Welcome to Subscribe On Youtube
Formatted question description: https://leetcode.ca/all/1724.html
1724. Checking Existence of Edge Length Limited Paths II
Level
Hard
Description
An undirected graph of n nodes is defined by edgeList, where edgeList[i] = [u_i, v_i, dis_i] denotes an edge between nodes u_i and v_i with distance dis_i. Note that there may be multiple edges between two nodes, and the graph may not be connected.
Implement the DistanceLimitedPathsExist class:
DistanceLimitedPathsExist(int n, int[][] edgeList)Initializes the class with an undirected graph.boolean query(int p, int q, int limit)Returnstrueif there exists a path fromptoqsuch that each edge on the path has a distance strictly less thanlimit, and otherwisefalse.
Example 1:
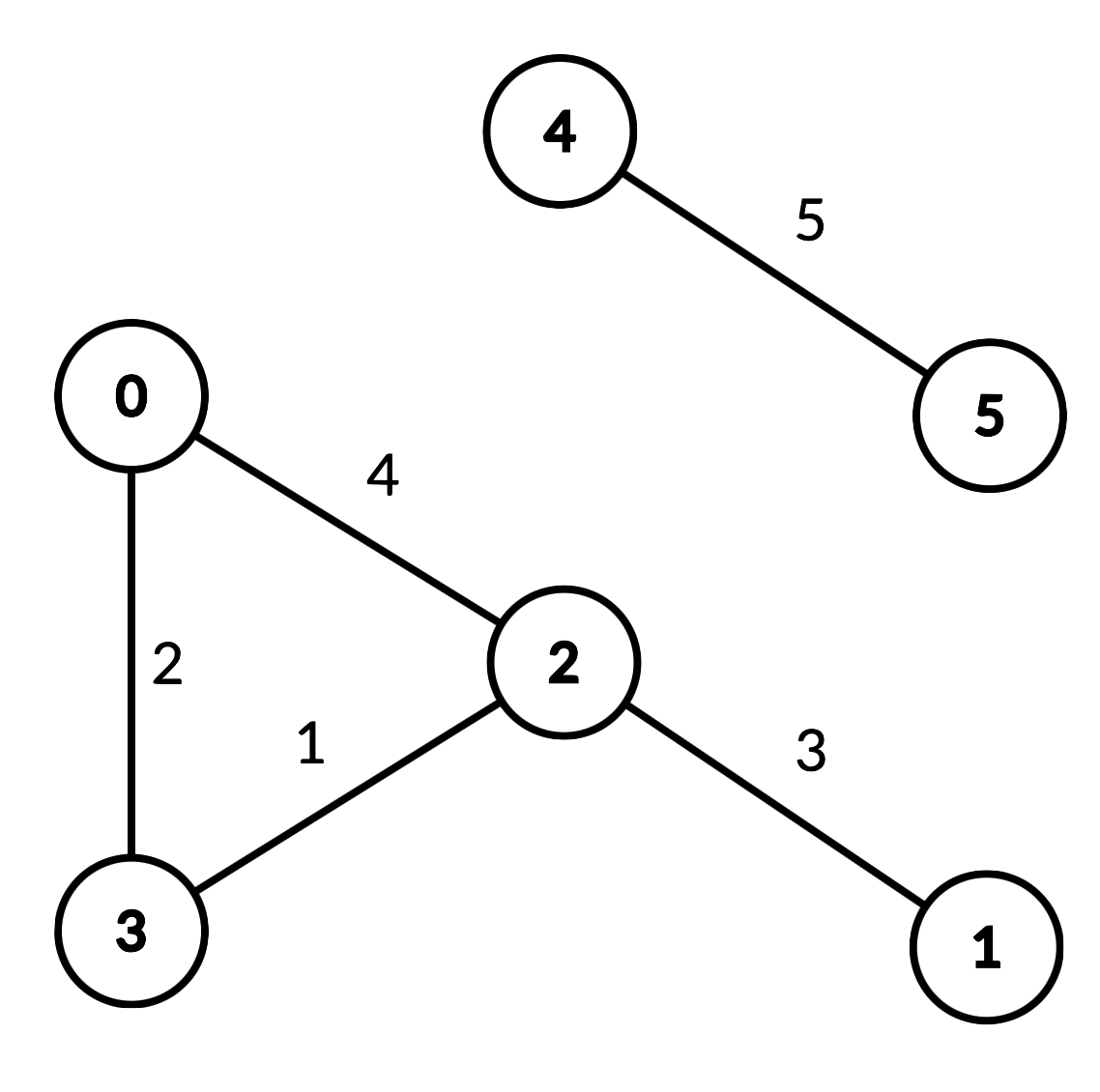
Input
["DistanceLimitedPathsExist", "query", "query", "query", "query"]
[[6, [[0, 2, 4], [0, 3, 2], [1, 2, 3], [2, 3, 1], [4, 5, 5]]], [2, 3, 2], [1, 3, 3], [2, 0, 3], [0, 5, 6]]
Output
[null, true, false, true, false]
Explanation
DistanceLimitedPathsExist distanceLimitedPathsExist = new DistanceLimitedPathsExist(6, [[0, 2, 4], [0, 3, 2], [1, 2, 3], [2, 3, 1], [4, 5, 5]]);
distanceLimitedPathsExist.query(2, 3, 2); // return true. There is an edge from 2 to 3 of distance 1, which is less than 2.
distanceLimitedPathsExist.query(1, 3, 3); // return false. There is no way to go from 1 to 3 with distances strictly less than 3.
distanceLimitedPathsExist.query(2, 0, 3); // return true. There is a way to go from 2 to 0 with distance < 3: travel from 2 to 3 to 0.
distanceLimitedPathsExist.query(0, 5, 6); // return false. There are no paths from 0 to 5.
Constraints:
2 <= n <= 10^40 <= edgeList.length <= 10^4edgeList[i].length == 30 <= u_i, v_i, p, q <= n-1u_i != v_ip != q1 <= dis_i, limit <= 10^9- At most
10^4calls will be made toquery.
Solution
The main idea of this problem is to create a minimum spanning tree from the edges and the nodes. In the constructor, create a minimum spanning tree using union find and Kruskal’s algorithm. For the method query, the idea is similar to finding the lowest common ancestor.
-
class DistanceLimitedPathsExist { int n; int bits; UnionFind uf; int[][] edgeList; Map<Integer, List<int[]>> mstEdges; int[][] parent; int[][] maxWeights; int[] depths; boolean[] visited; public DistanceLimitedPathsExist(int n, int[][] edgeList) { this.n = n; this.uf = new UnionFind(n); this.edgeList = edgeList; Arrays.sort(this.edgeList, new Comparator<int[]>() { public int compare(int[] edge1, int[] edge2) { return edge1[2] - edge2[2]; } }); mstEdges = new