + 1; depthFirstSearch(nums, i, u); } } pos[t] = p; } public int gcd(int a, int b) { while (a != 0 && b != 0) { if (a >= b) a %= b; else b %= a; } return a == 0 ? b : a; } } ############ class Solution { private List<Integer>[] g; private List<Integer>[] f; private Deque<int[]>[] stks; private int[] nums; private int[] ans; public int[] getCoprimes(int[] nums, int[][] edges) { int n = nums.length; g = new List[n]; Arrays.setAll(g, k -> new ArrayList<>()); for (var e : edges) { int u = e[0], v = e[1]; g[u].add(v); g[v].add(u); } f = new List[51]; stks = new Deque[51]; Arrays.setAll(f, k -> new ArrayList<>()); Arrays.setAll(stks, k -> new ArrayDeque<>()); for (int i = 1; i < 51; ++i) { for (int j = 1; j < 51; ++j) { if (gcd(i, j) == 1) { f[i].add(j); } } } this.nums = nums; ans = new int[n]; dfs(0, -1, 0); return ans; } private void dfs(int i, int fa, int depth) { int t = -1, k = -1; for (int v : f[nums[i]]) { var stk = stks[v]; if (!stk.isEmpty() && stk.peek()[1] > k) { t = stk.peek()[0]; k = stk.peek()[1]; } } ans[i] = t; for (int j : g[i]) { if (j != fa) { stks[nums[i]].push(new int[] {i, depth}); dfs(j, i, depth + 1); stks[nums[i]].pop(); } } } private int gcd(int a, int b) { return b == 0 ? a : gcd(b, a % b); } } -
class Solution: def getCoprimes(self, nums: List[int], edges: List[List[int]]) -> List[int]: def dfs(i, fa, depth): t = k = -1 for v in f[nums[i]]: stk = stks[v] if stk and stk[-1][1] > k: t, k = stk[-1] ans[i] = t for j in g[i]: if j != fa: stks[nums[i]].append((i, depth)) dfs(j, i, depth + 1) stks[nums[i]].pop() g = defaultdict(list) for u, v in edges: g[u].append(v) g[v].append(u) f = defaultdict(list) for i in range(1, 51): for j in range(1, 51): if gcd(i, j) == 1: f[i].append(j) stks = defaultdict(list) ans = [-1] * len(nums) dfs(0, -1, 0) return ans -
class Solution { public: vector<int> getCoprimes(vector<int>& nums, vector<vector<int>>& edges) { int n = nums.size(); vector<vector<int>> g(n); vector<vector<int>> f(51); vector<stack<pair<int, int>>> stks(51); for (auto& e : edges) { int u = e[0], v = e[1]; g[u].emplace_back(v); g[v].emplace_back(u); } for (int i = 1; i < 51; ++i) { for (int j = 1; j < 51; ++j) { if (__gcd(i, j) == 1) { f[i].emplace_back(j); } } } vector<int> ans(n); function<void(int, int, int)> dfs = [&](int i, int fa, int depth) { int t = -1, k = -1; for (int v : f[nums[i]]) { auto& stk = stks[v]; if (!stk.empty() && stk.top().second > k) { t = stk.top().first; k = stk.top().second; } } ans[i] = t; for (int j : g[i]) { if (j != fa) { stks[nums[i]].push({i, depth}); dfs(j, i, depth + 1); stks[nums[i]].pop(); } } }; dfs(0, -1, 0); return ans; } }; -
func getCoprimes(nums []int, edges [][]int) []int { n := len(nums) g := make([][]int, n) f := [51][]int{} type pair struct{ first, second int } stks := [51][]pair{} for _, e := range edges { u, v := e[0], e[1] g[u] = append(g[u], v) g[v] = append(g[v], u) } for i := 1; i < 51; i++ { for j := 1; j < 51; j++ { if gcd(i, j) == 1 { f[i] = append(f[i], j) } } } ans := make([]int, n) var dfs func(i, fa, depth int) dfs = func(i, fa, depth int) { t, k := -1, -1 for _, v := range f[nums[i]] { stk := stks[v] if len(stk) > 0 && stk[len(stk)-1].second > k { t, k = stk[len(stk)-1].first, stk[len(stk)-1].second } } ans[i] = t for _, j := range g[i] { if j != fa { stks[nums[i]] = append(stks[nums[i]], pair{i, depth}) dfs(j, i, depth+1) stks[nums[i]] = stks[nums[i]][:len(stks[nums[i]])-1] } } } dfs(0, -1, 0) return ans } func gcd(a, b int) int { if b == 0 { return a } return gcd(b, a%b) }