Welcome to Subscribe On Youtube
Formatted question description: https://leetcode.ca/all/1719.html
1719. Number Of Ways To Reconstruct A Tree
Level
Hard
Description
You are given an array pairs, where pairs[i] = [x_i, y_i], and:
- There are no duplicates.
x_i < y_i
Let ways be the number of rooted trees that satisfy the following conditions:
- The tree consists of nodes whose values appeared in
pairs. - A pair
[x_i, y_i]exists in pairs if and only ifx_iis an ancestor ofy_iory_iis an ancestor ofx_i. - Note: the tree does not have to be a binary tree.
Two ways are considered to be different if there is at least one node that has different parents in both ways.
Return:
0ifways == 01ifways == 12ifways > 1
A rooted tree is a tree that has a single root node, and all edges are oriented to be outgoing from the root.
An ancestor of a node is any node on the path from the root to that node (excluding the node itself). The root has no ancestors.
Example 1:
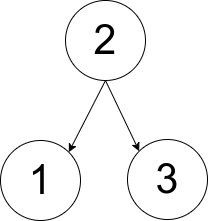
Input: pairs = [[1,2],[2,3]]
Output: 1
Explanation: There is exactly one valid rooted tree, which is shown in the above figure.
Example 2:
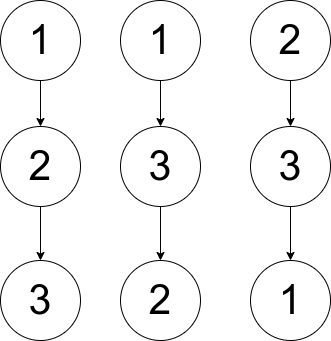
Input: pairs = [[1,2],[2,3],[1,3]]
Output: 2
Explanation: There are multiple valid rooted trees. Three of them are shown in the above figures.
Example 3:
Input: pairs = [[1,2],[2,3],[2,4],[1,5]]
Output: 0
Explanation: There are no valid rooted trees.
Constraints:
1 <= pairs.length <= 10^51 <= x_i < y_i <= 500- The elements in
pairsare unique.
Solution
Loop over pairs. Use a 2D matrix to store whether two nodes have a relation of pairs. Use an array of lists to store the related nodes of each node. Then sort the array of lists according to the lists’ sizes in ascending order. Node i is an ancestor of node j if and only if the size of node i is greater than or equal to the size of node j. If the sizes are equal, then the two nodes can be swapped. Use this way to determine the final result.
-
class Solution { public int checkWays(int[][] pairs) { int maxValue = 0; for (int[] pair : pairs) maxValue = Math.max(maxValue, Math.max(pair[0], pair[1])); boolean[][] relations = new boolean[maxValue + 1][maxValue + 1]; List<Integer>[] lists = new List[maxValue + 1]; for (int i = 0; i <= maxValue; i++) lists[i] = new ArrayList<Integer>(); for (int[] pair : pairs) { int value1 = pair[0], value2 = pair[1]; relations[value1][value2] = true; relations[value2][value1] = true; lists[value1].add(value2); lists[value2].add(value1); } List<Integer> indices = new ArrayList<Integer>(); for (int i = 1; i <= maxValue; i++) { if (!lists[i].isEmpty()) { indices.add(i); relations[i][i] = true; } } Collections.sort(indices, new Comparator<Integer>() { public int compare(Integer index1, Integer index2) { return lists[index1].size() - lists[index2].size(); } }); boolean equal = false; int rootCount = 0; int size = indices.size(); for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) { int j = i + 1; while (j < size && !relations[indices.get(i)][indices.get(j)]) j++; if (j < size) { if (lists[indices.get(i)].size() == lists[indices.get(j)].size()) equal = true; for (int value : lists[indices.get(i)]) { if (!relations[value][indices.get(j)]) return 0; } } else rootCount++; } if (rootCount > 1) return 0; else return equal ? 