HashMap<Integer, List<int[]>>(); bits = (int) (Math.log(n) / Math.log(2)) + 2; this.parent = new int[n][bits]; for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) Arrays.fill(this.parent[i], -1); this.maxWeights = new int[n][bits]; this.depths = new int[n]; this.visited = new boolean[n]; kruskal(); for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { if (!visited[i]) { depths[i] = 1; depthFirstSearch(i); parent[i][0] = i; } } for (int i = 1; i < bits; i++) { for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) { parent[j][i] = parent[parent[j][i - 1]][i - 1]; maxWeights[j][i] = Math.max(maxWeights[j][i - 1], maxWeights[parent[j][i - 1]][i - 1]); } } } public boolean query(int p, int q, int limit) { if (uf.find(p) != uf.find(q)) return false; else return lowestCommonAncestor(p, q) < limit; } private void kruskal() { int edgesCount = edgeList.length; for (int i = 0; i < edgesCount; i++) { int[] edge = edgeList[i]; int u = edge[0], v = edge[1], dist = edge[2]; if (uf.union(u, v)) { List<int[]> list1 = mstEdges.getOrDefault(u, new ArrayList<int[]>()); List<int[]> list2 = mstEdges.getOrDefault(v, new ArrayList<int[]>()); list1.add(new int[]{v, dist}); list2.add(new int[]{u, dist}); mstEdges.put(u, list1); mstEdges.put(v, list2); } } } private void depthFirstSearch(int u) { visited[u] = true; List<int[]> list = mstEdges.getOrDefault(u, new ArrayList<int[]>()); for (int[] array : list) { int v = array[0], dist = array[1]; if (!visited[v]) { depths[v] = depths[u] + 1; parent[v][0] = u; maxWeights[v][0] = dist; depthFirstSearch(v); } } } private int lowestCommonAncestor(int u, int v) { if (depths[u] > depths[v]) { int temp = u; u = v; v = temp; } int temp = depths[v] - depths[u]; int weight = 0; int index = 0; while (temp != 0) { if (temp % 2 != 0) { weight = Math.max(weight, maxWeights[v][index]); v = parent[v][index]; } temp >>= 1; index++; } if (u == v) return weight; for (int i = bits - 1; i >= 0; i--) { if (parent[u][i] != parent[v][i]) { weight = Math.max(weight, Math.max(maxWeights[u][i], maxWeights[v][i])); u = parent[u][i]; v = parent[v][i]; } } weight = Math.max(weight, Math.max(maxWeights[u][0], maxWeights[v][0])); return weight; } } class UnionFind { int n; int[] parent; public UnionFind(int n) { this.n = n; this.parent = new int[n]; for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { this.parent[i] = i; } } public boolean union(int index1, int index2) { int ancestor1 = find(index1), ancestor2 = find(index2); if (ancestor1 == ancestor2) return false; else { parent[find(index2)] = find(index1); return true; } } public int find(int index) { if (parent[index] != index) parent[index] = find(parent[index]); return parent[index]; } } /** * Your DistanceLimitedPathsExist object will be instantiated and called as such: * DistanceLimitedPathsExist obj = new DistanceLimitedPathsExist(n, edgeList); * boolean param_1 = obj.query(p,q,limit); */ -
