Welcome to Subscribe On Youtube
1886. Determine Whether Matrix Can Be Obtained By Rotation
Description
Given two n x n binary matrices mat and target, return true if it is possible to make mat equal to target by rotating mat in 90-degree increments, or false otherwise.
Example 1:
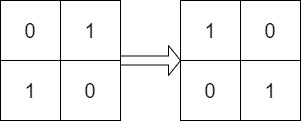
Input: mat = [[0,1],[1,0]], target = [[1,0],[0,1]] Output: true Explanation: We can rotate mat 90 degrees clockwise to make mat equal target.
Example 2:
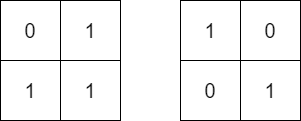
Input: mat = [[0,1],[1,1]], target = [[1,0],[0,1]] Output: false Explanation: It is impossible to make mat equal to target by rotating mat.
Example 3:

Input: mat = [[0,0,0],[0,1,0],[1,1,1]], target = [[1,1,1],[0,1,0],[0,0,0]] Output: true Explanation: We can rotate mat 90 degrees clockwise two times to make mat equal target.
Constraints:
n == mat.length == target.lengthn == mat[i].length == target[i].length1 <= n <= 10mat[i][j]andtarget[i][j]are either0or1.
Solutions
-
class Solution { public boolean findRotation(int[][] mat, int[][] target) { int times = 4; while (times-- > 0) { if (equals(mat, target)) { return true; } rotate(mat); } return false; } private void rotate(int[][] matrix) { int n = matrix.length; for (int i = 0; i < n / 2; ++i) { for (int j = i; j < n - 1 - i; ++j) { int t = matrix[i][j]; matrix[i][j] = matrix[n - j - 1][i]; matrix[n - j - 1][i] = matrix[n - i - 1][n - j - 1]; matrix[n - i - 1][n - j - 1] = matrix[j][n - i - 1]; matrix[j][n - i - 1] = t; } } } private boolean equals(int[][] nums1, int[][] nums2) { int n = nums1.length; for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) { for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) { if (nums1[i][j] != nums2[i][j]) { return false; } } } return true; } } -
class Solution { public: bool findRotation(vector<vector<int>>& mat, vector<vector<int>>& target) { int n = mat.size(); for (int k = 0; k < 4; ++k) { vector<vector<int>> g(n, vector<int>(n)); for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) g[i][j] = mat[j][n - i - 1]; if (g == target) return true; mat = g; } return false; } }; -
class Solution: def findRotation(self, mat: List[List[int]], target: List[List[int]]) -> bool: def rotate(matrix): n = len(matrix) for i in range(n // 2): for j in range(i, n - 1 - i): t = matrix[i][j] matrix[i][j] = matrix[n - j - 1][i] matrix[n - j - 1][i] = matrix[n - i - 1][n - j - 1] matrix[n - i - 1][n - j - 1] = matrix[j][n - i - 1] matrix[j][n - i - 1] = t for _ in range(4): if mat == target: return True rotate(mat) return False -
func findRotation(mat [][]int, target [][]int) bool { n := len(mat) for k := 0; k < 4; k++ { g := make([][]int, n) for i := range g { g[i] = make([]int, n) } for i := 0; i < n; i++ { for j := 0; j < n; j++ { g[i][j] = mat[j][n-i-1] } } if equals(g, target) { return true } mat = g } return false } func equals(a, b [][]int) bool { for i, row := range a { for j, v := range row { if v != b[i][j] { return false } } } return true } -
function findRotation(mat: number[][], target: number[][]): boolean { for (let k = 0; k < 4; k++) { rotate(mat); if (isEqual(mat, target)) { return true; } } return false; } function isEqual(A: number[][], B: number[][]) { const n = A.length; for (let i = 0; i < n; i++) { for (let j = 0; j < n; j++) { if (A[i][j] !== B[i][j]) { return false; } } } return true; } function rotate(matrix: number[][]): void { const n = matrix.length; for (let i = 0; i < n >> 1; i++) { for (let j = 0; j < (n + 1) >> 1; j++) { [ matrix[i][j], matrix[n - 1 - j][i], matrix[n - 1 - i][n - 1 - j], matrix[j][n - 1 - i], ] = [ matrix[n - 1 - j][i], matrix[n - 1 - i][n - 1 - j], matrix[j][n - 1 - i], matrix[i][j], ]; } } } -
impl Solution { pub fn find_rotation(mat: Vec<Vec<i32>>, target: Vec<Vec<i32>>) -> bool { let n = mat.len(); let mut is_equal = [true; 4]; for i in 0..n { for j in 0..n { if is_equal[0] && mat[i][j] != target[i][j] { is_equal[0] = false; } if is_equal[1] && mat[i][j] != target[j][n - 1 - i] { is_equal[1] = false; } if is_equal[2] && mat[i][j] != target[n - 1 - i][n - 1 - j] { is_equal[2] = false; } if is_equal[3] && mat[i][j] != target[n - 1 - j][i] { is_equal[3] = false; } } } is_equal.into_iter().any(|&v| v) } }