2 : 1; } } ############ class Solution { public int checkWays(int[][] pairs) { boolean[][] g = new boolean[510][510]; List<Integer>[] v = new List[510]; Arrays.setAll(v, k -> new ArrayList<>()); for (int[] p : pairs) { int x = p[0], y = p[1]; g[x][y] = true; g[y][x] = true; v[x].add(y); v[y].add(x); } List<Integer> nodes = new ArrayList<>(); for (int i = 0; i < 510; ++i) { if (!v[i].isEmpty()) { nodes.add(i); g[i][i] = true; } } nodes.sort(Comparator.comparingInt(a -> v[a].size())); boolean equal = false; int root = 0; for (int i = 0; i < nodes.size(); ++i) { int x = nodes.get(i); int j = i + 1; for (; j < nodes.size() && !g[x][nodes.get(j)]; ++j) ; if (j < nodes.size()) { int y = nodes.get(j); if (v[x].size() == v[y].size()) { equal = true; } for (int z : v[x]) { if (!g[y][z]) { return 0; } } } else { ++root; } } if (root > 1) { return 0; } return equal ? 2 : 1; } } -
// OJ: https://leetcode.com/problems/number-of-ways-to-reconstruct-a-tree/ class Solution { public: int checkWays(vector<vector<int>>& A) { unordered_map<int, unordered_set<int>> G; for (auto &p : A) { int u = p[0], v = p[1]; G[u].insert(v); G[v].insert(u); } function<int(vector<int>&)> solve = [&](vector<int> &nodes) { vector<pair<int, int>> pairs; // degree, node for (int n : nodes) pairs.emplace_back(G[n].size(), n); sort(begin(pairs), end(pairs), greater<>()); int rootDegree = nodes.size() - 1; if (pairs[0].first != rootDegree) return 0; // can't find root unordered_map<int, vector<int>> comp; unordered_set<int> seen; int id = 0, rootCnt = 0; function<void(int)> dfs = [&](int u) { seen.insert(u); comp[id].push_back(u); for (int v : G[u]) { if (seen.count(v) == 0) dfs(v); } }; for (auto &[deg, u] : pairs) { if (deg == rootDegree) { ++rootCnt; for (int v : G[u]) G[v].erase(u); } else if (seen.count(u) == 0) { dfs(u); // non-root nodes are split into different components. Each component is a subtree and solved independently. ++id; } } int ans = 1; for (auto &[i, ns] : comp) { int cnt = solve(ns); if (cnt == 0) return 0; if (cnt == 2) ans = 2; } return rootCnt > 1 ? 2 : ans; }; vector<int> nodes; for (auto &[u, _] : G) nodes.push_back(u); return solve(nodes); } }; -
class Solution: def checkWays(self, pairs: List[List[int]]) -> int: g = [[False] * 510 for _ in range(510)] v = defaultdict(list) for x, y in pairs: g[x][y] = g[y][x] = True v[x].append(y) v[y].append(x) nodes = [] for i in range(510): if v[i]: nodes.append(i) g[i][i] = True nodes.sort(key=lambda x: len(v[x])) equal = False root = 0 for i, x in enumerate(nodes): j = i + 1 while j < len(nodes) and not g[x][nodes[j]]: j += 1 if j < len(nodes): y = nodes[j] if len(v[x]) == len(v[y]): equal = True for z in v[x]: if not g[y][z]: return 0 else: root += 1 if root > 1: return 0 return 2 if equal else 1 -
func checkWays(pairs [][]int) int { g := make([][]bool, 510) v := make([][]int, 510) for i := range g { g[i] = make([]bool, 510) } for _, p := range pairs { x, y := p[0], p[1] g[x][y] = true g[y][x] = true v[x] = append(v[x], y) v[y] = append(v[y], x) } var nodes []int for i := 1; i <= 500; i++ { if len(v[i]) > 0 { nodes = append(nodes, i) g[i][i] = true } } sort.Slice(nodes, func(i, j int) bool { return len(v[nodes[i]]) < len(v[nodes[j]]) }) equal := false root := 0 for i, x := range nodes { j := i + 1 for ; j < len(nodes) && !g[x][nodes[j]]; j++ { } if j < len(nodes) { y := nodes[j] if len(v[x]) == len(v[y]) { equal = true } for _, z := range v[x] { if !g[y][z] { return 0 } } } else { root++ } } if root > 1 { return 0 } if equal { return 2 } return 1 }