class PersistentUnionFind { private: vector<int> rank; vector<int> parent; vector<int> version; public: PersistentUnionFind(int n) : rank(n, 0) , parent(n) , version(n, INT_MAX) { for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { parent[i] = i; } } int find(int x, int t) { if (parent[x] == x || version[x] >= t) { return x; } return find(parent[x], t); } bool unionSet(int a, int b, int t) { int pa = find(a, INT_MAX); int pb = find(b, INT_MAX); if (pa == pb) { return false; } if (rank[pa] > rank[pb]) { version[pb] = t; parent[pb] = pa; } else { version[pa] = t; parent[pa] = pb; if (rank[pa] == rank[pb]) { rank[pb]++; } } return true; } }; class DistanceLimitedPathsExist { private: PersistentUnionFind puf; public: DistanceLimitedPathsExist(int n, vector<vector<int>>& edgeList) : puf(n) { sort(edgeList.begin(), edgeList.end(), [](const vector<int>& a, const vector<int>& b) { return a[2] < b[2]; }); for (const auto& edge : edgeList) { puf.unionSet(edge[0], edge[1], edge[2]); } } bool query(int p, int q, int limit) { return puf.find(p, limit) == puf.find(q, limit); } }; /** * Your DistanceLimitedPathsExist object will be instantiated and called as such: * DistanceLimitedPathsExist* obj = new DistanceLimitedPathsExist(n, edgeList); * bool param_1 = obj->query(p,q,limit); */ -
class PersistentUnionFind: def __init__(self, n): self.rank = [0] * n self.p = list(range(n)) self.version = [inf] * n def find(self, x, t=inf): if self.p[x] == x or self.version[x] >= t: return x return self.find(self.p[x], t) def union(self, a, b, t): pa, pb = self.find(a), self.find(b) if pa == pb: return False if self.rank[pa] > self.rank[pb]: self.version[pb] = t self.p[pb] = pa else: self.version[pa] = t self.p[pa] = pb if self.rank[pa] == self.rank[pb]: self.rank[pb] += 1 return True class DistanceLimitedPathsExist: def __init__(self, n: int, edgeList: List[List[int]]): self.puf = PersistentUnionFind(n) edgeList.sort(key=lambda x: x[2]) for u, v, dis in edgeList: self.puf.union(u, v, dis) def query(self, p: int, q: int, limit: int) -> bool: return self.puf.find(p, limit) == self.puf.find(q, limit) -
type PersistentUnionFind struct { rank []int parent []int version []int } func NewPersistentUnionFind(n int) *PersistentUnionFind { rank := make([]int, n) parent := make([]int, n) version := make([]int, n) for i := 0; i < n; i++ { parent[i] = i } return &PersistentUnionFind{ rank: rank, parent: parent, version: version, } } func (uf *PersistentUnionFind) find(x int, t int) int { if uf.parent[x] == x || uf.version[x] >= t { return x } return uf.find(uf.parent[x], t) } func (uf *PersistentUnionFind) union(a, b, t int) bool { pa := uf.find(a, int(^uint(0)>>1)) pb := uf.find(b, int(^uint(0)>>1)) if pa == pb { return false } if uf.rank[pa] > uf.rank[pb] { uf.version[pb] = t uf.parent[pb] = pa } else { uf.version[pa] = t uf.parent[pa] = pb if uf.rank[pa] == uf.rank[pb] { uf.rank[pb]++ } } return true } type DistanceLimitedPathsExist struct { puf *PersistentUnionFind } func Constructor(n int, edgeList [][]int) DistanceLimitedPathsExist { sort.Slice(edgeList, func(i, j int) bool { return edgeList[i][2] < edgeList[j][2] }) puf := NewPersistentUnionFind(n) for _, edge := range edgeList { puf.union(edge[0], edge[1], edge[2]) } return DistanceLimitedPathsExist{ puf: puf, } } func (dle *DistanceLimitedPathsExist) Query(p, q, limit int) bool { return dle.puf.find(p, limit) == dle.puf.find(q, limit) } /** * Your DistanceLimitedPathsExist object will be instantiated and called as such: * obj := Constructor(n, edgeList); * param_1 := obj.Query(p,q,limit); */ -
class PersistentUnionFind { private rank: number[]; private parent: number[]; private version: number[]; constructor(n: number) { this.rank = Array(n).fill(0); this.parent = Array.from({ length: n }, (_, i) => i); this.version = Array(n).fill(Infinity); } find(x: number, t: number): number { if (this.parent[x] === x || this.version[x] >= t) { return x; } return this.find(this.parent[x], t); } union(a: number, b: number, t: number): boolean { const pa = this.find(a, Infinity); const pb = this.find(b, Infinity); if (pa === pb) { return false; } if (this.rank[pa] > this.rank[pb]) { this.version[pb] = t; this.parent[pb] = pa; } else { this.version[pa] = t; this.parent[pa] = pb; if (this.rank[pa] === this.rank[pb]) { this.rank[pb]++; } } return true; } } class DistanceLimitedPathsExist { private puf: PersistentUnionFind; constructor(n: number, edgeList: number[][]) { this.puf = new PersistentUnionFind(n); edgeList.sort((a, b) => a[2] - b[2]); for (const [u, v, dis] of edgeList) { this.puf.union(u, v, dis); } } query(p: number, q: number, limit: number): boolean { return this.puf.find(p, limit) === this.puf.find(q, limit); } } /** * Your DistanceLimitedPathsExist object will be instantiated and called as such: * var obj = new DistanceLimitedPathsExist(n, edgeList) * var param_1 = obj.query(p,q,limit) */